|
FM Towns Marty
The FM Towns Marty is a home video game console released in 1993 by Fujitsu, exclusively for the Japanese market. It uses the AMD 386SX, a CPU that is internally 32-bit but with a 16-bit data bus. The console comes with a built-in CD-ROM drive and disk drive. It was based on the earlier FM Towns computer system Fujitsu had released in 1989. The Marty was backward-compatible with older FM Towns games. In 1994, a new version of the console called the was released. It featured a darker gray shell and a lower price ( ¥66,000 or , but was otherwise identical to the first Marty. It was widely believed that the FM Towns Marty 2 would feature similar improvements to the FM Towns 2, which had a swifter CPU than the first, but this was not the case. It has also been speculated that the Marty 2 featured an Intel 486 CPU, but this was also discovered to be false. There is also the for installation in automobiles. It included a built-in navigation system with audio and video gui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Yen
The is the official currency of Japan. It is the third-most traded currency in the foreign exchange market, after the United States dollar and the euro. It is also widely used as a third reserve currency after the US dollar and the euro. The New Currency Act of 1871 introduced Japan's modern currency system, with the yen defined as of gold, or of silver, and divided decimally into 100 ''sen'' or 1,000 ''rin''. The yen replaced the previous Tokugawa coinage as well as the various ''hansatsu'' paper currencies issued by feudal ''han'' (fiefs). The Bank of Japan was founded in 1882 and given a monopoly on controlling the money supply. Following World War II, the yen lost much of its pre-war value as Japan faced a debt crisis and hyperinflation. Under the Bretton Woods system, the yen was pegged to the US dollar alongside other major currencies. After this system was abandoned in 1971 with the Nixon shock, Nixon Shock, the short-lived Smithsonian Agreement temporarily reinstat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
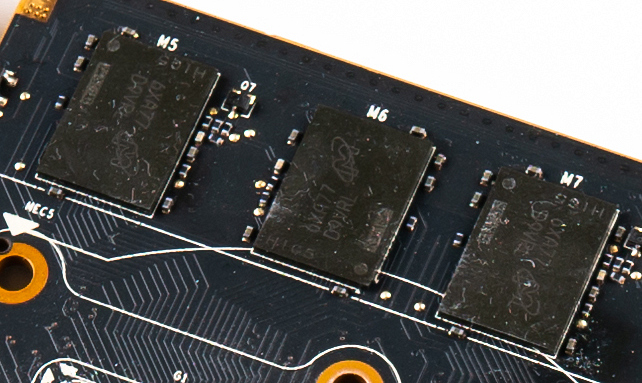
Video Memory
Video random-access memory (VRAM) is dedicated computer memory used to store the pixels and other graphics data as a framebuffer to be rendered on a computer monitor. It often uses a different technology than other computer memory, in order to be read quickly for display on a screen. Relation to GPUs Many modern GPUs rely on VRAM. In contrast, a GPU that does ''not'' use VRAM, and relies instead on system RAM, is said to have a unified memory architecture, or shared graphics memory. System RAM and VRAM have been segregated due to the bandwidth requirements of GPUs, and to achieve lower latency, since VRAM is physically closer to the GPU die. Modern VRAM is typically found in a BGA package soldered onto a graphics card. The VRAM is cooled along with the GPU by the GPU heatsink. Technologies * Dual-ported video RAM, used in the 1990s and at the time often called "VRAM" * SGRAM * GDDR SDRAM * High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) See also * Graphics processing unit * Tiled render ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kibibyte
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit of memory in many computer architectures. To disambiguate arbitrarily sized bytes from the common 8-bit definition, network protocol documents such as the Internet Protocol () refer to an 8-bit byte as an octet. Those bits in an octet are usually counted with numbering from 0 to 7 or 7 to 0 depending on the bit endianness. The size of the byte has historically been hardware-dependent and no definitive standards existed that mandated the size. Sizes from 1 to 48 bits have been used. The six-bit character code was an often-used implementation in early encoding systems, and computers using six-bit and nine-bit bytes were common in the 1960s. These systems often had memory words of 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 48, or 60 bits, corresponding to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mebibyte
The byte is a units of information, unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character (computing), character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest address space, addressable unit of Computer memory, memory in many computer architectures. To disambiguate arbitrarily sized bytes from the common 8-bit computing, 8-bit definition, Computer network, network protocol documents such as the Internet Protocol () refer to an 8-bit byte as an Octet (computing), octet. Those bits in an octet are usually counted with numbering from 0 to 7 or 7 to 0 depending on the bit numbering, bit endianness. The size of the byte has historically been Computer hardware, hardware-dependent and no definitive standards existed that mandated the size. Sizes from 1 to 48 bits have been used. The six-bit character code was an often-used implementation in early encoding systems, and compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Million Instructions Per Second
Instructions per second (IPS) is a measure of a computer's processor speed. For complex instruction set computers (CISCs), different instructions take different amounts of time, so the value measured depends on the instruction mix; even for comparing processors in the same family the IPS measurement can be problematic. Many reported IPS values have represented "peak" execution rates on artificial instruction sequences with few branches and no cache contention, whereas realistic workloads typically lead to significantly lower IPS values. Memory hierarchy also greatly affects processor performance, an issue barely considered in IPS calculations. Because of these problems, synthetic benchmarks such as Dhrystone are now generally used to estimate computer performance in commonly used applications, and raw IPS has fallen into disuse. The term is commonly used in association with a metric prefix (k, M, G, T, P, or E) to form kilo instructions per second (kIPS), mega instructio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock Rate
Clock rate or clock speed in computing typically refers to the frequency at which the clock generator of a processor can generate pulses used to synchronize the operations of its components. It is used as an indicator of the processor's speed. Clock rate is measured in the SI unit of frequency hertz (Hz). The clock rate of the first generation of computers was measured in hertz or kilohertz (kHz), the first personal computers from the 1970s through the 1980s had clock rates measured in megahertz (MHz). In the 21st century the speed of modern CPUs is commonly advertised in gigahertz (GHz). This metric is most useful when comparing processors within the same family, holding constant other features that may affect performance. Determining factors Binning Manufacturers of modern processors typically charge higher prices for processors that operate at higher clock rates, a practice called binning. For a given CPU, the clock rates are determined at the end of the manufact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit (CPU). The IC is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, Clock signal, clock-driven, Processor register, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary code, binary data as input, processes it according to instruction (computing), instructions stored in its computer memory, memory, and provides results (also in binary form) as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential logic, sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system. The integration of a whole CPU on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vehicle Information And Communication System
A vehicle () is a machine designed for self-propulsion, usually to transport people, cargo, or both. The term "vehicle" typically refers to land vehicles such as human-powered vehicles (e.g. bicycles, tricycles, velomobiles), animal-powered transports (e.g. horse-drawn carriages/wagons, ox carts, dog sleds), motor vehicles (e.g. motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters) and railed vehicles (trains, trams and monorails), but more broadly also includes cable transport ( cable cars and elevators), watercraft (ships, boats and underwater vehicles), amphibious vehicles (e.g. screw-propelled vehicles, hovercraft, seaplanes), aircraft (airplanes, helicopters, gliders and aerostats) and space vehicles (spacecraft, spaceplanes and launch vehicles). This article primarily concerns the more ubiquitous land vehicles, which can be broadly classified by the type of contact interface with the ground: wheels, tracks, rails or skis, as well as the non-contact technologies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
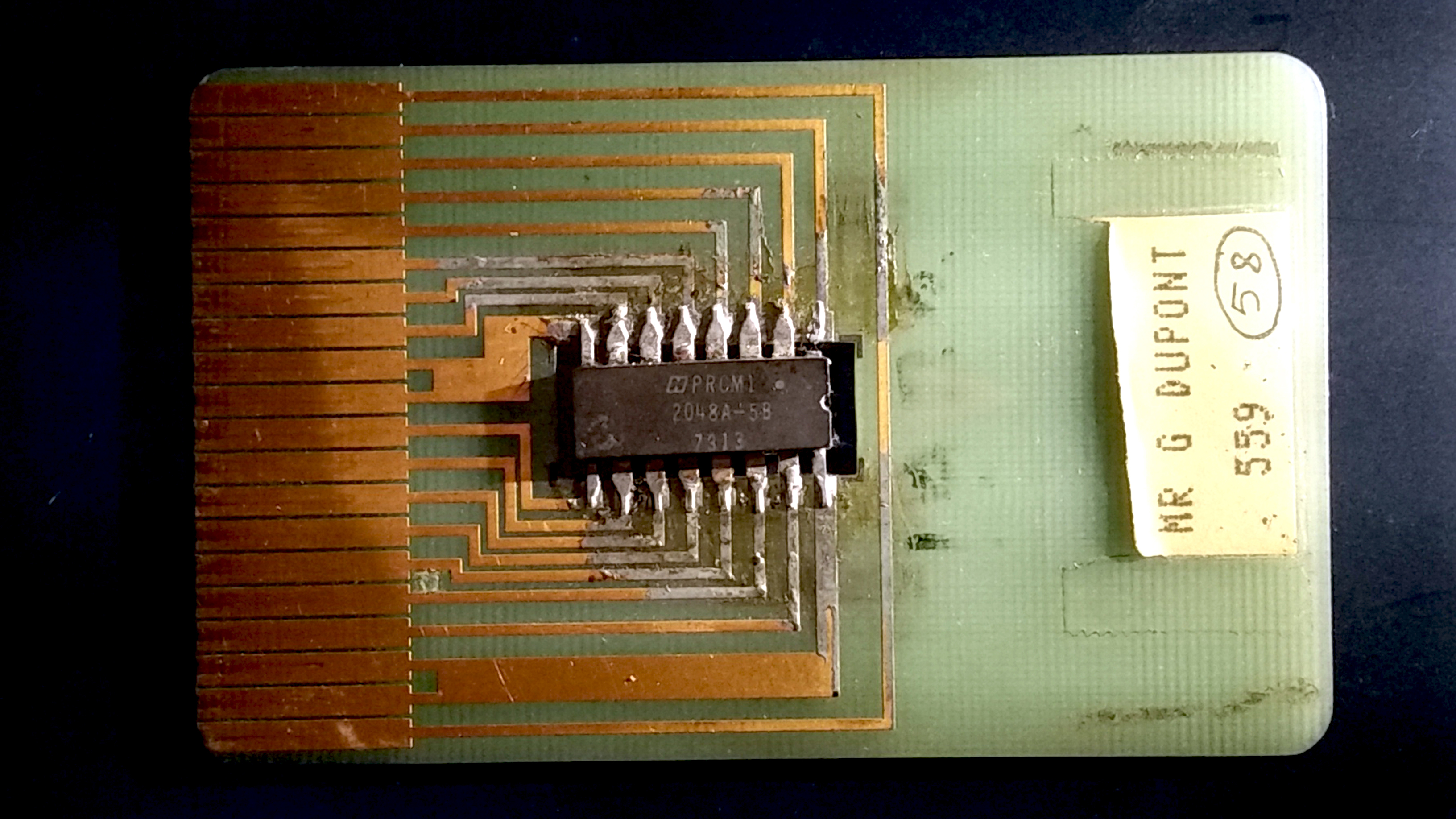
IC Card
A smart card (SC), chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC or IC card), is a card used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an embedded integrated circuit (IC) chip. Many smart cards include a pattern of metal contacts to electrically connect to the internal chip. Others are contactless, and some are both. Smart cards can provide personal identification, authentication, data storage, and application processing. Applications include identification, financial, public transit, computer security, schools, and healthcare. Smart cards may provide strong security authentication for single sign-on (SSO) within organizations. Numerous nations have deployed smart cards throughout their populations. The universal integrated circuit card (UICC) for mobile phones, installed as pluggable SIM card or embedded eSIM, is also a type of smart card. , 10.5billion smart card IC chips are manufactured annually, including 5.44billion SIM card IC c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ziff Davis
Ziff Davis, Inc. is an American digital media and internet company. Founded in 1927 by William Bernard Ziff Sr. and Bernard George Davis, the company primarily owns technology- and health-oriented media websites, online shopping-related services, internet connectivity services, gaming and entertainment brands, and cybersecurity and martech (marketing technology) tools. Previously, the company was predominantly a publisher of hobbyist magazines. History The company was founded by William B. Ziff Company publisher Bill Ziff Sr. with Bernard Davis. Upon Bill Ziff's death in 1953, William B. Ziff Jr., his son, returned from Germany to lead the company. In 1958, Bernard Davis sold Ziff Jr. his share of Ziff Davis to found Davis Publications, Inc.; Ziff Davis continued to use the Davis surname as Ziff-Davis. Throughout most of Ziff Davis' history, it was a publisher of hobbyist magazines, often ones devoted to expensive, advertiser-rich technical hobbies such as cars, photograp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Gaming Monthly
''Electronic Gaming Monthly'' (''EGM'') is a monthly American video game magazine. It offers video game news, coverage of industry events, interviews with gaming figures, editorial content and product reviews. History The magazine was founded in 1988 as U.S. National Video Game Team's ''Electronic Gaming Monthly'' under Sendai Publications. In 1994, ''EGM'' spun off '' EGM²'', which focused on expanded cheats and tricks (i.e., with maps and guides). It eventually became '' Expert Gamer'' and finally the defunct '' GameNOW''. After 83 issues (up to June 1996), ''EGM'' switched publishers from Sendai Publishing to Ziff Davis. Until January 2009, ''EGM'' only covered gaming on console hardware and software. In 2002, the magazine's subscription increased by more than 25 percent. The magazine was discontinued by Ziff Davis in January 2009, following the sale of '' 1UP.com'' to UGO Networks. The magazine's February 2009 issue was already completed, but was not published. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |