|
Eraillure
In lithic analysis (a subdivision of archaeology), an eraillure is a flake removed from a lithic flake's bulb of applied force, bulb of force, which is a lump left on the ventral surface of a flake after it is detached from a core of tool stone during the process of lithic reduction.Hiscock, Peter. (1997Glossary of Terms used in "Lithic" Analysis." Australian National University. Retrieved 2011-12-14. The mechanics of eraillure formation are related to the propagation of a Hertzian cone of force through the cryptocrystalline matrix of the stone, but the particulars are poorly understood. Eraillures usually form only when a hammerstone is used for lithic reduction, and then only occasionally; use of 'soft' hammer fabricators made from bone, antler, and wood produce different flake characteristics but may also produce an eraillure in rare cases. See also * Stone tool References {{Prehistoric technology Lithics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithic Flake
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and may also be referred to as simply a ''flake'', or collectively as debitage. The objective piece, or the rock being reduced by the removal of flakes, is known as a core.Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press Once the proper tool stone has been selected, a percussor or pressure flaker (e.g., an antler tine) is used to direct a sharp blow, or apply sufficient force, respectively, to the surface of the stone, often on the edge of the piece. The energy of this blow propagates through the material, often ( but not always) producing a Hertzian cone of force which causes the rock to fracture in a controllable fashion. Since cores are often struck on an edge with a suitable angle (<90° ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
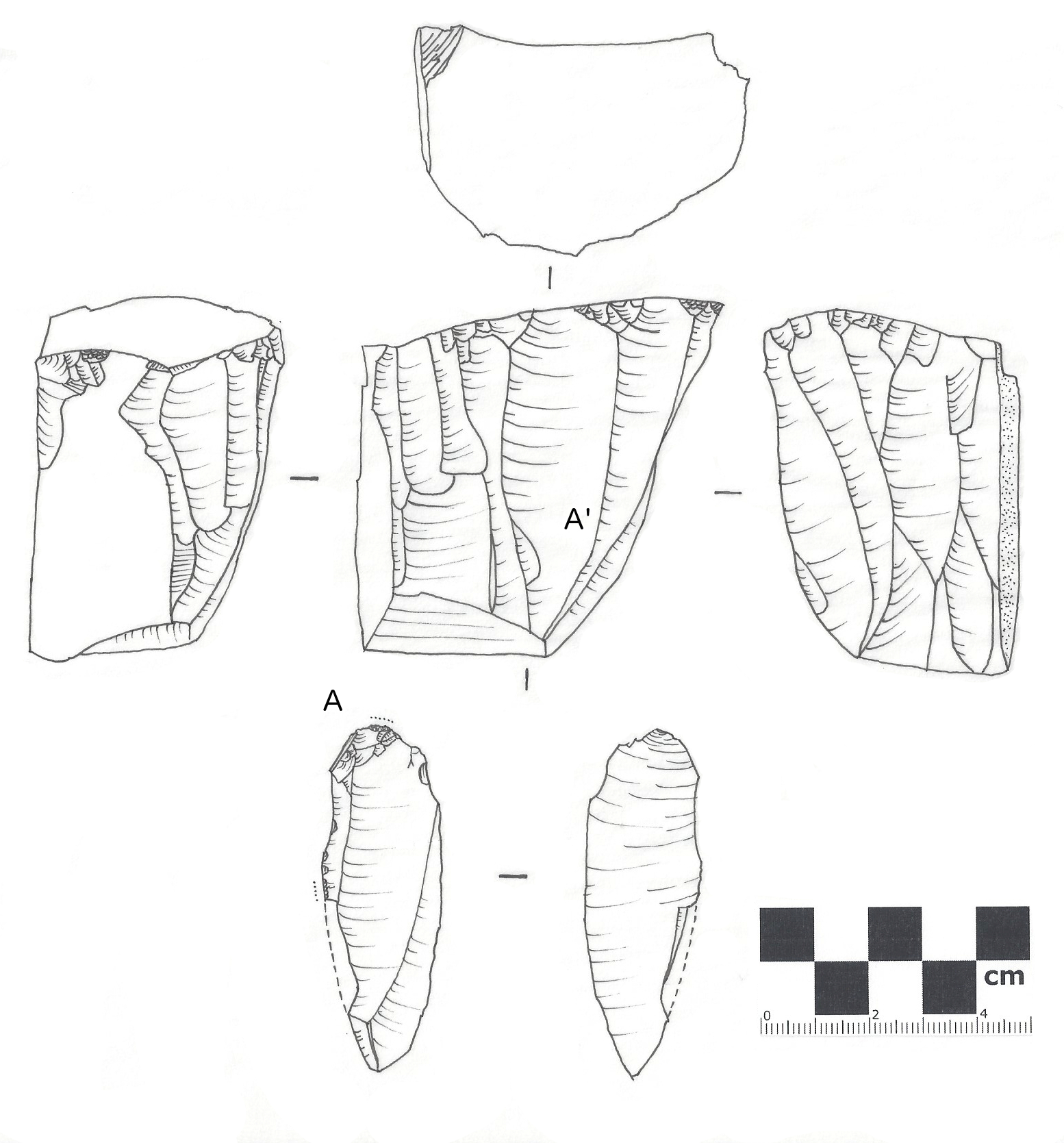
Lithic Analysis
In archaeology, lithic analysis is the analysis of stone tools and other chipped stone artifacts using basic scientific techniques. At its most basic level, lithic analyses involve an analysis of the artifact’s morphology, the measurement of various physical attributes, and examining other visible features (such as noting the presence or absence of cortex, for example). The term 'lithic analysis' can technically refer to the study of any anthropogenic (human-created) stone, but in its usual sense it is applied to archaeological material that was produced through lithic reduction (knapping) or ground stone. A thorough understanding of the lithic reduction and ground stone processes, in combination with the use of statistics, can allow the analyst to draw conclusions concerning the type of lithic manufacturing techniques used at a prehistoric archaeological site. For example, they can make certain equation between each the factors of flake to predict original shape. These d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulb Of Applied Force
In lithic analysis, a subdivision of archaeology, a bulb of applied force (also known as a bulb of percussion or simply bulb of force) is a defining characteristic of a lithic flake. Bulb of applied force was first correctly described by Sir John Evans, the cofounder of prehistoric archeology. However, bulb of percussion was coined scientifically by W.J. Sollas. When a flake is detached from its parent core, a portion of the Hertzian cone of force caused by the detachment blow is detached with it, leaving a distinctive bulb on the flake and a corresponding flake scar on the core. In the case of a unidirectional core, the bulb of applied force is produced by an initiated crack formed at the point of contact, which begins producing the Hertzian cone. The outward pressure increases causing the crack to curve away from the core and the bulb formation. The bulb of applied force forms below the striking platform as a slight bulge. If the flake is completely crushed the bulb will not be vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tool Stone
A tool is an object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many animals use simple tools, only human beings, whose use of stone tools dates back hundreds of millennia, have been observed using tools to make other tools. Early human tools, made of such materials as stone, bone, and wood, were used for preparation of food, hunting, manufacture of weapons, and working of materials to produce clothing and useful artifacts. The development of metalworking made additional types of tools possible. Harnessing energy sources, such as animal power, wind, or steam, allowed increasingly complex tools to produce an even larger range of items, with the Industrial Revolution marking an inflection point in the use of tools. The introduction of widespread automation in the 19th and 20th centuries allowed tools to operate with minimal human supervision, further increasing the productivity of hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithic Reduction
In archaeology, in particular of the Stone Age, lithic reduction is the process of fashioning stones or rocks from their natural state into tools or weapons by removing some parts. It has been intensely studied and many archaeological industries are identified almost entirely by the lithic analysis of the precise style of their tools and the chaîne opératoire of the reduction techniques they used. Normally the starting point is the selection of a piece of tool stone that has been detached by natural geological processes, and is an appropriate size and shape. In some cases solid rock or larger boulders may be quarried and broken into suitable smaller pieces, and in others the starting point may be a piece of the debitage, a flake removed from a previous operation to make a larger tool. The selected piece is called the lithic core (also known as the "objective piece"). A basic distinction is that between flaked or knapped stone, the main subject here, and ground stone ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertzian Cone
A Hertzian cone is the cone produced when an object passes through a solid, such as a bullet through glass. More technically, it is a cone of force that propagates through a brittle, amorphous, or cryptocrystalline solid material from a point of impact. This force eventually removes a full or partial cone in the material. This is the physical principle that explains the form and characteristics of the flakes removed from a core of tool stone during the process of lithic reduction. This phenomenon is named after the German physicist Heinrich Rudolf Hertz, who first described this type of wave-front propagation through various media. Although it might not be agreed by all, natural phenomena which have been grouped with the Hertzian cone phenomena include the crescentic "chatter marks" made on smoothed bedrock by glacial ice dragging along boulders at its base, the numerous crescentic impact marks sometimes seen on pebbles and cobbles, and the shatter cones found at bolide impact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

