|
Farrowing
Pig farming or pork farming or hog farming is the raising and breeding of domestic pigs as livestock, and is a branch of animal husbandry. Pigs are farmed principally for food (e.g. pork: bacon, ham, gammon) and skins. Pigs are amenable to many different styles of farming: intensive commercial units, commercial free range enterprises, or extensive farming (being allowed to wander around a village, town or city, or tethered in a simple shelter or kept in a pen outside the owner's house). Historically, farm pigs were kept in small numbers and were closely associated with the residence of the owner, or in the same village or town. They were valued as a source of meat and fat, and for their ability to convert inedible food into meat and manure, and were often fed household food waste when kept on a homestead. Pigs have been farmed to dispose of municipal garbage on a large scale. All these forms of pig farm are in use today, though intensive farms are by far the most popular, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intensive Pig Farming
Intensive pig farming, also known as pig factory farming, is the primary method of pig production, in which grower pigs are housed indoors in group-housing or straw-lined sheds, whilst pregnant sows are housed in gestation crates or pens and give birth in farrowing crates. The use of gestation crates for pregnant sows has lowered birth production costs; however, this practice has led to more significant animal cruelty. Many of the world's largest producers of pigs ( US, China, and Mexico) use gestation crates. The European Union has banned the use of gestation crates after the fourth week of pregnancy. Intensive pig farmers often cut off tails, testes or teeth of pigs without anaesthetic. The environmental impacts of pig farming include problems posed to drinking water and algal bloom events. Description Intensive piggeries are generally large warehouse-like buildings or barns with little exposure to sunlight or the outdoors. Most pigs are officially entitled to less t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
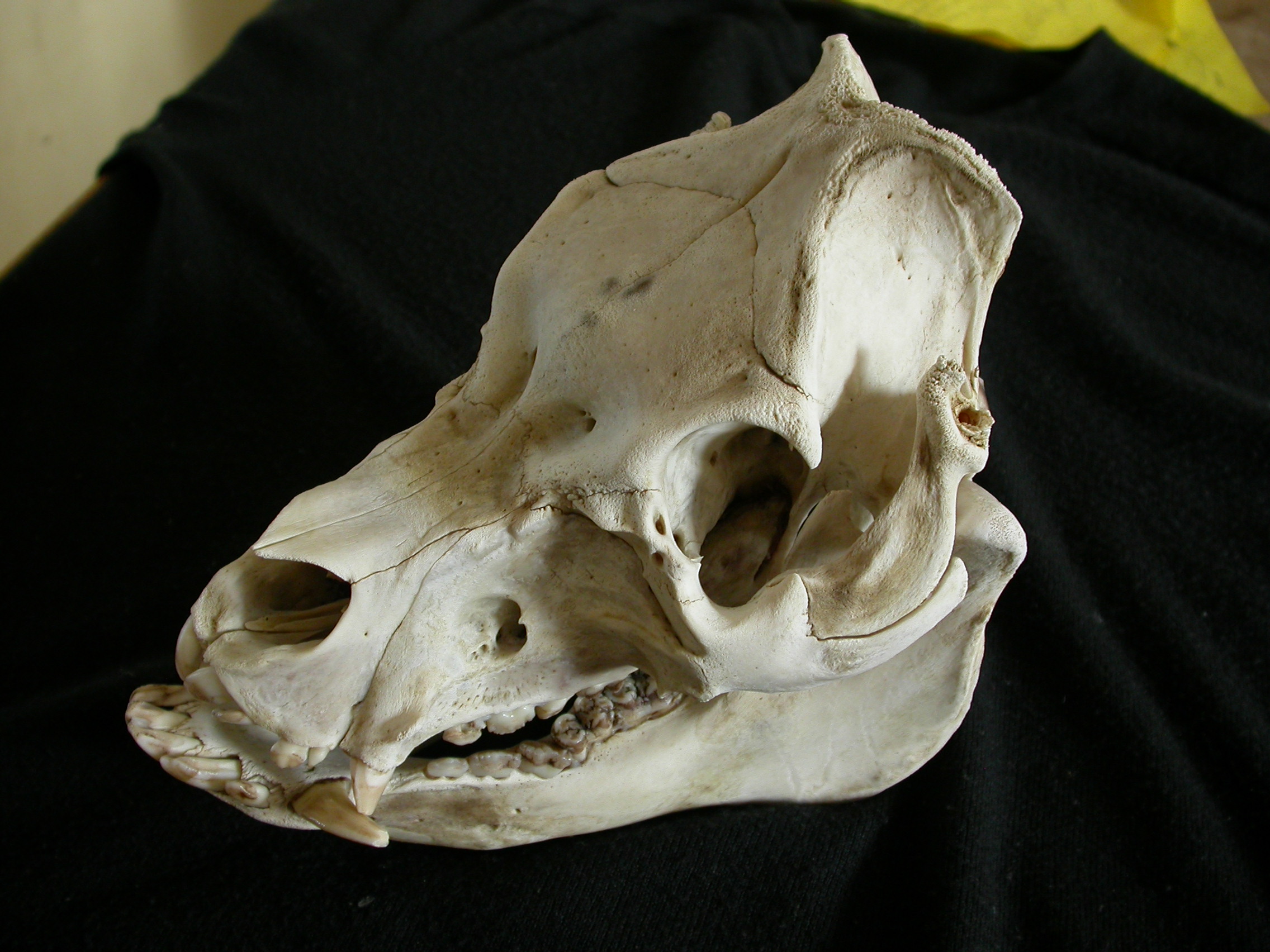
Domestic Pig
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus ''Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus scrofa'' (the wild boar or Eurasian boar) or a distinct species. The pig's head-plus-body length ranges from , and adult pigs typically weigh between , with well-fed individuals even exceeding this range. The size and weight of hogs largely depends on their breed. Compared to other artiodactyls, a pig's head is relatively long and pointed. Most even-toed ungulates are herbivorous, but pigs are omnivores, like their wild relative. Pigs grunt and make snorting sounds. When used as livestock, pigs are farmed primarily for the production of meat, called pork. A group of pigs is called a ''passel'', a ''team'', or a ''sounder''. The animal's bones, hide, and bristles are also used in products. Pigs, especially miniature breeds, are kept a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitterlings
Chitterlings (), sometimes spelled chitlins or chittlins, are the small intestines of domestic animals. They are usually made from pigs' intestines. They may also be filled with a forcemeat to make sausage.'' Oxford English Dictionary'', 1st edition, updated March 2021''s.v.''/ref> Intestine from other animals, such as beef, lamb, and goat is also used for making chitterling. Etymology and early usage ''Chitterling'' is first documented in Middle English in the form , . Various other spellings and dialect forms were used. The primary form and derivation are uncertain. A 1743 English cookery book ''The Lady's Companion: or, An Infallible Guide to the Fair Sex'' contained a recipe for "Calf's Chitterlings" which was essentially a bacon and offal sausage in a calf's intestine casing. The recipe explained the use of calves', rather than the more usual pigs', intestines with the comment that " hesesort of... puddings must be made in summer, when hogs are seldom killed". This re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Pudding
, type = , course = , place_of_origin = Great Britain and Ireland , region =England, Ireland, Scotland , associated_cuisine = United Kingdom and Ireland , creator = , year = , mintime = , maxtime = , served = Hot, occasionally cold , main_ingredient = Pork blood, fat, oats, or barley , minor_ingredient = Mint, thyme, marjoram, spices , variations = Drisheen, Sneem Black Pudding, Stornoway black pudding , serving_size = 100 g , calories = , calories_ref = , protein = , fat = , carbohydrate = , glycemic_index = , similar_dish = , , other = Black pudding is a distinct regional type of blood sausage originating in the United Kingdom and Ireland. It is made from pork or beef blood, with pork fat or beef suet, and a cereal, usually oatmeal, oat groats, or barley groats. The high proportion of cereal, along with the use of certain herbs such as pennyroyal, serves to distinguish black pudding from blood sausages eaten in other parts of the world ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feed Conversion Ratio
In animal husbandry, feed conversion ratio (FCR) or feed conversion rate is a ratio or rate measuring of the efficiency with which the bodies of livestock convert animal feed into the desired output. For dairy cows, for example, the output is milk, whereas in animals raised for meat (such as beef cows,Dan Shike, University of IllinoiBeef Cattle Feed Efficiency/ref> pigs, chickens, and fish) the output is the flesh, that is, the body mass gained by the animal, represented either in the final mass of the animal or the mass of the dressed output. FCR is the mass of the input divided by the output (thus mass of feed per mass of milk or meat). In some sectors, feed efficiency, which is the output divided by the input (i.e. the inverse of FCR), is used. These concepts are also closely related to efficiency of conversion of ingested foods (ECI). Background Feed conversion ratio (FCR) is the ratio of inputs to outputs; it is the inverse of "feed efficiency" which is the ratio of outp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Price
A product's average price is the result of dividing the product's total sales revenue by the total units sold. When one product is sold in variants, such as bottle sizes, managers must define "comparable" units. Average prices can be calculated by weighting different unit selling prices by the percentage of unit sales (mix) for each product variant. If we use a standard, rather than an actual mix of sizes and product varieties, the result is price per statistical unit. Statistical units are also called equivalent units. Average price per unit and prices per statistical unit are needed by marketers who sell the same product in different packages, sizes, forms, or configurations at a variety of different prices. As in analyses of different channels, these product and price variations must be reflected accurately in overall average prices. If they are not, marketers may lose sight of what is happening to prices and why. If the price of each product variant remained unchanged, for ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meat Industry
The meat industry are the people and companies engaged in modern industrialized livestock agriculture for the production, packing, preservation and marketing of meat (in contrast to dairy products, wool, etc.). In economics, the meat industry is a fusion of primary (agriculture) and secondary (industry) activity and hard to characterize strictly in terms of either one alone. The greater part of the meat industry is the meat packing industry – the segment that handles the slaughtering, processing, packaging, and distribution of animals such as poultry, cattle, pigs, sheep and other livestock. A great portion of the ever-growing meat branch in the food industry involves intensive animal farming in which livestock are kept almost entirely indoors or in restricted outdoor settings like pens. Many aspects of the raising of animals for meat have become industrialized, even many practices more associated with smaller family farms, e.g. gourmet foods such as foie gras. The product ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Feed
Animal feed is food given to domestic animals, especially livestock, in the course of animal husbandry. There are two basic types: fodder and forage. Used alone, the word ''feed'' more often refers to fodder. Animal feed is an important input to animal agriculture, and is frequently the main cost of the raising or keeping of animals. Farms typically try to reduce cost for this food, by growing their own, grazing animals, or supplementing expensive feeds with substitutes, such as food waste like spent grain from beer brewing. Animal wellbeing is highly dependent on feed that reflects a well balanced nutrition. Some modern agricultural practices, such as fattening cows on grains or in feed lots, have detrimental effects on the environment and animals. For example, increased corn or other grain in feed for cows, makes their microbiomes more acidic weakening their immune systems and making cows a more likely vector for E.coli. While other feeding practices can improve animal impa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Cheese
Head cheese (Dutch language, Dutch: ''hoofdkaas'') or brawn is a cold cut terrine (food), terrine or meat jelly that originated in Europe. It is made with flesh from the head of a Calf (animal), calf or pig (less commonly a sheep or cow), typically set in aspic, and usually eaten cold, at room temperature, or in a sandwich. Despite its name the dish is not a cheese and contains no dairy products. The parts of the head used vary, and may include the tongue and sometimes the feet and heart but do not commonly include the brain, eyes or ears. Trimmings from more commonly eaten cuts of pork and veal are often used, with gelatin added as a binder (material), binder. Variations of head cheese exist throughout Europe and the rest of the world, with differences in construction and ingredients. A version pickled with vinegar is known as ''souse''. Historically, meat jellies were made of the head of an animal, less its organs, which would be simmered to produce a naturally gelatinous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cattle Prod
A cattle prod, also called a stock prod or a hot stick, is a handheld device commonly used to make cattle or other livestock move by striking or poking them. An electric cattle prod is a stick with electrodes on the end which is used to make cattle move via a relatively high-voltage, low-current electric shock. The electric cattle prod is said to have been invented by Texas cattle baron Robert J. Kleberg, Jr. of the King Ranch around 1930, although versions were sold as early as 1917. Electric prods A hotshot is typically cylindrical, and can carry an open electric current at the "shock end" when activated. The electric current at the shock end runs through two metal electrodes. Anything that touches the electric current receives a high-voltage low- current shock, not strong enough to kill a human or a large animal such as a cow or sheep from short-term exposure, but strong enough to cause significant pain. The electric cattle prod is designed to inflict a painful shock t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |