|
FIPS 153
PHIGS (Programmer's Hierarchical Interactive Graphics System) is an application programming interface (API) standard for rendering 3D computer graphics, considered to be the 3D graphics standard for the 1980s through the early 1990s. Subsequently, a combination of features and power led to the rise of OpenGL, which became the most popular professional 3D API of the mid to late 1990s. Large vendors typically offered versions of PHIGS for their platforms, including DEC PHIGS, IBM's graPHIGS and Sun's SunPHIGS. It could also be used within the X Window System, supported via PEX. PEX consisted of an extension to X, adding commands that would be forwarded from the X server to the PEX system for rendering. Workstations were placed in windows typically, but could also be forwarded to take over the whole screen, or to various printer-output devices. PHIGS was designed in the 1980s, inheriting many of its ideas from the 2D Graphical Kernel System (GKS) of the late 1970s, and became a stan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American National Standards Institute
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organization also coordinates U.S. standards with international standards so that American products can be used worldwide. ANSI accredits standards that are developed by representatives of other standards organizations, government agencies, consumer groups, companies, and others. These standards ensure that the characteristics and performance of products are consistent, that people use the same definitions and terms, and that products are tested the same way. ANSI also accredits organizations that carry out product or personnel certification in accordance with requirements defined in international standards. The organization's headquarters are in Washington, D.C. ANSI's operations office is located in New York City. The ANSI annual operating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texture Mapping
Texture mapping is a term used in computer graphics to describe how 2D images are projected onto 3D models. The most common variant is the UV unwrap, which can be described as an inverse paper cutout, where the surfaces of a 3D model are cut apart so that it can be unfolded into a 2D coordinate space (UV Space). Semantic Texture mapping can both refer to the task of unwrapping a 3D model, the abstract that a 3D model has textures applied to it and the related algorithm of the 3D software. Texture map refers to a Raster graphics also called image, texture. If the texture stores a specific property it's also referred to as color map, roughness map, etc. The coordinate space which converts from the 3D space of a 3D model into a 2D space so that it can sample from the Texture map is called: UV Space, UV Coordinates, Texture Space. Algorithm A simplified explanation of how an algorithm could work to render an image: # For each pixel we trace the coordinates of the screen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphics Standards
An image file format is a file format for a digital image. There are many formats that can be used, such as JPEG, PNG, and GIF. Most formats up until 2022 were for storing 2D images, not 3D ones. The data stored in an image file format may be compressed or uncompressed. If the data is compressed, it may be done so using lossy compression or lossless compression. For graphic design applications, vector formats are often used. Some image file formats support transparency. Raster formats are for 2D images. A 3D image can be represented within a 2D format, as in a stereogram or autostereogram, but this 3D image will not be a true light field, and thereby may cause the vergence-accommodation conflict. Image files are composed of digital data in one of these formats so that the data can be displayed on a digital (computer) display or printed out using a printer. A common method for displaying digital image information has historically been rasterization. Image file sizes The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphics Libraries
A graphics library or graphics application programming interface, API is a Computer program, program Library (computing), library designed to aid in rendering computer graphics to a monitor. This typically involves providing optimized versions of functions that handle common Rendering (computer graphics), rendering tasks. This can be done purely in Computer software, software and running on the Central processing unit, CPU, common in embedded systems, or being hardware accelerated by a Graphics processing unit, GPU, more common in Personal computer, PCs. By employing these functions, a program can assemble an image to be output to a monitor. This relieves the programmer of the task of creating and optimizing these functions, and allows them to focus on building the graphics program. Graphics libraries are mainly used in video games and Simulation video game, simulations. The use of graphics libraries in connection with video production systems, such as Pixar RenderMan, is not covere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American National Standards Institute Standards
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label that was previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Scenegraph APIs
3D, 3-D, 3d, or Three D may refer to: Science, technology, and mathematics * A three-dimensional space in mathematics Relating to three-dimensionality * 3D computer graphics, computer graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data * 3D display, a type of information display that conveys depth to the viewer * 3D film, a motion picture that gives the illusion of three-dimensional perception * 3D modeling, developing a representation of any three-dimensional surface or object * 3D printing, making a three-dimensional solid object of a shape from a digital model * 3D television, television that conveys depth perception to the viewer * 3D projection * 3D rendering * 3D scanning, making a digital representation of three-dimensional objects * 3D video game * Stereoscopy, any technique capable of recording three-dimensional visual information or creating the illusion of depth in an image * Three-dimensional space Other uses in science and technology * 3-D Sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DirectX
Microsoft DirectX is a collection of application programming interfaces (APIs) for handling tasks related to multimedia, especially game programming and video, on Microsoft platforms. Originally, the names of these APIs all began with "Direct", such as Direct3D, DirectDraw, DirectMusic, DirectPlay, DirectSound, and so forth. The name ''DirectX'' was coined as a shorthand term for all of these APIs (the ''X'' standing in for the particular API names) and soon became the name of the collection. When Microsoft later set out to develop a Video game console, gaming console, the ''X'' was used as the basis of the name Xbox (console), Xbox to indicate that the console was based on DirectX technology. The ''X'' initial has been carried forward in the naming of APIs designed for the Xbox such as DirectInput, XInput and the Cross-platform Audio Creation Tool (XACT), while the DirectX pattern has been continued for Windows APIs such as Direct2D and DirectWrite. Direct3D (the 3D graphics A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulkan
Vulkan is a cross-platform API and open standard for 3D graphics and computing. It was intended to address the shortcomings of OpenGL, and allow developers more control over the GPU. It is designed to support a wide variety of GPUs, CPUs and operating systems, and it is also designed to work with modern multi-core CPUs. Microsoft supports Vulkan 1.2 (and more) on Windows 10 and 11, with a downloadable compatibility pack. Overview Vulkan targets high-performance real-time 3D-graphics applications, such as video games and interactive media, and highly parallelized computing. Vulkan is intended to offer higher performance and more efficient CPU and GPU usage compared to the older OpenGL and Direct3D 11 APIs. It does so by providing a considerably lower-level API for the application than the older APIs, that more closely resembles how modern GPUs work. Vulkan is comparable to Apple's Metal API and Microsoft's Direct3D 12. In addition to its lower CPU usage, Vulkan is design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XFree86
XFree86 is an implementation of the X Window System. It was originally written for Unix-like operating systems on IBM PC compatibles and was available for many other operating systems and platforms. It is free software, free and Open-source software, open source software under the XFree86 License version 1.1. It was developed by the XFree86 Project, Inc. The lead developer was David Dawes. The last released version was 4.8.0, released December 2008. The last XFree86 Concurrent Versions System, CVS commit was made on May 18, 2009; the project was confirmed dormant in December 2011. For most of the 1990s and early 2000s, the project was the source of most innovation in X and was the ''de facto'' steward of X development. Until early 2004, it was almost universal on Linux and the Berkeley Software Distribution, BSDs. In February 2004, with version 4.4.0, The XFree86 Project began distributing new code with a copyright license that the Free Software Foundation considered GNU General ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Processing Unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions of a computer program, such as arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations. This role contrasts with that of external components, such as main memory and I/O circuitry, and specialized coprocessors such as graphics processing units (GPUs). The form, CPU design, design, and implementation of CPUs have changed over time, but their fundamental operation remains almost unchanged. Principal components of a CPU include the arithmetic–logic unit (ALU) that performs arithmetic operation, arithmetic and Bitwise operation, logic operations, processor registers that supply operands to the ALU and store the results of ALU operations, and a control unit that orchestrates the #Fetch, fetching (from memory), #Decode, decoding and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
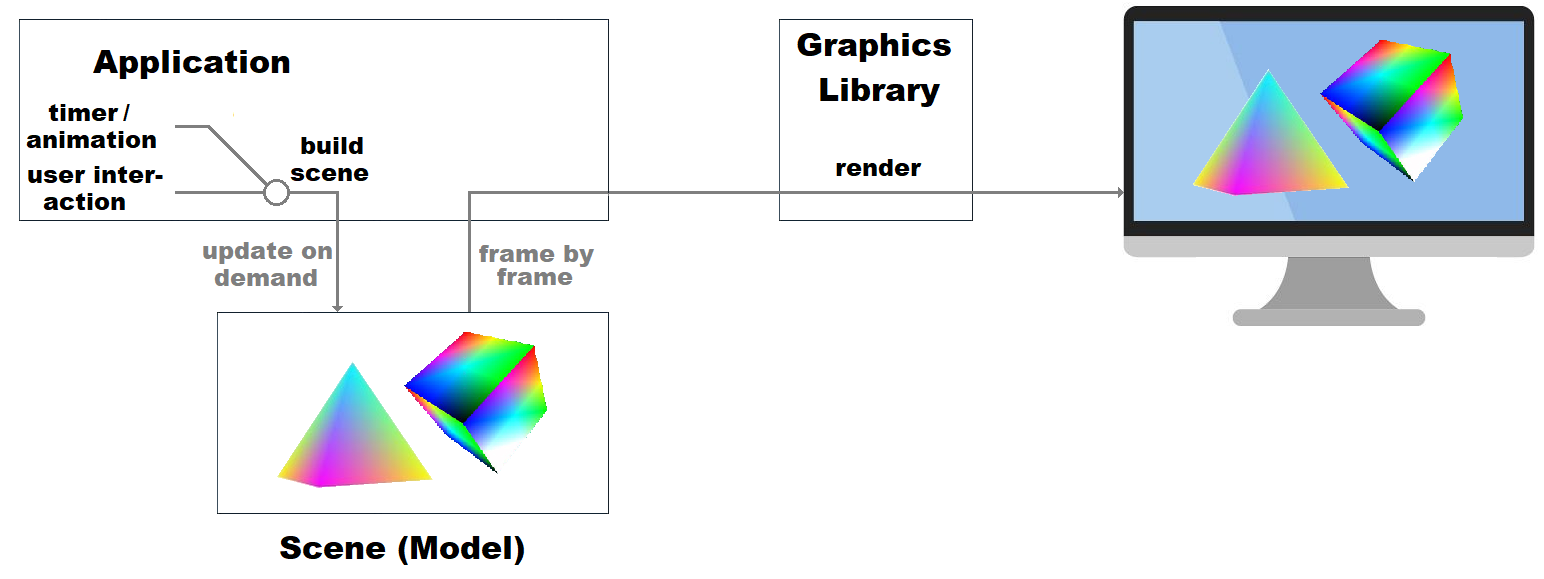
Immediate Mode (computer Graphics)
Immediate mode is an application programming interface, API design pattern in computer graphics libraries, in which * the Client (computing), client calls directly cause Rendering (computer graphics), rendering of graphics objects to the display, or in which * the data to describe rendering primitives is inserted Film frame, frame by frame directly from the Client (computing), client into a command list (in the case of ''#Immediate mode primitive rendering, immediate mode primitive rendering''), without the use of extensive indirection – thus'' immediate ''– to retained resources. It does not preclude the use of Multiple buffering, double-buffering. Retained mode is an alternative approach. Historically, retained mode has been the dominant style in Graphical user interface, GUI libraries; however, both can coexist in the same library and are not necessarily exclusive in practice. Overview In immediate mode, the scene (complete object model of the rendering primitives) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-uniform Rational B-spline
Non-uniform rational basis spline (NURBS) is a mathematical model using B-spline, basis splines (B-splines) that is commonly used in computer graphics for representing curves and Surface (mathematics), surfaces. It offers great flexibility and precision for handling both analytic (defined by common mathematical formulae) and 3D modeling, modeled shapes. It is a type of 3D modeling#Process, curve modeling, as opposed to polygonal modeling or digital sculpting. NURBS curves are commonly used in computer-aided design (CAD), Computer-aided manufacturing, manufacturing (CAM), and Computer-aided engineering, engineering (CAE). They are part of numerous industry-wide standards, such as IGES, ISO 10303, STEP, ACIS, and PHIGS. Tools for creating and editing NURBS surfaces are found in various 3D computer graphics software, 3D graphics, Rendering (computer graphics), rendering, and 3D Animation, animation software packages. They can be efficiently handled by computer programs yet allow for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |