|
Enchelii
The Enchelei were an ancient people that lived around the region of Lake Shkodra and Lake Ohrid,Strabo, Geography (ed. H.C. Hamilton, Esq., W. Falconer, M.A.), book 7, chapter 7: "...had established their sway, and Enchelii, who are also called Sesarethii. Then come the Lyncestæ, the territory Deuriopus, Pelagonia-Tripolitis..." in modern-day Albania, Montenegro, and North Macedonia. They are one of the oldest known peoples of the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. In ancient sources they sometimes appear as an ethnic group distinct from the Illyrians, but they are mostly mentioned as one of the Illyrian tribes. The name Sesarethii was used by Strabo as an alternative name for the Enchelei in the lakeland area of Ohrid. Mentioned for the first time by Hecataeus of Miletus in the 6th century BC, the name ''Sesarethii/Sesarethioi'' is also considered a variant of '' Dassaretii/Dassaretioi'', an Illyrian tribe that has been recorded since Roman times and that is attested in coinage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmus
In Greek mythology, Cadmus (; grc-gre, Κάδμος, Kádmos) was the legendary Phoenician founder of Boeotian Thebes. He was the first Greek hero and, alongside Perseus and Bellerophon, the greatest hero and slayer of monsters before the days of Heracles. Commonly stated to be a prince of Phoenicia, the son of king Agenor and queen Telephassa of Tyre, the brother of Phoenix, Cilix and Europa, Cadmus could trace his origins back to Zeus. Originally, he was sent by his royal parents to seek out and escort his sister Europa back to Tyre after she was abducted from the shores of Phoenicia by Zeus. In early accounts, Cadmus and Europa were instead the children of Phoenix. Scholia on Homer, '' Iliad'' B, 494, p. 80, 43 ed. Bekk. as cited in Hellanicus' ''Boeotica'' Cadmus founded the Greek city of Thebes, the acropolis of which was originally named ''Cadmeia'' in his honour. Cadmus' homeland was the subject of significant disagreement among ancient authors. Apollodorus ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sesarethus
Sesarethus ( grc, Σεσάρηθος) was an ancient city in southern Illyria. Stephanus of Byzantium from the 6th century AD reports, citing Hecataeus (6th century BC), that Sesarethos was a Taulantian city, and that ''Sesarethioi'' was its ''ethnicon''. The city and the tribal name Sessarethes have been related by modern scholars to the Illyrian tribe of Dassaretii. The variant ''Sesarethii'' is also mentioned by Strabo (1st century BC – 1st century AD) as an alternative name of the Enchelei.Strabo, ''Geography'', book 7, chapter 7: "...had established their sway, and Enchelii, who are also called Sesarethii. Then come the Lyncestæ, the territory Deuriopus, Pelagonia-Tripolitis..." See also * List of settlements in Illyria This is a list of settlements in Illyria founded by Illyrians (southern Illyrians, Dardanians, Pannonians), Liburni, Ancient Greeks and the Roman Empire. A number of cities in Illyria and later Illyricum were built on the sites or close to the s ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibliotheca (Pseudo-Apollodorus)
The ''Bibliotheca'' (Ancient Greek: grc, Βιβλιοθήκη, lit=Library, translit=Bibliothēkē, label=none), also known as the ''Bibliotheca'' of Pseudo-Apollodorus, is a compendium of Greek mythology, Greek myths and Greek hero, heroic legends, arranged in three books, generally dated to the first or second century AD. The author was traditionally thought to be Apollodorus of Athens, but that attribution is now regarded as false, and so "Pseudo-" was added to Apollodorus. The ''Bibliotheca'' has been called "the most valuable mythographical work that has come down from ancient times." An epigram recorded by the important intellectual Patriarch Photius I of Constantinople expressed its purpose:Victim of its own suggestions, the Epigraph (literature), epigraph, ironically, does not survive in the manuscripts. For the classic examples of Epitome, epitomes and Encyclopedia, encyclopedias substituting in Christian hands for the literature of Classical Antiquity itself, see Isido ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebes, Greece
Thebes (; ell, Θήβα, ''Thíva'' ; grc, Θῆβαι, ''Thêbai'' .) is a city in Boeotia, Central Greece. It played an important role in Greek myths, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus, Heracles and others. Archaeological excavations in and around Thebes have revealed a Mycenaean settlement and clay tablets written in the Linear B script, indicating the importance of the site in the Bronze Age. Thebes was the largest city of the ancient region of Boeotia and was the leader of the Boeotian confederacy. It was a major rival of ancient Athens, and sided with the Persians during the 480 BC invasion under Xerxes I. Theban forces under the command of Epaminondas ended Spartan hegemony at the Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC, with the Sacred Band of Thebes, an elite military unit of male lovers celebrated as instrumental there. Macedonia would rise in power at the Battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC, bringing decisive victory to Philip II over an alliance of Theb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their history, and they possessed several enclaves such as Arwad and Tell Sukas (modern Syria). The core region in which the Phoenician culture developed and thrived stretched from Tripoli and Byblos in northern Lebanon to Mount Carmel in modern Israel. At their height, the Phoenician possessions in the Eastern Mediterranean stretched from the Orontes River mouth to Ashkelon. Beyond its homeland, the Phoenician civilization extended to the Mediterranean from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula. The Phoenicians were a Semitic-speaking people of somewhat unknown origin who emerged in the Levant around 3000 BC. The term ''Phoenicia'' is an ancient Greek exonym that most likely described one of their most famous exports, a dye also known as Tyrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelidonioi
Taulantii or Taulantians ('swallow-men'; Ancient Greek: , or , ; la, Taulantii) were an Illyrian people that lived on the Adriatic coast of southern Illyria (modern Albania). They dominated at various times much of the plain between the rivers Drin (''Drilon'') and Vjosa (''Aoös''). Their central area was the hinterland of Epidamnos-Dyrrhachion, corresponding to present-day Tirana and the region between the valleys of Mat and Shkumbin (''Genusus''). The Taulantii are among the oldest attested Illyrian peoples, who established a powerful kingdom in southern Illyria. They are among the peoples who most marked Illyrian history, and thus found their place in the numerous works of historians in classical antiquity. Name The Taulantii, along with the Eneti, are the oldest attested peoples expressly considered Illyrian in early Greek historiography. The Taulantii were firstly recorded by ancient Greek writer Hecataeus of Miletus in the 6th century BC. The ''Taulantii'' are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
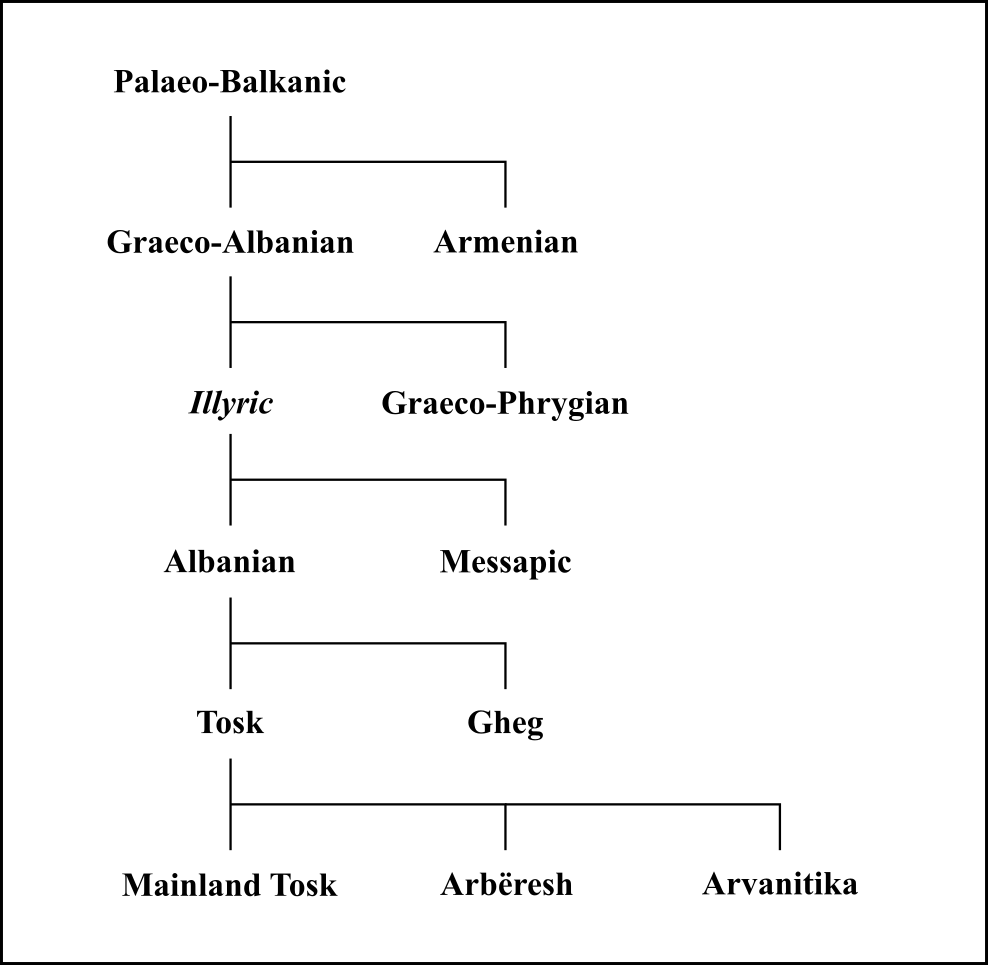
Paleo-Balkan Languages
The Paleo-Balkan languages or Palaeo-Balkan languages is a grouping of various extinct Indo-European languages that were spoken in the Balkans and surrounding areas in ancient times. Paleo-Balkan studies are obscured by the scarce attestation of these languages outside of Ancient Greek and, to a lesser extent, Messapic and Phrygian. Although linguists consider each of them to be a member of the Indo-European family of languages, the internal relationships are still debated. Due to the processes of Hellenization, Romanization and Slavicization in the region, the only modern descendants of Paleo-Balkan languages are Modern Greek—which is descended from Ancient Greek—and Albanian—which evolved from either Illyrian, Thracian, Dacian or another related tongue. Classification *Proto-Indo-European **Paleo-Balkan linguistic area ***Unclassified ****Illyrian languages ( onomastic areas) *****Illyrian proper (or Southeast Dalmatian) *****Central Dalmatian (or Dalmatian-Pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mnaseas
Mnaseas of Patrae ( grc, Μνασέας ὁ Πατρεύς) or of Patara, whether that in Lycia or perhaps the Patara in Cappadocia was a Greek historian of the late 3rd century BCE, who is reckoned to have been a pupil in Alexandria of Eratosthenes. His ''Periegesis'' or ''Periplus'' described Europe, Western Asia and North Africa, but whether in six or eight books cannot now be determined. His ''On Oracles'' appears to have consisted of a catalogue of oracular responses with commentary. Only fragments of his work survive, some found in fragmentary papyri at Oxyrhynchus, others embedded as scholia Scholia (singular scholium or scholion, from grc, σχόλιον, "comment, interpretation") are grammatical, critical, or explanatory comments – original or copied from prior commentaries – which are inserted in the margin of t ... or as quotations in other works, often selected, apparently, because of the unusual interpretations they offer. A modern edition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail. Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed constitution or the separation of powers in government, his in-depth discussion of checks and balances to limit power, and his introduction of "the people", which influenced Montesquieu's '' The Spirit of the Laws'', John Locke's '' Two Treatises of Government'', and the framers of the United States Constitution. The leading expert on Polybius for nearly a century was F. W. Walbank (1909–2008), who published studies related to him for 50 years, including a long commentary of his ''Histories'' and a biography. Early life Polybius was born around 200 BC in Megalopolis, Arcadia, when it was an active member of the Achaean League. The town was revived, along with other Achaean states, a century before he was born. Polybius' father, Lyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illyrian Languages
The Illyrian language () was an Indo-European language or group of languages spoken by the Illyrians in Southeast Europe during antiquity. The language is unattested with the exception of personal names and placenames. Just enough information can be drawn from these to allow the conclusion that it belonged to the Indo-European language family. In ancient sources, the term " Illyrian" is applied to a wide range of tribes settling in a large area of southeastern Europe, including Ardiaei, Autariatae, Delmatae, Dassareti, Enchelei, Labeatae, Pannonii, Parthini, Taulantii and others (see list of ancient tribes in Illyria). It is not known to what extent all of these tribes formed a homogeneous linguistic group, but the study of the attested eponyms has led to the identification of a linguistic core area in the south of this zone, roughly around what is now Albania and Montenegro, where Illyrian proper is believed to have been spoken. Little is known about the relationships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_singing.jpg)