|
Exposure Sheet
An exposure sheet (also referred to as camera instruction sheet, dope sheet or X-sheet) is a traditional animation tool that allows an animator to organize their thinking and give instructions to the camera operator on how the animation is to be shot. It consists of five sections, and is a bit longer and a bit narrower, than A4. Every eighth line down is marked thicker than the rest and shows half a foot of film. One second of animation would take three of these sections (hence every line represents 1/24th of a second). Sound breakdown was often done on separate sheets called bar sheets made by the editor, and given to the animator who would transpose them to his dope sheet. Layout The typical dope sheet is divided into sections which are separated by many vertical and horizontal lines, the horizontal lines represent one frame of film while the vertical ones separate the sections, for example: # The column on the far left is used by the animator to jot down notes on the path of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Animation
Traditional animation (or classical animation, cel animation, or hand-drawn animation) is an animation technique in which each frame is drawn by hand. The technique was the dominant form of animation in cinema until computer animation. Process Writing and storyboarding Animation production usually begins after a story is converted into an animation film script, from which a storyboard is derived. A storyboard has an appearance somewhat similar to comic book panels, and is a shot by shot breakdown of the staging, acting and any camera moves that will be present in the film. The images allow the animation team to plan the flow of the plot and the composition of the imagery. Storyboard artists will have regular meetings with the director and may redraw or "re-board" a sequence many times before it meets final approval. Voice recording Before animation begins, a preliminary soundtrack or scratch track is recorded so that the animation may be more precisely synchronized t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animator
An animator is an artist who creates multiple images, known as frames, which give an illusion of movement called animation when displayed in rapid sequence. Animators can work in a variety of fields including film, television, and video games. Animation is closely related to filmmaking and like filmmaking is extremely labor-intensive, which means that most significant works require the collaboration of several animators. The methods of creating the images or frames for an animation piece depend on the animators' artistic styles and their field. Other artists who contribute to animated cartoons, but who are not animators, include layout artists (who design the backgrounds, lighting, and camera angles), storyboard artists (who draw panels of the action from the script), and background artists (who paint the "scenery"). Animated films share some film crew positions with regular live action films, such as director, producer, sound engineer, and editor, but differ radically i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
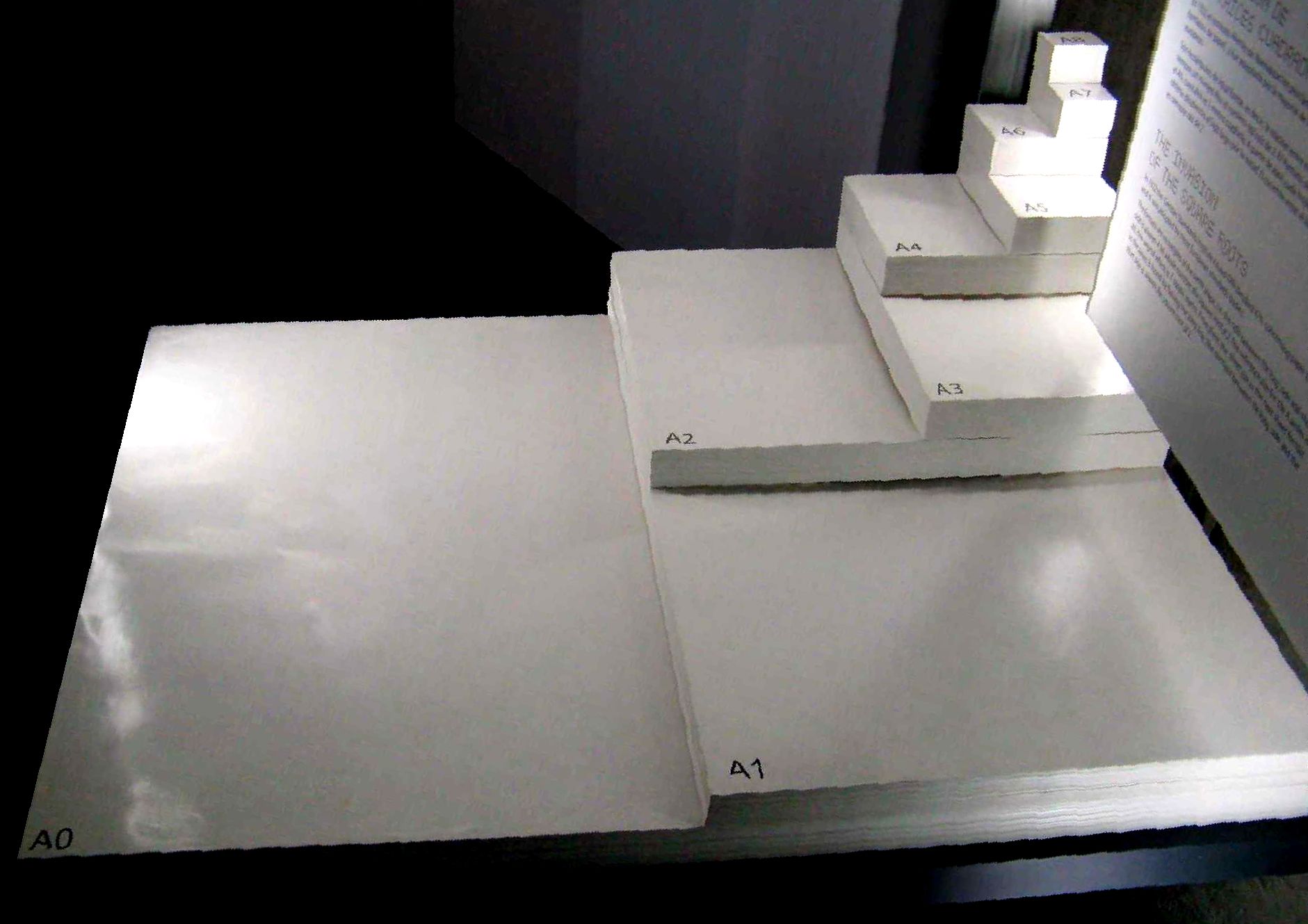
ISO 216
ISO 216 is an international standard for paper sizes, used around the world except in North America and parts of Latin America. The standard defines the "A", "B" and "C" series of paper sizes, including A4, the most commonly available paper size worldwide. Two supplementary standards, ISO 217 and ISO 269, define related paper sizes; the ISO 269 "C" series is commonly listed alongside the A and B sizes. All ISO 216, ISO 217 and ISO 269 paper sizes (except some envelopes) have the same aspect ratio, , within rounding to millimetres. This ratio has the unique property that when cut or folded in half widthways, the halves also have the same aspect ratio. Each ISO paper size is one half of the area of the next larger size in the same series. Dimensions of A, B and C series History The oldest known mention of the advantages of basing a paper size on an aspect ratio of is found in a letter written on 25 October 1786 by the German scientist Georg Christoph Lichtenberg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonetic
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that studies how humans produce and perceive sounds, or in the case of sign languages, the equivalent aspects of sign. Linguists who specialize in studying the physical properties of speech are phoneticians. The field of phonetics is traditionally divided into three sub-disciplines based on the research questions involved such as how humans plan and execute movements to produce speech ( articulatory phonetics), how various movements affect the properties of the resulting sound ( acoustic phonetics), or how humans convert sound waves to linguistic information ( auditory phonetics). Traditionally, the minimal linguistic unit of phonetics is the phone—a speech sound in a language which differs from the phonological unit of phoneme; the phoneme is an abstract categorization of phones. Phonetics deals with two aspects of human speech: production—the ways humans make sounds—and perception—the way speech is understood. The communicative mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panning (camera)
In cinematography and photography panning means swivelling a still or video camera horizontally from a fixed position. This motion is similar to the motion of a person when they turn their head on their neck from left to right. In the resulting image, the view seems to "pass by" the spectator as new material appears on one side of the screen and exits from the other, although perspective lines reveal that the entire image is seen from a fixed point of view. The term ''panning'' is derived from ''panorama'', suggesting an expansive view that exceeds the gaze, forcing the viewer to turn their head in order to take everything in. Panning, in other words, is a device for gradually revealing and incorporating off-screen space into the image. Panning should never be confused with tracking or "travelling," in which the camera is not just swivelled but is physically displaced left or right, generally by being rolled parallel to its subject. In video technology, panning refers to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Animation
Traditional animation (or classical animation, cel animation, or hand-drawn animation) is an animation technique in which each frame is drawn by hand. The technique was the dominant form of animation in cinema until computer animation. Process Writing and storyboarding Animation production usually begins after a story is converted into an animation film script, from which a storyboard is derived. A storyboard has an appearance somewhat similar to comic book panels, and is a shot by shot breakdown of the staging, acting and any camera moves that will be present in the film. The images allow the animation team to plan the flow of the plot and the composition of the imagery. Storyboard artists will have regular meetings with the director and may redraw or "re-board" a sequence many times before it meets final approval. Voice recording Before animation begins, a preliminary soundtrack or scratch track is recorded so that the animation may be more precisely synchronized t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animation
Animation is a method by which still figures are manipulated to appear as moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on transparent celluloid sheets to be photographed and exhibited on film. Today, most animations are made with computer-generated imagery (CGI). Computer animation can be very detailed 3D animation, while 2D computer animation (which may have the look of traditional animation) can be used for stylistic reasons, low bandwidth, or faster real-time renderings. Other common animation methods apply a stop motion technique to two- and three-dimensional objects like paper cutouts, puppets, or clay figures. A cartoon is an animated film, usually a short film, featuring an exaggerated visual style. The style takes inspiration from comic strips, often featuring anthropomorphic animals, superheroes, or the adventures of human protagonists. Especially with animals that form a natural predator/prey relationship (e.g. cats and mice, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animation Camera
An animation camera, a type of rostrum camera, is a movie camera specially adapted for frame-by-frame shooting of animation. It consists of a camera body with lens and film magazines, and is most often placed on a stand that allows the camera to be raised and lowered above a table often having both top and underneath lighting. The artwork to be photographed is placed on this table. For stop motion photography, the camera can also be mounted on a tripod or other support, pointing in any desired direction. Since most animation is now produced digitally, new animation cameras are not widely manufactured. Image scanners, video cameras and digital SLRs have taken their place. Examples of professional animation cameras (16 and 35 mm) A partial list of manufacturers of animation cameras includes: * Acme Tool and Manufacturing (USA) * Crass (Germany) * Neilson-Hordell (UK) * Oxberry (USA) * Double M Industries (USA) * A.I.A. Productions (USA) * Mechanical Concepts (USA) The B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |