|
Edward Adrian Wilson
Edward Adrian Wilson (23 July 1872 – 29 March 1912) was an English polar explorer, ornithologist, natural historian, physician and artist. Early life Born in Cheltenham on 23 July 1872, Wilson was the second son and fifth child of physician Edward Thomas Wilson and his wife, Mary Agnes, née Whishaw. A clever, sensitive, but boisterous boy, he developed a love of the countryside, natural history and drawing from an early age. He was sent as a boarder to a preparatory school in Clifton, Bristol, but after failing to gain a scholarship to public school, he attended Cheltenham College for boys as a day pupil. His mother was a poultry breeder and he spent much of his youth at The Crippetts farm, Leckhampton near Cheltenham. By the age of nine, he had announced to his parents that he was going to become a naturalist. With encouragement and tuition from his father, he started to draw pictures of the wildlife and fauna in the fields around the farm. After passing his exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
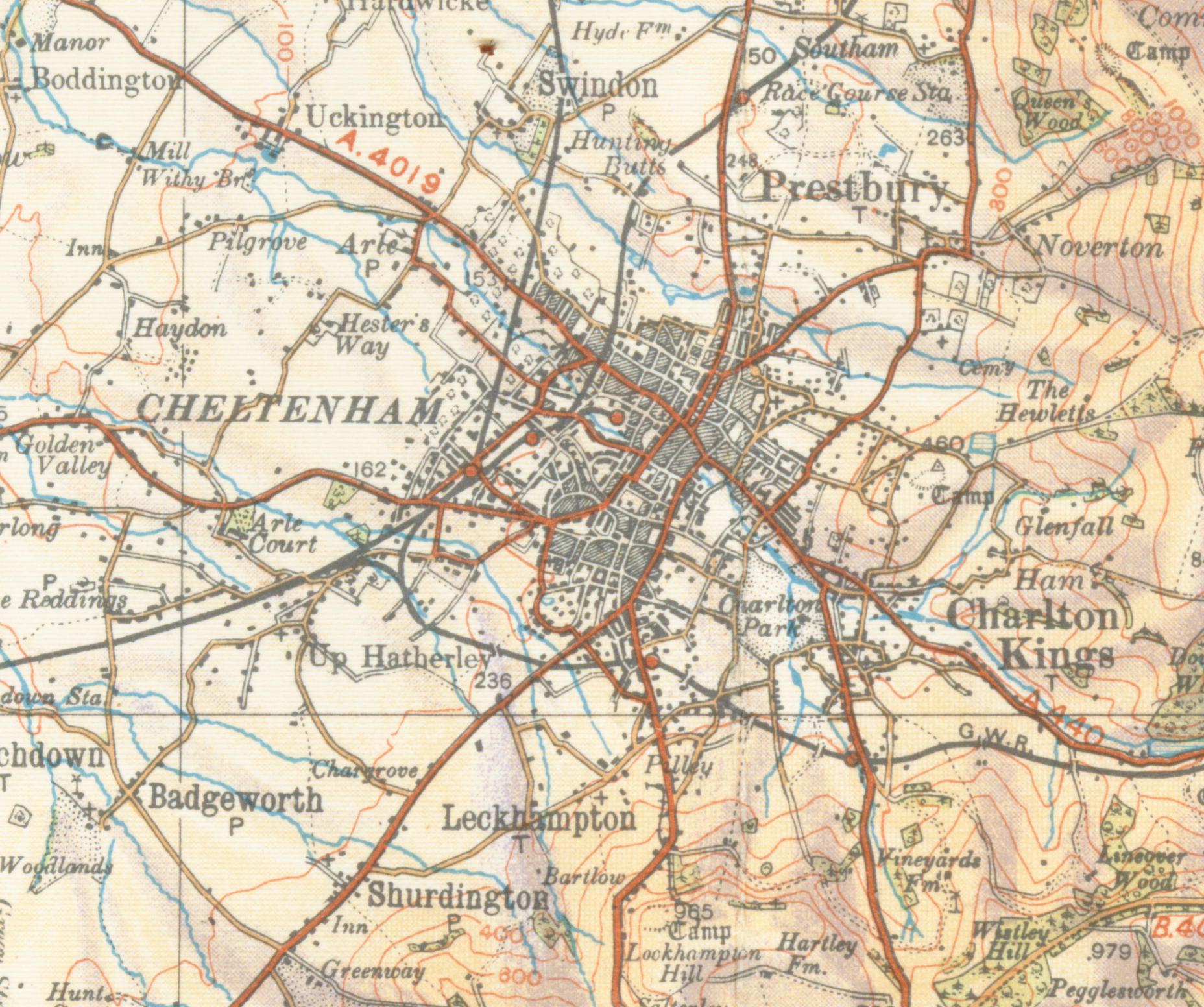
Cheltenham
Cheltenham (), also known as Cheltenham Spa, is a spa town and borough on the edge of the Cotswolds in the county of Gloucestershire, England. Cheltenham became known as a health and holiday spa town resort, following the discovery of mineral springs in 1716, and claims to be the most complete Regency town in Britain. The town hosts several festivals of culture, often featuring nationally and internationally famous contributors and attendees; they include the Cheltenham Literature Festival, the Cheltenham Jazz Festival, the Cheltenham Science Festival, the Cheltenham Music Festival, the Cheltenham Cricket Festival and the Cheltenham Food & Drink Festival. In steeplechase horse racing, the Gold Cup is the main event of the Cheltenham Festival, held every March. History Cheltenham stands on the small River Chelt, which rises nearby at Dowdeswell and runs through the town on its way to the Severn. It was first recorded in 803, as ''Celtan hom''; the meaning has not been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leckhampton
Leckhampton is a Gloucestershire village and a district in south Cheltenham, Gloucestershire, England. The area is in the civil parish of Leckhampton with Warden Hill and is part of the district of Cheltenham. The population of the civil parish taken at the 2011 census was 4,409. History Leckhampton is mentioned in the Domesday Book (1086) as 'Lechametone' and 'Lechantone', meaning 'homestead where garlic or leeks are grown'. The earliest recorded mention comes from the 8th century, as the home farm of the royal manor of Cheltenham. There are remnants of a moat at Church Farm that dates from Saxon times (}) The old village of Leckhampton stands at the foot of Leckhampton Hill, around the medieval parish church of St Peter's. During the 19th and 20th centuries, there was residential development in the direction of Cheltenham. Leckhampton Court is a medieval manor house dating from about 1320, built by the Giffard family of Brimpsfield. It is now a Sue Ryder Care hospice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilton, Huntingdonshire
Hilton is a village and civil parish in Cambridgeshire, England. Hilton lies approximately north-west of Cambridge. Hilton is situated within Huntingdonshire, which is a non-metropolitan district of Cambridgeshire as well as being a historic county of England. The parish adjoins those of Elsworth, Fenstanton, Hemingford Abbots, Hemingford Grey, Papworth Everard and Papworth St Agnes. The Church of England parish church is dedicated to St Mary Magdalene and is a Grade I listed building; it has a peal of six bells. Historically, the village was in Huntingdonshire for over 1,000 years until 1974. A fragment of a wall painting on plaster, made for Captain Sparrow (1601–1651), at Park Farm, Hilton, probably around the time of his marriage in 1633, is now in the Victoria & Albert Museum, London. The fragment depicts two figures representing the senses of Taste and Sight and was donated by David Garnett and his wife Angelica Bell of Hilton Hall, who were members of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Falcon Scott
Captain Robert Falcon Scott, , (6 June 1868 – c. 29 March 1912) was a British Royal Navy officer and explorer who led two expeditions to the Antarctic regions: the ''Discovery'' expedition of 1901–1904 and the ill-fated ''Terra Nova'' expedition of 1910–1913. On the first expedition, he set a new southern record by marching to latitude 82°S and discovered the Antarctic Plateau, on which the South Pole is located. On the second venture, Scott led a party of five which reached the South Pole on 17 January 1912, less than five weeks after Amundsen's South Pole expedition. A planned meeting with supporting dog teams from the base camp failed, despite Scott's written instructions, and at a distance of 162 miles (261 km) from their base camp at Hut Point and approximately 12.5 miles (20 km) from the next depot, Scott and his companions died. When Scott and his party's bodies were discovered, they had in their possession the first Antarctic fossils ever disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archives Hub
The Archives Hub is a Jisc service, and is freely available to all. It provides a cross-search of descriptions of archives held across the United Kingdom, in over 320 institutions, including universities, colleges, specialist repositories, charities, businesses and other institutions. It includes over 1,000,000 descriptions of archive materials on all manner of subjects, which represents over 30,000 archive collections. It also describes content available through topic-based websites, often created as a result of digitisation projects. The Hub does not hold archives. Rather, it maintains finding aids, which help researchers to locate archives, by enabling them to search across descriptions. Each description provides a direct email link to the contact details for the repository that holds the archive. It enables researchers to search and filter by various criteria including keyword, title, creator, person, organisation, subject and date in order to bring together archives held a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-registration House Officer
Pre-registration house officer (PRHO), often known as a houseman or house officer, is a former official term for a grade of junior doctor that was, until 2005, the only job open to medical graduates in the United Kingdom who had just passed their final examinations at medical school and had received their medical degrees. The term "house officer" is still used to refer to foundation doctors (in Foundation Years 1 and 2 known as FY1s and FY2s). Newly qualified doctors are only allowed provisional registration with the General Medical Council, hence their first jobs are prior to full registration with the GMC and these jobs were named pre-registration house officer jobs, usually consisting of two six-month jobs; one predominantly involved with general surgery (often being called a house surgeon), and one predominantly involved with general medicine (often being called a house physician). After 1948, PRHO was the lowest grade in the medical hierarchy of qualified doctors in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is spread from one person to the next through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with Latent TB do not spread the disease. Active infection occurs more often in people with HIV/AIDS and in those who smoke. Diagnosis of active TB is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
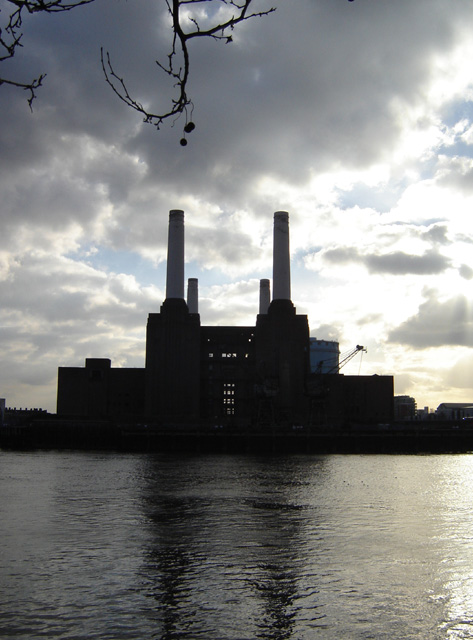
Battersea
Battersea is a large district in south London, part of the London Borough of Wandsworth, England. It is centred southwest of Charing Cross and extends along the south bank of the River Thames. It includes the Battersea Park. History Battersea is mentioned in the few surviving Anglo-Saxon geographical accounts as ''Badrices īeg'' meaning "Badric's Island" and later "Patrisey". As with many former parishes beside tidal flood plains the lowest land was reclaimed for agriculture by draining marshland and building culverts for streams. Alongside this was the Heathwall tide mill in the north-east with a very long mill pond regularly draining and filling to the south. The settlement appears in the Domesday Book of 1086 as ''Patricesy'', a vast manor held by St Peter's Abbey, Westminster. Its ''Domesday'' Assets were: 18 hides and 17 ploughlands of cultivated land; 7 mills worth £42 9s 8d per year, of meadow, woodland worth 50 hogs. It rendered (in total): £75 9s 8d. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St George's Hospital Medical School
St George's, University of London (legally St George's Hospital Medical School, informally St George's or SGUL), is a University located in Tooting in South London and is a constituent college of the University of London. St George's has its origins in 1733, and was the second institution in England to provide formal training courses for doctors (after the University of Oxford). St George's affiliated with the University of London soon after the latter's establishment in 1836. St George's is closely affiliated to St George's Hospital and is one of the United Hospitals. History St George’s Hospital Medical School was originally established in 1733 as part of St George's Hospital at Hyde Park Corner (now the site of The Lanesborough hotel), in central London. The medical school was relocated, together with St George's Hospital to Tooting, South London in 1980. A joint faculty with Kingston University, the Faculty of Health and Social Care Sciences, has increased the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bachelor Of Medicine
Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery ( la, Medicinae Baccalaureus, Baccalaureus Chirurgiae; abbreviated most commonly MBBS), is the primary medical degree awarded by medical schools in countries that follow the tradition of the United Kingdom. The historical degree nomenclature states that they are two separate undergraduate degrees. In practice, however, they are usually combined as one and conferred together, and may also be awarded at graduate-level medical schools. It usually takes five to six years to complete this degree. Bachelor of Medicine (MB, also BM, BMed) is the primary medical degree awarded by medical schools in China and some medical schools in Australia and UK. It usually takes five years to complete. These medical graduates with an MB degree can still practice surgery. Both medical degrees are considered MD-equivalent in US universities and medical institutions. In North America, the equivalent medical degree is awarded as Doctor of Medicine (MD) or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asceticism
Asceticism (; from the el, ἄσκησις, áskesis, exercise', 'training) is a lifestyle characterized by abstinence from sensual pleasures, often for the purpose of pursuing spiritual goals. Ascetics may withdraw from the world for their practices or continue to be part of their society, but typically adopt a frugal lifestyle, characterised by the renunciation of material possessions and physical pleasures, and also spend time fasting while concentrating on the practice of religion or reflection upon spiritual matters. Various individuals have also attempted an ascetic lifestyle to free themselves from addictions, some of them particular to modern life, such as money, alcohol, tobacco, drugs, entertainment, sex, food, etc. Asceticism has been historically observed in many religious traditions, including Buddhism, Jainism, Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Judaism, Stoicism and Pythagoreanism and contemporary practices continue amongst some religious followers. The pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |