|
Echinopsis Lageniformis
''Echinopsis lageniformis'' (syn. ''Trichocereus bridgesii''), the Bolivian torch cactus, is a fast-growing columnar cactus from the high deserts of Bolivia. Among the indigenous populations of Bolivia, it is sometimes called ''achuma'' or ''wachuma'', although these names are also applied to related species such as ''Echinopsis pachanoi'' which are also used for their psychedelic effects. Description The plant has a greenish to bluish color and usually has four to eight ribs. It can grow tall with stems of up to in diameter. Spines can range in coloration from honey-coloured to brown, and are located on the nodes in groups of up to four. These spines can grow up to 6–7 cm in length and in fully grown plants are spaced evenly on the ribs, 2.5 to 3 cm apart. Cultivars Several varieties of this species are highly prized by ornamental cactus collectors. These include a cristate variety, two variants of monstrose growth, and a more recently developed clone that e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cactus
A cactus (, or less commonly, cactus) is a member of the plant family Cactaceae, a family comprising about 127 genera with some 1750 known species of the order Caryophyllales. The word ''cactus'' derives, through Latin, from the Ancient Greek word (''káktos''), a name originally used by Theophrastus for a spiny plant whose identity is now not certain. Cacti occur in a wide range of shapes and sizes. Although some species live in quite humid environments, most cacti live in habitats subject to at least some drought. Many live in extremely dry environments, even being found in the Atacama Desert, one of the driest places on Earth. Because of this, cacti show many adaptations to conserve water. For example, almost all cacti are succulents, meaning they have thickened, fleshy parts adapted to store water. Unlike many other succulents, the stem is the only part of most cacti where this vital process takes place. Most species of cacti have lost true leaves, retaining only spine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychoactive
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior. These substances may be used medically, recreationally or spiritually to a. Purposefully improve one’s perceived performance b. Alter one's consciousness (such as with entheogens for ritual, spiritual or shamanic purposes) or c. For research. Some categories of psychoactive drugs - which are believed, by some, to have therapeutic value - may be prescribed by some physicians and other healthcare practitioners. Examples of medication categories that may contain potentially beneficial psychoactive drugs include, but are not limited to: # Anesthetics # Analgesics # Anticonvulsants # Anti-Parkinson’s medications # Medications used to treat Neuropsychiatric Disorders a. Antidepressants b. Anxiolytics c. Antipsychotics d. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbal And Fungal Hallucinogens
A herbal is a book containing the names and descriptions of plants, usually with information on their medicinal, tonic, culinary, toxic, hallucinatory, aromatic, or magical powers, and the legends associated with them.Arber, p. 14. A herbal may also classify the plants it describes, may give recipes for herbal extracts, tinctures, or potions, and sometimes include mineral and animal medicaments in addition to those obtained from plants. Herbals were often illustrated to assist plant identification.Anderson, p. 2. Herbals were among the first literature produced in Ancient Egypt, China, India, and Europe as the medical wisdom of the day accumulated by herbalists, apothecaries and physicians. Herbals were also among the first books to be printed in both China and Europe. In Western Europe herbals flourished for two centuries following the introduction of moveable type (c. 1470–1670). In the late 17th century, the rise of modern chemistry, toxicology and pharmacology reduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entheogens
Entheogens are psychoactive substances that induce alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition, or behavior for the purposes of engendering spiritual development or otherwiseRätsch, Christian, ''The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Plants: Ethnopharmacology and Its Applications'' pub. Park Street Press 2005 in sacred contexts. Anthropological study has established that entheogens are used for religious, magical, shamanic, or spiritual purposes in many parts of the world. Entheogens have traditionally been used to supplement many diverse practices geared towards achieving transcendence, including divination, meditation, yoga, sensory deprivation, healings, asceticism, prayer, trance, rituals, chanting, imitation of sounds, hymns like peyote songs, drumming, and ecstatic dance. The psychedelic experience is often compared to non-ordinary forms of consciousness such as those experienced in meditation, near-death experiences, and mystical experiences. Ego dissolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Flora Of Bolivia
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cacti Of South America
A cactus (, or less commonly, cactus) is a member of the plant family Cactaceae, a family comprising about 127 genera with some 1750 known species of the order Caryophyllales. The word ''cactus'' derives, through Latin, from the Ancient Greek word (''káktos''), a name originally used by Theophrastus for a spiny plant whose identity is now not certain. Cacti occur in a wide range of shapes and sizes. Although some species live in quite humid environments, most cacti live in habitats subject to at least some drought. Many live in extremely dry environments, even being found in the Atacama Desert, one of the driest places on Earth. Because of this, cacti show many adaptations to conserve water. For example, almost all cacti are succulents, meaning they have thickened, fleshy parts adapted to store water. Unlike many other succulents, the stem is the only part of most cacti where this vital process takes place. Most species of cacti have lost true leaves, retaining only spines, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinopsis
''Echinopsis'' is a large genus of cacti native to South America, sometimes known as hedgehog cactus, sea-urchin cactus or Easter lily cactus. One small species, ''E. chamaecereus'', is known as the peanut cactus. The 128 species range from large and treelike types to small globose cacti. The name derives from ''echinos'' hedgehog or sea urchin, and ''opsis'' appearance, a reference to these plants' dense coverings of spines. They are remarkable for the great size, length of tube, and beauty of their flowers, which, borne upon generally small and dumpy stems, appear much larger and more attractive than would be expected. Taxonomy Studies in the 1970s and 1980s resulted in several formerly separate genera being absorbed into ''Echinopsis'': Some have proposed merging ''Rebutia'' as well. Like several other taxonomic changes in Cactaceae, this one has not been universally accepted. Amateur and professional growers still use names like ''Echinopsis'' (in the older sense), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
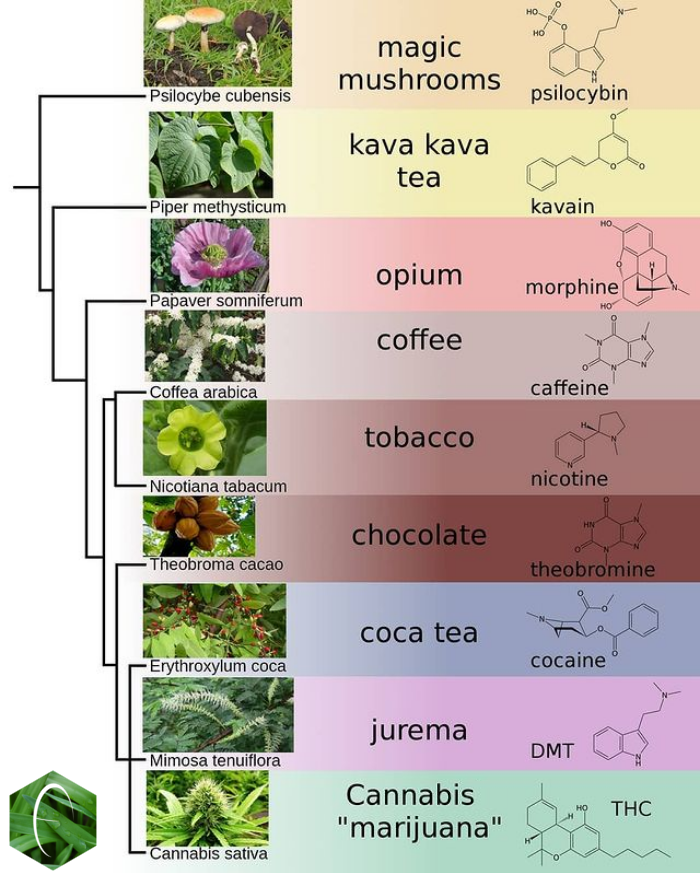
Psychedelic Plants
Psychoactive plants are plants, or preparations thereof, that upon ingestion induce psychotropic effects. As stated in a reference work: Psychoactivity may include sedative, stimulant, euphoric, deliriant, and hallucinogenic effects. Several hundred psychoactive plants are known. Some popular examples of psychoactive plants include '' Coffea arabica'' (coffee), '' Camellia sinensis'' (tea), ''Nicotiana tabacum'' (tobacco), and ''Cannabis'' (including hashish). Psychoactive plants have been used ritually (''e.g.'', peyote as an entheogen), medicinally (''e.g.'', opium as an analgesic), and therapeutically (''e.g.'', cannabis as a drug) for thousands of years. Hence, the sociocultural and economic significance of psychoactive plants is enormous. Examples of psychoactive plants In the table below, a few examples of significant psychoactive plants and their effects are shown. For further examples, see List of psychoactive plants. Botanical taxonomy Botanical taxono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamanism
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritual energies into the physical world for the purpose of healing, divination, or to aid human beings in some other way. Beliefs and practices categorized as "shamanic" have attracted the interest of scholars from a variety of disciplines, including anthropologists, archeologists, historians, religious studies scholars, philosophers and psychologists. Hundreds of books and academic papers on the subject have been produced, with a peer-reviewed academic journal being devoted to the study of shamanism. In the 20th century, non- Indigenous Westerners involved in countercultural movements, such as hippies and the New Age created modern magicoreligious practices influenced by their ideas of various Indigenous religions, creating what has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Paz
La Paz (), officially known as Nuestra Señora de La Paz (Spanish pronunciation: ), is the seat of government of the Plurinational State of Bolivia. With an estimated 816,044 residents as of 2020, La Paz is the third-most populous city in Bolivia. Its metropolitan area, which is formed by La Paz, El Alto, Achocalla, Viacha, and Mecapaca makes up the second most populous urban area in Bolivia, with a population of 2.0 million, after Santa Cruz de la Sierra with a population of 2.3 million. It is also the capital of the La Paz Department. The city, in west-central Bolivia southeast of Lake Titicaca, is set in a canyon created by the Choqueyapu River. It is in a bowl-like depression, part of the Amazon basin, surrounded by the high mountains of the Altiplano. Overlooking the city is the towering, triple-peaked Illimani. Its peaks are always snow-covered and can be seen from many parts of the city. At an elevation of roughly above sea level, La Paz is the highest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mescaline
Mescaline or mescalin (3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine) is a naturally occurring psychedelic protoalkaloid of the substituted phenethylamine class, known for its hallucinogenic effects comparable to those of LSD and psilocybin. Biological sources It occurs naturally in several species of cacti. It is also found in small amounts in certain members of the bean family, Fabaceae, including '' Acacia berlandieri''. However those claims concerning ''Acacia'' species have been challenged and have been unsupported in any additional analysis. History and use Peyote has been used for at least 5,700 years by Indigenous peoples of the Americas in Mexico. Europeans noted use of peyote in Native American religious ceremonies upon early contact, notably by the Huichols in Mexico. Other mescaline-containing cacti such as the San Pedro have a long history of use in South America, from Peru to Ecuador. While religious and ceremonial peyote use was widespread in the Aztec empire and nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloids
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including , , [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)