|
Euploca Filiformis
''Euploca'' is an almost cosmopolitan genus of plants with around 100 species. It was first described by Thomas Nuttall in 1837. While part of the broadly defined Boraginaceae in the APG IV system from 2016, a revision of the order Boraginales from the same year includes ''Euploca'' in the separate family Heliotropiaceae. Its species used to be classified in the genera ''Hilgeria'' and ''Schleidenia'' and in ''Heliotropium ''Heliotropium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the heliotrope family, Heliotropiaceae. There are around 325 species in this almost cosmopolitan genus, which are commonly known as heliotropes (sg. ). It is highly toxic for dogs and cats. ...'' sect. ''Orthostachys'', but were found to form an independent lineage in a molecular phylogenetic analysis, more closely related to '' Myriopus'' than to ''Heliotropium''. While many species use the photosynthetic pathway, there are also – intermediate species. Species have leaves with a -typical Kranz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euploca Salicoides
''Euploca'' is an almost cosmopolitan genus of plants with around 100 species. It was first described by Thomas Nuttall in 1837. While part of the broadly defined Boraginaceae in the APG IV system from 2016, a revision of the order Boraginales from the same year includes ''Euploca'' in the separate family Heliotropiaceae. Its species used to be classified in the genera ''Hilgeria'' and ''Schleidenia'' and in ''Heliotropium ''Heliotropium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the heliotrope family, Heliotropiaceae. There are around 325 species in this almost cosmopolitan genus, which are commonly known as heliotropes (sg. ). It is highly toxic for dogs and cats. ...'' sect. ''Orthostachys'', but were found to form an independent lineage in a molecular phylogenetic analysis, more closely related to '' Myriopus'' than to ''Heliotropium''. While many species use the photosynthetic pathway, there are also – intermediate species. Species have leaves with a -typical Kranz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
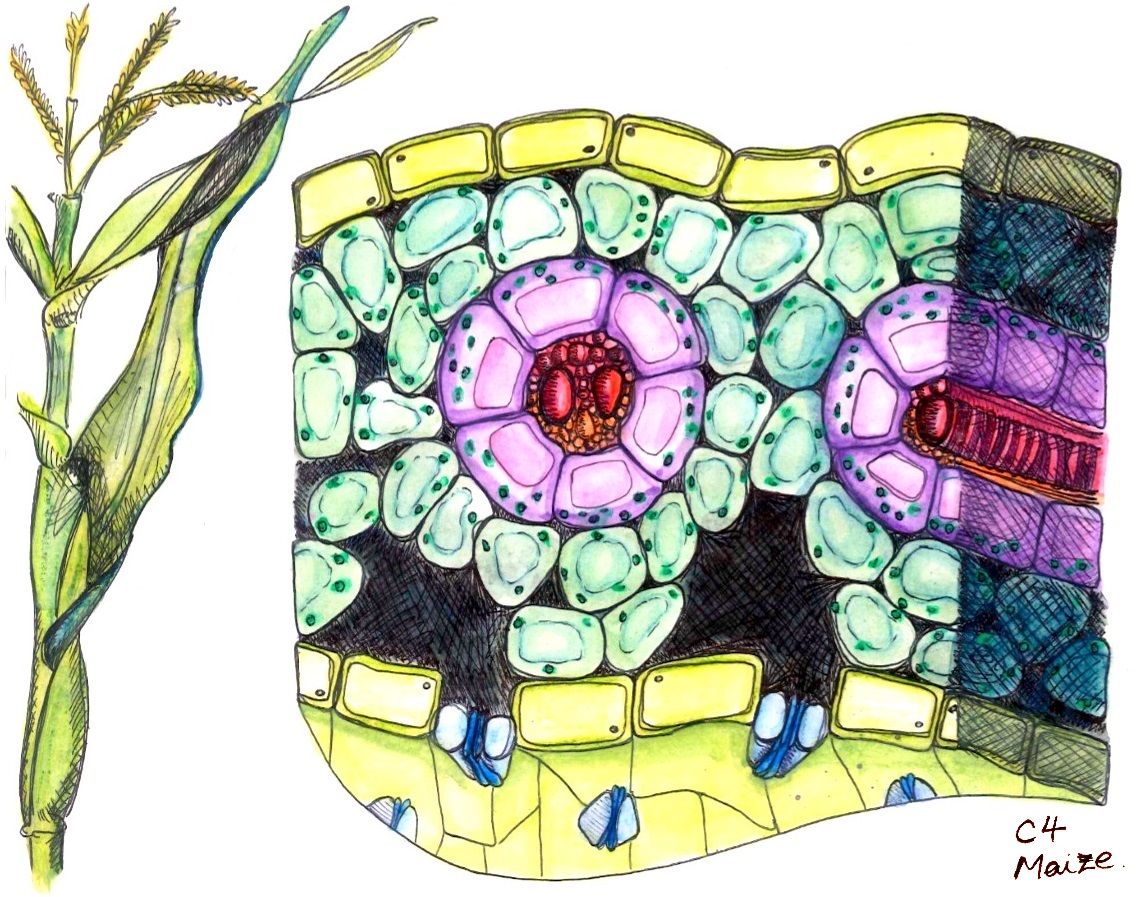
Kranz Anatomy
carbon fixation or the Hatch–Slack pathway is one of three known photosynthetic processes of carbon fixation in plants. It owes the names to the 1960's discovery by Marshall Davidson Hatch and Charles Roger Slack that some plants, when supplied with 14, incorporate the 14C label into four-carbon molecules first. fixation is an addition to the ancestral and more common carbon fixation. The main carboxylating enzyme in photosynthesis is called RuBisCO, which catalyses two distinct reactions using either (carboxylation) or oxygen (oxygenation) as a substrate. The latter process, oxygenation, gives rise to the wasteful process of photorespiration. photosynthesis reduces photorespiration by concentrating around RuBisCO. To ensure that RuBisCO works in an environment where there is a lot of carbon dioxide and very little oxygen, leaves generally differentiate two partially isolated compartments called mesophyll cells and bundle-sheath cells. is initially fixed in the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euploca Strigosa
''Euploca'' is an almost cosmopolitan genus of plants with around 100 species. It was first described by Thomas Nuttall in 1837. While part of the broadly defined Boraginaceae in the APG IV system from 2016, a revision of the order Boraginales from the same year includes ''Euploca'' in the separate family Heliotropiaceae. Its species used to be classified in the genera ''Hilgeria'' and ''Schleidenia'' and in ''Heliotropium ''Heliotropium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the heliotrope family, Heliotropiaceae. There are around 325 species in this almost cosmopolitan genus, which are commonly known as heliotropes (sg. ). It is highly toxic for dogs and cats. ...'' sect. ''Orthostachys'', but were found to form an independent lineage in a molecular phylogenetic analysis, more closely related to '' Myriopus'' than to ''Heliotropium''. While many species use the photosynthetic pathway, there are also – intermediate species. Species have leaves with a -typical Kranz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euploca Pulvina
''Euploca'' is an almost cosmopolitan genus of plants with around 100 species. It was first described by Thomas Nuttall in 1837. While part of the broadly defined Boraginaceae in the APG IV system from 2016, a revision of the order Boraginales from the same year includes ''Euploca'' in the separate family Heliotropiaceae. Its species used to be classified in the genera ''Hilgeria'' and ''Schleidenia'' and in ''Heliotropium ''Heliotropium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the heliotrope family, Heliotropiaceae. There are around 325 species in this almost cosmopolitan genus, which are commonly known as heliotropes (sg. ). It is highly toxic for dogs and cats. ...'' sect. ''Orthostachys'', but were found to form an independent lineage in a molecular phylogenetic analysis, more closely related to '' Myriopus'' than to ''Heliotropium''. While many species use the photosynthetic pathway, there are also – intermediate species. Species have leaves with a -typical Kranz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euploca Procumbens
''Euploca'' is an almost cosmopolitan genus of plants with around 100 species. It was first described by Thomas Nuttall in 1837. While part of the broadly defined Boraginaceae in the APG IV system from 2016, a revision of the order Boraginales from the same year includes ''Euploca'' in the separate family Heliotropiaceae. Its species used to be classified in the genera ''Hilgeria'' and ''Schleidenia'' and in ''Heliotropium ''Heliotropium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the heliotrope family, Heliotropiaceae. There are around 325 species in this almost cosmopolitan genus, which are commonly known as heliotropes (sg. ). It is highly toxic for dogs and cats. ...'' sect. ''Orthostachys'', but were found to form an independent lineage in a molecular phylogenetic analysis, more closely related to '' Myriopus'' than to ''Heliotropium''. While many species use the photosynthetic pathway, there are also – intermediate species. Species have leaves with a -typical Kranz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euploca Polyphylla
''Euploca'' is an almost cosmopolitan genus of plants with around 100 species. It was first described by Thomas Nuttall in 1837. While part of the broadly defined Boraginaceae in the APG IV system from 2016, a revision of the order Boraginales from the same year includes ''Euploca'' in the separate family Heliotropiaceae. Its species used to be classified in the genera ''Hilgeria'' and ''Schleidenia'' and in ''Heliotropium ''Heliotropium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the heliotrope family, Heliotropiaceae. There are around 325 species in this almost cosmopolitan genus, which are commonly known as heliotropes (sg. ). It is highly toxic for dogs and cats. ...'' sect. ''Orthostachys'', but were found to form an independent lineage in a molecular phylogenetic analysis, more closely related to '' Myriopus'' than to ''Heliotropium''. While many species use the photosynthetic pathway, there are also – intermediate species. Species have leaves with a -typical Kranz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euploca Ovalifolia
''Euploca'' is an almost cosmopolitan genus of plants with around 100 species. It was first described by Thomas Nuttall in 1837. While part of the broadly defined Boraginaceae in the APG IV system from 2016, a revision of the order Boraginales from the same year includes ''Euploca'' in the separate family Heliotropiaceae. Its species used to be classified in the genera ''Hilgeria'' and ''Schleidenia'' and in ''Heliotropium ''Heliotropium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the heliotrope family, Heliotropiaceae. There are around 325 species in this almost cosmopolitan genus, which are commonly known as heliotropes (sg. ). It is highly toxic for dogs and cats. ...'' sect. ''Orthostachys'', but were found to form an independent lineage in a molecular phylogenetic analysis, more closely related to '' Myriopus'' than to ''Heliotropium''. While many species use the photosynthetic pathway, there are also – intermediate species. Species have leaves with a -typical Kranz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euploca Humilis
''Euploca humilis'' (syn. ''Tournefortia humilis''), the dwarf tournefortia, is a species of flowering plant in the family Boraginaceae. It is native to Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean, Colombia, Venezuela, Guyana, and most of Brazil. Originally described by Linnaeus in 1753, molecular and morphological evidence led to its transfer from ''Tournefortia'' to ''Euploca ''Euploca'' is an almost cosmopolitan genus of plants with around 100 species. It was first described by Thomas Nuttall in 1837. While part of the broadly defined Boraginaceae in the APG IV system from 2016, a revision of the order Boraginales ...'' in 2016. References Heliotropioideae Flora of Mexico Flora of Central America Flora of the Caribbean Flora of Colombia Flora of Venezuela Flora of Guyana Flora of North Brazil Flora of Northeast Brazil Flora of West-Central Brazil Flora of Southeast Brazil Plants described in 2016 Flora without expected TNC conservation status {{Asterid- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euploca Greggii
''Euploca'' is an almost cosmopolitan genus of plants with around 100 species. It was first described by Thomas Nuttall in 1837. While part of the broadly defined Boraginaceae in the APG IV system from 2016, a revision of the order Boraginales from the same year includes ''Euploca'' in the separate family Heliotropiaceae. Its species used to be classified in the genera ''Hilgeria'' and ''Schleidenia'' and in ''Heliotropium ''Heliotropium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the heliotrope family, Heliotropiaceae. There are around 325 species in this almost cosmopolitan genus, which are commonly known as heliotropes (sg. ). It is highly toxic for dogs and cats. ...'' sect. ''Orthostachys'', but were found to form an independent lineage in a molecular phylogenetic analysis, more closely related to '' Myriopus'' than to ''Heliotropium''. While many species use the photosynthetic pathway, there are also – intermediate species. Species have leaves with a -typical Kranz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euploca Fruticosa
''Euploca'' is an almost cosmopolitan genus of plants with around 100 species. It was first described by Thomas Nuttall in 1837. While part of the broadly defined Boraginaceae in the APG IV system from 2016, a revision of the order Boraginales from the same year includes ''Euploca'' in the separate family Heliotropiaceae. Its species used to be classified in the genera ''Hilgeria'' and ''Schleidenia'' and in ''Heliotropium ''Heliotropium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the heliotrope family, Heliotropiaceae. There are around 325 species in this almost cosmopolitan genus, which are commonly known as heliotropes (sg. ). It is highly toxic for dogs and cats. ...'' sect. ''Orthostachys'', but were found to form an independent lineage in a molecular phylogenetic analysis, more closely related to '' Myriopus'' than to ''Heliotropium''. While many species use the photosynthetic pathway, there are also – intermediate species. Species have leaves with a -typical Kranz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euploca Filiformis
''Euploca'' is an almost cosmopolitan genus of plants with around 100 species. It was first described by Thomas Nuttall in 1837. While part of the broadly defined Boraginaceae in the APG IV system from 2016, a revision of the order Boraginales from the same year includes ''Euploca'' in the separate family Heliotropiaceae. Its species used to be classified in the genera ''Hilgeria'' and ''Schleidenia'' and in ''Heliotropium ''Heliotropium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the heliotrope family, Heliotropiaceae. There are around 325 species in this almost cosmopolitan genus, which are commonly known as heliotropes (sg. ). It is highly toxic for dogs and cats. ...'' sect. ''Orthostachys'', but were found to form an independent lineage in a molecular phylogenetic analysis, more closely related to '' Myriopus'' than to ''Heliotropium''. While many species use the photosynthetic pathway, there are also – intermediate species. Species have leaves with a -typical Kranz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C4 Carbon Fixation
carbon fixation or the Hatch–Slack pathway is one of three known photosynthetic processes of carbon fixation in plants. It owes the names to the 1960's discovery by Marshall Davidson Hatch and Charles Roger Slack that some plants, when supplied with 14, incorporate the 14C label into four-carbon molecules first. fixation is an addition to the ancestral and more common carbon fixation. The main carboxylating enzyme in photosynthesis is called RuBisCO, which catalyses two distinct reactions using either (carboxylation) or oxygen (oxygenation) as a substrate. The latter process, oxygenation, gives rise to the wasteful process of photorespiration. photosynthesis reduces photorespiration by concentrating around RuBisCO. To ensure that RuBisCO works in an environment where there is a lot of carbon dioxide and very little oxygen, leaves generally differentiate two partially isolated compartments called mesophyll cells and bundle-sheath cells. is initially fixed in the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |