|
Fermionic Condensate
A fermionic condensate (or Fermi–Dirac condensate) is a superfluid phase formed by fermionic particles at low temperatures. It is closely related to the Bose–Einstein condensate, a superfluid phase formed by bosonic atoms under similar conditions. Examples of fermionic condensates include superconductors and the superfluid phase of helium-3. The first fermionic condensate in dilute atomic gases was created by a team led by Deborah S. Jin using potassium-40 atoms at the University of Colorado Boulder in 2003. Background Superfluidity Fermionic condensates are attained at lower temperatures than Bose–Einstein condensates. Fermionic condensates are a type of superfluid. As the name suggests, a superfluid possesses fluid properties similar to those possessed by ordinary liquids and gases, such as the lack of a definite shape and the ability to flow in response to applied forces. However, superfluids possess some properties that do not appear in ordinary matter. For insta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superfluid
Superfluidity is the characteristic property of a fluid with zero viscosity which therefore flows without any loss of kinetic energy. When stirred, a superfluid forms vortex, vortices that continue to rotate indefinitely. Superfluidity occurs in two isotopes of helium (helium-3 and helium-4) when they are liquefied by cooling to cryogenic temperatures. It is also a property of various other exotic State of matter, states of matter theorized to exist in astrophysics, high-energy physics, and theories of quantum gravity. The theory of superfluidity was developed by Soviet theoretical physicists Lev Landau and Isaak Khalatnikov. Superfluidity often co-occurs with Bose–Einstein condensate, Bose–Einstein condensation, but neither phenomenon is directly related to the other; not all Bose–Einstein condensates can be regarded as superfluids, and not all superfluids are Bose–Einstein condensates. Even when superfluidity and condensation co-occur, their magnitudes are not linked: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BCS Theory
In physics, the Bardeen–Cooper–Schrieffer (BCS) theory (named after John Bardeen, Leon Cooper, and John Robert Schrieffer) is the first microscopic theory of superconductivity since Heike Kamerlingh Onnes's 1911 discovery. The theory describes superconductivity as a microscopic effect caused by a condensation of Cooper pairs. The theory is also used in nuclear physics to describe the pairing interaction between nucleons in an atomic nucleus. It was proposed by Bardeen, Cooper, and Schrieffer in 1957; they received the Nobel Prize in Physics for this theory in 1972. History Rapid progress in the understanding of superconductivity gained momentum in the mid-1950s. It began with the 1948 paper, "On the Problem of the Molecular Theory of Superconductivity", where Fritz London proposed that the phenomenological London equations may be consequences of the coherence of a quantum state. In 1953, Brian Pippard, motivated by penetration experiments, proposed that this would mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Innsbruck
The University of Innsbruck (; ) is a public research university in Innsbruck, the capital of the Austrian federal state of Tyrol (state), Tyrol, founded on October 15, 1669. It is the largest education facility in the Austrian States of Austria, Bundesland of Tyrol (state), Tirol, and the third largest in Austria behind the University of Vienna and the University of Graz. Significant contributions have been made in many branches, most of all in the Quantum teleportation, physics department. Further, regarding the number of ''Web of Science''-listed publications, it occupies the third rank worldwide in the area of mountain research. History In 1562, a Jesuit grammar school was established in Innsbruck by Peter Canisius, today called "Akademisches Gymnasium Innsbruck". It was financed by the salt mines in Hall in Tirol, and was re-chartered as a university on October 15, 1669, by Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor, Leopold I with four faculties. In 1782 this was reduced to a mere lyceu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf Grimm
Rudolf Grimm (born 10 November 1961) is an experimental physicist from Austria. His work centres on ultracold atoms and quantum gases. He was the first scientist worldwide who, with his team, succeeded in realizing a Bose–Einstein condensation of non-polar molecules. Career Grimm graduated in physics from the University of Hannover in 1986. From 1986 to 1989 he was a post-graduate researcher at the ETH Zurich (Swiss Federal Institute of Technology), then went on to the Institute of Spectroscopy of the USSR Academy of Sciences in Troitsk near Moscow for half a year. He spent the next ten years in Heidelberg as a researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics. In 1994, Grimm applied to the University of Heidelberg to qualify as a professor by receiving the "venia docendi" in experimental physics. In the year 2000, he was appointed to a chair in experimental physics at the University of Innsbruck, where he has been Dean of the Faculty for Mathematics, Computer Scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, electric currents, and electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function (mathematics), function assigning a Euclidean vector, vector to each point of space, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JILA
JILA, formerly known as the Joint Institute for Laboratory Astrophysics, is a physical science research institute in the United States. JILA is located on the University of Colorado Boulder campus. JILA was founded in 1962 as a joint institute of The University of Colorado Boulder and the National Institute of Standards & Technology. Research JILA is one of the nation’s leading research institutes in the physical sciences. The world's first Bose–Einstein condensate was created at JILA by Eric Cornell and Carl Wieman in 1995. The first frequency comb demonstration was led by John L. Hall at JILA. The first demonstrations of a Fermionic condensate and BEC-BCS crossover physics were done by Deborah S. Jin. JILA’s faculty members hold appointments in a wide range of disciplines, including the Departments of Physics, Astrophysical and Planetary Science, Chemistry and Biochemistry, and Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology, as well as Engineering. Many faculty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished from each other by the number of protons that are in their atoms. For example, any atom that contains 11 protons is sodium, and any atom that contains 29 protons is copper. Atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons are called isotopes of the same element. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. A human hair is about a million carbon atoms wide. Atoms are smaller than the shortest wavelength of visible light, which means humans cannot see atoms with conventional microscopes. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics is not possible due to quantum mechanics, quantum effects. More than 99.94% of an atom's mass is in the nucleus. Protons hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubidium
Rubidium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Rb and atomic number 37. It is a very soft, whitish-grey solid in the alkali metal group, similar to potassium and caesium. Rubidium is the first alkali metal in the group to have a density higher than Properties of water, water. On Earth, natural rubidium comprises two isotopes: 72% is a stable isotope Rb, and 28% is slightly radioactive Rb, with a half-life of 48.8 billion years – more than three times as long as the estimated age of the universe. German chemists Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff discovered rubidium in 1861 by the newly developed technique, Atomic emission spectroscopy#Flame emission spectroscopy, flame spectroscopy. The name comes from the Latin word , meaning deep red, the color of its emission spectrum. Rubidium's compounds have various chemical and electronic applications. Rubidium metal is easily vaporized and has a convenient spectral absorption range, making it a frequent target for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Wieman
Carl Edwin Wieman (born March 26, 1951) is an American physicist and educationist at Stanford University, and currently the A. D. White Professor at Large at Cornell University. In 1995, while at the University of Colorado Boulder, he and Eric Allin Cornell produced the first true Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) and, in 2001, they and Wolfgang Ketterle (for further BEC studies) were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics. Wieman currently holds a joint appointment as Professor of Physics and Professor in the Stanford Graduate School of Education, as well as the DRC Professor in the Stanford University School of Engineering. In 2020, Wieman was awarded the Yidan Prize in Education Research for "his contribution in developing new techniques and tools in STEM education". Biography Wieman was born in Corvallis, Oregon to N. Orr Wieman and Alison Marjorie Fry in the United States and graduated from Corvallis High School. His paternal grandfather Henry Nelson Wieman was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric Cornell
Eric Allin Cornell (born December 19, 1961) is an American physicist who, along with Carl E. Wieman, was able to synthesize the first Bose–Einstein condensate in 1995. For their efforts, Cornell, Wieman, and Wolfgang Ketterle shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2001. Biography Cornell was born in Palo Alto, California, where his parents were completing graduate degrees at nearby Stanford University. Two years later he moved to Cambridge, Massachusetts, where his father was a professor of civil engineering at MIT. Here he grew up with his younger brother and sister, with year-long stints in Berkeley, California, and Lisbon, Portugal, accompanying his father whilst on sabbatical. In Cambridge he attended Cambridge Rindge and Latin School. The year before his graduation he moved back to California with his mother and finished high school at San Francisco's Lowell High School, a local magnet school for academically talented students. After high school he enrolled at Stanford ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas D
Douglas may refer to: People * Douglas (given name) * Douglas (surname) Animals * Douglas (parrot), macaw that starred as the parrot ''Rosalinda'' in Pippi Longstocking * Douglas the camel, a camel in the Confederate Army in the American Civil War Businesses * Douglas Aircraft Company * Douglas (cosmetics), German cosmetics retail chain in Europe * Douglas Holding, former German company * Douglas (motorcycles), British motorcycle manufacturer Peerage and Baronetage * Duke of Douglas * Earl of Douglas, or any holder of the title * Marquess of Douglas, or any holder of the title * Douglas baronets Peoples * Clan Douglas, a Scottish kindred * Dougla people, West Indians of both African and East Indian heritage Places Australia * Douglas, Queensland, a suburb of Townsville * Douglas, Queensland (Toowoomba Region), a locality * Port Douglas, North Queensland, Australia * Shire of Douglas, in northern Queensland Canada * Douglas, New Brunswick * Douglas Parish, New Brunswic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
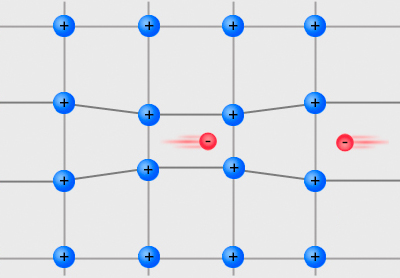
Cooper Pair
In condensed matter physics, a Cooper pair or BCS pair (Bardeen–Cooper–Schrieffer pair) is a pair of electrons (or other fermions) bound together at low temperatures in a certain manner first described in 1956 by American physicist Leon Cooper. Description Cooper showed that an arbitrarily small attraction between electrons in a metal can cause a paired state of electrons to have a lower energy than the Fermi energy, which implies that the pair is bound. In conventional superconductors, this attraction is due to the electron–phonon interaction. The Cooper pair state is responsible for superconductivity, as described in the BCS theory developed by John Bardeen, Leon Cooper, and John Schrieffer for which they shared the 1972 Nobel Prize in Physics. Although Cooper pairing is a quantum effect, the reason for the pairing can be seen from a simplified classical explanation. An electron in a metal normally behaves as a free particle. The electron is repelled from other electrons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |