|
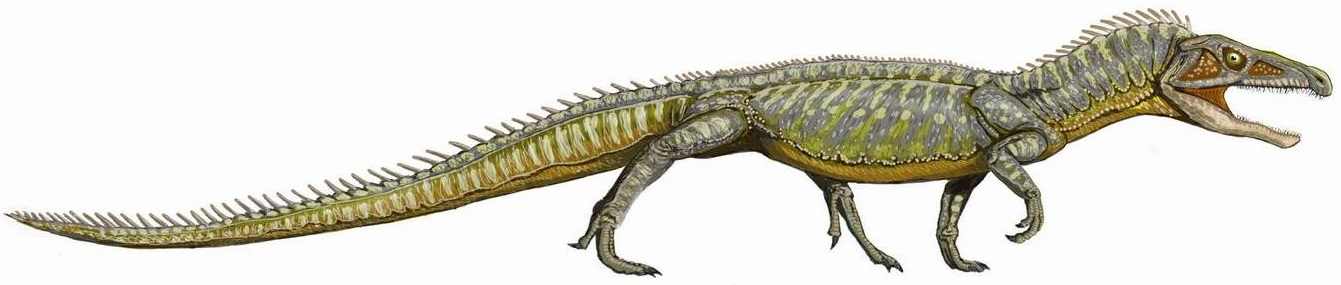
Erythrosuchus
''Erythrosuchus'' (from el, ἐρυθρός , 'red' and el, σοῦχος , 'crocodile') is an extinct genus of archosauriform reptile from the Triassic of South Africa. Remains have been found from the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group in the Karoo of South Africa. In the Late Triassic, the ecological niche left by ''Erythrosuchus'' was filled by archosaurs like '' Saurosuchus'' and ''Postosuchus''. Description ''Erythrosuchus'' was the largest predator of its time, and was around long. It walked on all fours and had limbs which were positioned semi-vertically under its body, unlike the more sprawling gait of most earlier reptiles. Its head was large and theropod-like, reaching a length of , and had sharp, conical teeth. ''Erythrosuchus'' was the largest erythrosuchid, but apart from its size, was largely similar in appearance to other related genera. It had a large head and comparatively short neck. One of the few distinguishing features of ''Erythrosuch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauriform
Archosauriformes (Greek for 'ruling lizards', and Latin for 'form') is a clade of diapsid reptiles that developed from archosauromorph ancestors some time in the Latest Permian (roughly 252 million years ago). It was defined by Jacques Gauthier (1994) as the clade stemming from the last common ancestor of Proterosuchidae and Archosauria (the group that contains crocodiles, pterosaurs and dinosaurs ncluding birds; Phil Senter">bird">ncluding_bird<_a>s.html" ;"title="bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds">bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds; Phil Senter (2005) defined it as the most exclusive clade containing ''Proterosuchus'' and Archosauria. These reptiles, which include members of the Family (biology), family Proterosuchidae and more advanced forms, were originally superficially crocodile-like animals with sprawling gaits and long snouts. Unlike the bulk of their therapsid contemporaries, the proterosuchids survived the catastrophe at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynognathus Assemblage Zone
The ''Cynognathus'' Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod biozone utilized in the Karoo Basin of South Africa. It is equivalent to the Burgersdorp Formation, the youngest lithostratigraphic formation in the Beaufort Group, which is part of the fossiliferous and geologically important Karoo Supergroup. The '' Cynognathus'' Assemblage Zone is the youngest of the eight biozones found in the Beaufort Group, and is considered to be late Early Triassic (Olenekian) to early Middle Triassic (Anisian) in age (around 247 Ma). The name of the biozone refers to '' Cynognathus crateronotus'', a large and carnivorous cynodont therapsid which occurs throughout the entire biozone. History The first fossils to be found in the Beaufort Group rocks that encompass the current eight biozones were discovered by Andrew Geddes Bain in 1856. However, it was not until 1892 that it was observed that the geological strata of the Beaufort Group could be differentiated based on their fossil taxa. The initial under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch (late Permian, Paleozoic Era) and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages. The Lower Triassic series is coeval with the Scythian Stage, which is today not included in the official timescales but can be found in older literature. In Europe, most of the Lower Triassic is composed of Buntsandstein, a lithostratigraphic unit of continental red beds. The Early Triassic and partly also the Middle Triassic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Largest Prehistoric Animals
The largest prehistoric animals include both vertebrate and invertebrate species. Many of them are described below, along with their typical range of size (for the general dates of extinction, see the link to each). Many species mentioned might not actually be the largest representative of their clade due to the incompleteness of the fossil record and many of the sizes given are merely estimates since no complete specimen have been found. Their body mass, especially, is largely conjecture because soft tissue was rarely fossilized. Generally the size of extinct species was subject to energetic and biomechanical constraints. Non-mammalian synapsids (Synapsida) Caseasaurs (Caseasauria) The herbivorous ''Alierasaurus'' was the largest caseid and the largest amniote to have lived at the time, with an estimated length around . ''Cotylorhynchus hancocki'' is also large, with an estimated length and weight of at least and more than . Edaphosaurids (Edaphosauridae) The larges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaufort Group
The Beaufort Group is the third of the main subdivisions of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. It is composed of a lower Adelaide Subgroup and an upper Tarkastad Subgroup. It follows conformably after the Ecca Group and unconformably underlies the Stormberg Group. Based on stratigraphic position, lithostratigraphic and biostratigraphic correlations, palynological analyses, and other means of geological dating, the Beaufort Group rocks are considered to range between Middle Permian ( Wordian) to Early Triassic (Anisian) in age. Background During the period when sedimentation of the Beaufort Group rocks took place, the Ecca sea had retreated to the northeastern Karoo Basin. All sediment deposition at this time took place in a terrestrial, although in a predominantly fluvial or alluvial environment that was seasonally arid. This environment covered a vast area and deposition was influenced by a retroarc foreland basin. This foreland system was caused by crustal uplift ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History Museum, London
The Natural History Museum in London is a museum that exhibits a vast range of specimens from various segments of natural history. It is one of three major museums on Exhibition Road in South Kensington, the others being the Science Museum and the Victoria and Albert Museum. The Natural History Museum's main frontage, however, is on Cromwell Road. The museum is home to life and earth science specimens comprising some 80 million items within five main collections: botany, entomology, mineralogy, palaeontology and zoology. The museum is a centre of research specialising in taxonomy, identification and conservation. Given the age of the institution, many of the collections have great historical as well as scientific value, such as specimens collected by Charles Darwin. The museum is particularly famous for its exhibition of dinosaur skeletons and ornate architecture—sometimes dubbed a ''cathedral of nature''—both exemplified by the large ''Diplodocus'' cast that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Von Huene
Friedrich von Huene, born Friedrich Richard von Hoinigen, (March 22, 1875 – April 4, 1969) was a German paleontologist who renamed more dinosaurs in the early 20th century than anyone else in Europe. He also made key contributions about various Permo-Carboniferous limbed vertebrates. Biography Huene was born in Tübingen, Kingdom of Württemberg. His discoveries include the skeletons of more than 35 individuals of ''Plateosaurus'' in the famous Trossingen quarry, the early proto-dinosaur ''Saltopus'' in 1910, ''Proceratosaurus'' in 1926, the giant ''Antarctosaurus'' in 1929, and numerous other dinosaurs and fossilized animals like pterosaurs. He also was the first to naming several higher taxa, including Prosauropoda and Sauropodomorpha. In 1941 he found a stone that had petrified wood in it, sadly, He thought that it was a dinosaur. However a couple Polish paleontologists. The “dinosaur” was called the Succinodon He visited the Geopark of Paleorrota in 1928, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study their interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek (, "old, ancient"), (, ( gen. ), "being, creature"), and (, "speech, thought, study"). Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of anatomically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics, and engineer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans as ''Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city#National capitals, Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national Government of the United Kingdom, government and Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the Counties of England, counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its 16 constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of . It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and Czechia to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in what is now Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |