|
Eidophor
An Eidophor was a video projector used to create theater-sized images from an analog video signal. The name Eidophor is derived from the Greek word-roots ''eido'' and ''phor'' meaning 'image' and 'bearer' (carrier). Its basic technology was the use of electrostatic charges to deform an oil surface. Origins and use The idea for the original Eidophor was conceived in 1939 in Zurich by Swiss physicist Fritz Fischer, professor at the ''Labor für technische Physik'' of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, with the first prototype being unveiled in 1943. A basic patent was filed on November 8, 1939, in SwitzerlandMonika Burri''Der Eidophor-Projektor.''ETH History 1855 - 2005. Retrieved 26 September 2019 and granted by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (patent no. 2,391,451) to Friederich Ernst Fischer for the ''Process and appliance for projecting television pictures'' on 25 December 1945. During the Second World War, Edgar Gretener worked together with Fischer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eidophor
An Eidophor was a video projector used to create theater-sized images from an analog video signal. The name Eidophor is derived from the Greek word-roots ''eido'' and ''phor'' meaning 'image' and 'bearer' (carrier). Its basic technology was the use of electrostatic charges to deform an oil surface. Origins and use The idea for the original Eidophor was conceived in 1939 in Zurich by Swiss physicist Fritz Fischer, professor at the ''Labor für technische Physik'' of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, with the first prototype being unveiled in 1943. A basic patent was filed on November 8, 1939, in SwitzerlandMonika Burri''Der Eidophor-Projektor.''ETH History 1855 - 2005. Retrieved 26 September 2019 and granted by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (patent no. 2,391,451) to Friederich Ernst Fischer for the ''Process and appliance for projecting television pictures'' on 25 December 1945. During the Second World War, Edgar Gretener worked together with Fischer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eidophor Back
An Eidophor was a video projector used to create theater-sized images from an analog video signal. The name Eidophor is derived from the Greek word-roots ''eido'' and ''phor'' meaning 'image' and 'bearer' (carrier). Its basic technology was the use of electrostatic charges to deform an oil surface. Origins and use The idea for the original Eidophor was conceived in 1939 in Zurich by Swiss physicist Fritz Fischer, professor at the ''Labor für technische Physik'' of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, with the first prototype being unveiled in 1943. A basic patent was filed on November 8, 1939, in SwitzerlandMonika Burri''Der Eidophor-Projektor.''ETH History 1855 - 2005. Retrieved 26 September 2019 and granted by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (patent no. 2,391,451) to Friederich Ernst Fischer for the ''Process and appliance for projecting television pictures'' on 25 December 1945. During the Second World War, Edgar Gretener worked together with Fischer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eidophor Front
An Eidophor was a video projector used to create theater-sized images from an analog video signal. The name Eidophor is derived from the Greek word-roots ''eido'' and ''phor'' meaning 'image' and 'bearer' (carrier). Its basic technology was the use of electrostatic charges to deform an oil surface. Origins and use The idea for the original Eidophor was conceived in 1939 in Zurich by Swiss physicist Fritz Fischer, professor at the ''Labor für technische Physik'' of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, with the first prototype being unveiled in 1943. A basic patent was filed on November 8, 1939, in SwitzerlandMonika Burri''Der Eidophor-Projektor.''ETH History 1855 - 2005. Retrieved 26 September 2019 and granted by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (patent no. 2,391,451) to Friederich Ernst Fischer for the ''Process and appliance for projecting television pictures'' on 25 December 1945. During the Second World War, Edgar Gretener worked together with Fischer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eidophor Display Mission Control Center Houston
An Eidophor was a video projector used to create theater-sized images from an analog video signal. The name Eidophor is derived from the Greek word-roots ''eido'' and ''phor'' meaning 'image' and 'bearer' (carrier). Its basic technology was the use of electrostatic charges to deform an oil surface. Origins and use The idea for the original Eidophor was conceived in 1939 in Zurich by Swiss physicist Fritz Fischer, professor at the ''Labor für technische Physik'' of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, with the first prototype being unveiled in 1943. A basic patent was filed on November 8, 1939, in SwitzerlandMonika Burri''Der Eidophor-Projektor.''ETH History 1855 - 2005. Retrieved 26 September 2019 and granted by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (patent no. 2,391,451) to Friederich Ernst Fischer for the ''Process and appliance for projecting television pictures'' on 25 December 1945. During the Second World War, Edgar Gretener worked together with Fischer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edgar Gretener
Edgar Gretener (2 March 1902 in Lucerne – 21 October 1958 in Zurich) was a Swiss electrical engineer. Gretener was the twelfth of 14 siblings. He studied electrical engineering at Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH Zurich), where he received his Ph.D. in 1929. He then became head of development at the Albiswerk factory in Zurich. In 1930, he worked as head of the telegraph laboratory of Siemens & Halske in Berlin. There he got in contact with Fritz Fischer (physicist), another Swiss engineer, working as a manager at the central research labs of Siemens. When Fritz Fischer got the call to become professor at the ETH Zurich in 1932, he made Gretener his chief assistant a few years later. Fischer invented the Eidophor video projection system. Gretener was in charge of its implementation. When World War II started, the Swiss authorities asked Gretener to develop an encryption device for teleprinters. For this purpose the Dr. Edgar Gretener AG was set up as a company in 194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Thiemann
Hugo Thiemann (February 2, 1917 – June 10, 2012) was a Swiss R&D manager and visionary. He was a founding member of the ''Club of Rome''. Life Hugo Ernst Thiemann was born in Heiden, Switzerland, then educated in nearby St. Gallen, Switzerland. He studied electrical engineering at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich (ETH Zurich), graduated in 1939 and got his PhD in 1947. There, he was assistant to Professor Fritz Fischer (physicist), known as the inventor of the Eidophor large-screen video projection system, at the Institute of Technical Physics. Thiemann was leading the Eidophor project from 1941 onwards. He lost an eye during his education according to his autobiography (unpublished). In 1946 he married Marianne Beatrice Sturzenegger. When the Eidophor project was transferred from the ETH to Dr. Edgar Gretener AG, a small Swiss company, he joined this company, which was founded by his former colleague Gretener. Later, Thiemann joined the European subsidiar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fritz Fischer (physicist)
Fritz Fischer (9 February 1898, Oberdiessbach im Emmenthal BE, Switzerland – 28 December 1947, Zurich, Switzerland) was a technical physicist, engineer and inventor. He was married to Maud Schätti.Borgnis, Fritz''Fischer, Fritz''.In: ''Neue Deutsche Biographie'' 5 (1961), p. 185. Retrieved 2020-04-13. Fritz Fischer studied electrical engineering at the ETH Zurich from 1917 till 1921 and graduated as Dr. sc. tech in 1924. Working at the ''Telephonwerke Albisrieden'' he improved the transmission quality of speech, whereupon he was called to the central laboratories of the mother company Siemens & Halske in Berlin. There he built the first remotely controlled ships and airplanes and investigated the physical properties of colour film. Over 70 patent applications resulted from his work at Siemens. He was lecturer at the Technical University of Berlin. 1932 he received a call to the ETH Zurich, where he became professor and founded the Institute of Technical Physics. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Projector
A video projector is an image projector that receives a video signal and projects the corresponding image on a projection screen using a lens system. Video projectors use a very bright ultra-high-performance lamp (a special mercury arc lamp), Xenon arc lamp, LED or solid state blue, RB, RGB or remote fiber optic RGB lasers to provide the illumination required to project the image, and most modern ones can correct any curves, blurriness, and other inconsistencies through manual settings. If a blue laser is used, a phosphor wheel is used to turn blue light into white light, which is also the case with white LEDs. (White LEDs do not use lasers.) A wheel is used in order to prolong the lifespan of the phosphor, as it is degraded by the heat generated by the laser diode. Remote fiber optic RGB laser racks can be placed far away from the projector, and several racks can be housed in a single, central room. Each projector can use up to two racks, and several monochrome lasers are mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
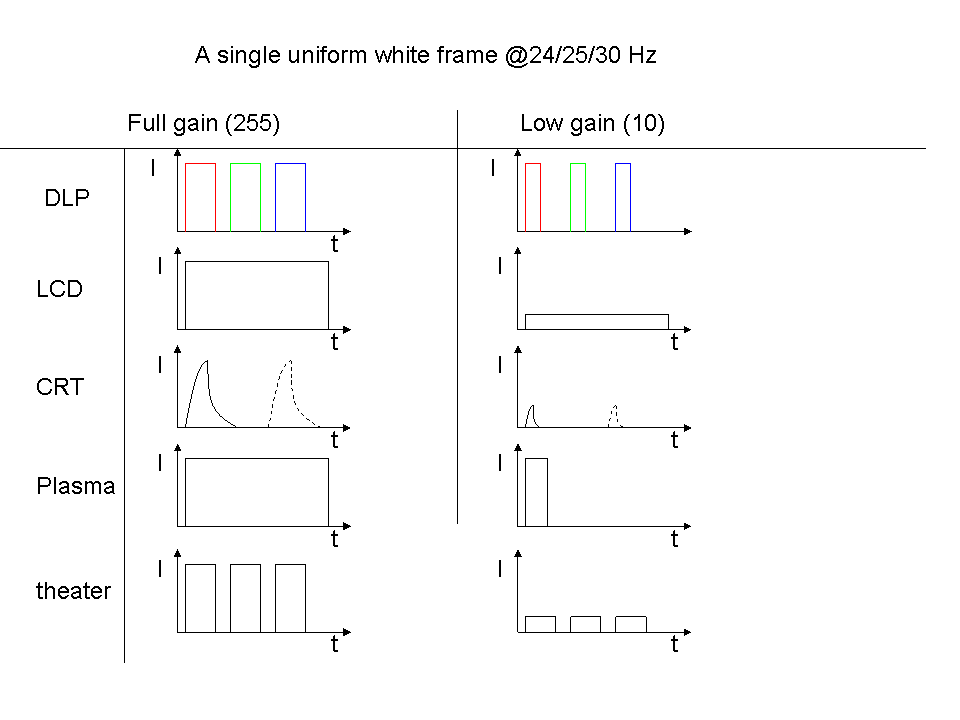
Comparison Of Display Technology
This is a comparison of various properties of different display technologies. General characteristics Major technologies are Cathode ray tube, CRT, LCD and its derivatives (Quantum dot display, LED backlit LCD, WLCD, OLCD), Plasma display, Plasma, and OLED and its derivatives (Transparent OLED, PMOLED, AMOLED). An emerging technology is Micro LED and cancelled and now obsolete technologies are Surface-conduction electron-emitter display, SED and Field emission display, FED. Temporal characteristics Different display technologies have vastly different temporal characteristics, leading to perceptual differences for motion, flicker, etc. The figure shows a sketch of how different technologies present a single white/grey frame. Time and intensity is not to scale. Notice that some have a fixed intensity, while the illuminated period is variable. This is a kind of pulse-width modulation. Others can vary the actual intensity in response to the input signal. *Single-chip DLPs us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Live Event Visual Amplification
Live event support includes staging, scenery, mechanicals, sound, lighting, video, special effects, transport, packaging, communications, costume and makeup for live performance events including theater, music, dance, and opera. They all share the same goal: to convince live audience members that there is no better place that they could be at the moment. This is achieved through establishing a bond between performer and audience. Live performance events tend to use visual scenery, lighting, costume amplification and a shorter history of visual projection and sound amplification reinforcement. Visual support Live event visual amplification Introduction Live event visual amplification is the display of live and pre- recorded images as a part of a live stage event. Visual amplification began when films, projected onto a stage, added characters or background information to a production. 35 mm motion picture projectors became available in 1910 - but which theatre or opera com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Wheel (optics) ), while non-wheel devices include scrollers and semaphore types with lever arms (e.g., on the 1897-1917 Grand Army Plaza fountain).
A color wheel or other switch for changing a projected hue (e.g., for an optical display) is a device that uses different optics filters or color gels within a light beam. Common usage includes continuously-rotating wheels for seasonal home displays (e.g., at Christmas) and controllable color wheels for a particular instrument (e.g., SeaChanger Color Engine for stage lighting Stage lighting is the craft of lighting as it applies to the production of theater, dance, opera, and other performance arts. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Light Processing
Digital Light Processing (DLP) is a set of chipsets based on optical micro-electro-mechanical technology that uses a digital micromirror device. It was originally developed in 1987 by Larry Hornbeck of Texas Instruments. While the DLP imaging device was invented by Texas Instruments, the first DLP-based projector was introduced by Digital Projection Ltd in 1997. Digital Projection and Texas Instruments were both awarded Emmy Awards in 1998 for the DLP projector technology. DLP is used in a variety of display applications from traditional static displays to interactive displays and also non-traditional embedded applications including medical, security, and industrial uses. DLP technology is used in DLP front projectors (standalone projection units for classrooms and business primarily), DLP rear projection television sets, and digital signs. It is also used in about 85% of digital cinema projection, and in additive manufacturing as a light source in some printers to cure resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |