|
East Yi West Xia
East Yi West Xia () is an obsolete theory about the origin of prehistory culture in current China which says that the culture of Shang dynasty was established by two ethnic groups; namely, that the Western part of the Shang dynasty was developed by Xia ethnic group, and the eastern part of Shang dynasty was developed by Yi ethnic group. History of the theory This theory was suggested by future linguist Fu Sinian in his thesis 1933. It was further expanded by Liang Siyong who suggested that the newly discovered Yangshao culture was established by the Xia in the west and the Longshan culture by the Yi peoples of the east. For Chinese and Western historians this hypothesis became the prevailing theory to interpret Chinese prehistory and remained so until about 1960.Andersson, J.G., "Researches into the Prehistory of the Chinese" in ''Bulletin of the Museum of Far Eastern Antiquities'', 15 (1943), pp. 29-91 Further archaeological discoveries made the theory obsolete. In 1950s it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shang Dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou dynasty. The classic account of the Shang comes from texts such as the '' Book of Documents'', '' Bamboo Annals'' and '' Records of the Grand Historian''. According to the traditional chronology based on calculations made approximately 2,000 years ago by Liu Xin, the Shang ruled from 1766 to 1122 BC, but according to the chronology based upon the "current text" of ''Bamboo Annals'', they ruled from 1556 to 1046 BC. Comparing the same text with dates of five-planet conjunctions, David Pankenier, supported by David Nivison, proposed dates of the establishment of the dynasty to 1554 BC. The Xia–Shang–Zhou Chronology Project dated the establishment to c. 1600 BC based on the carbon-14 dates of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
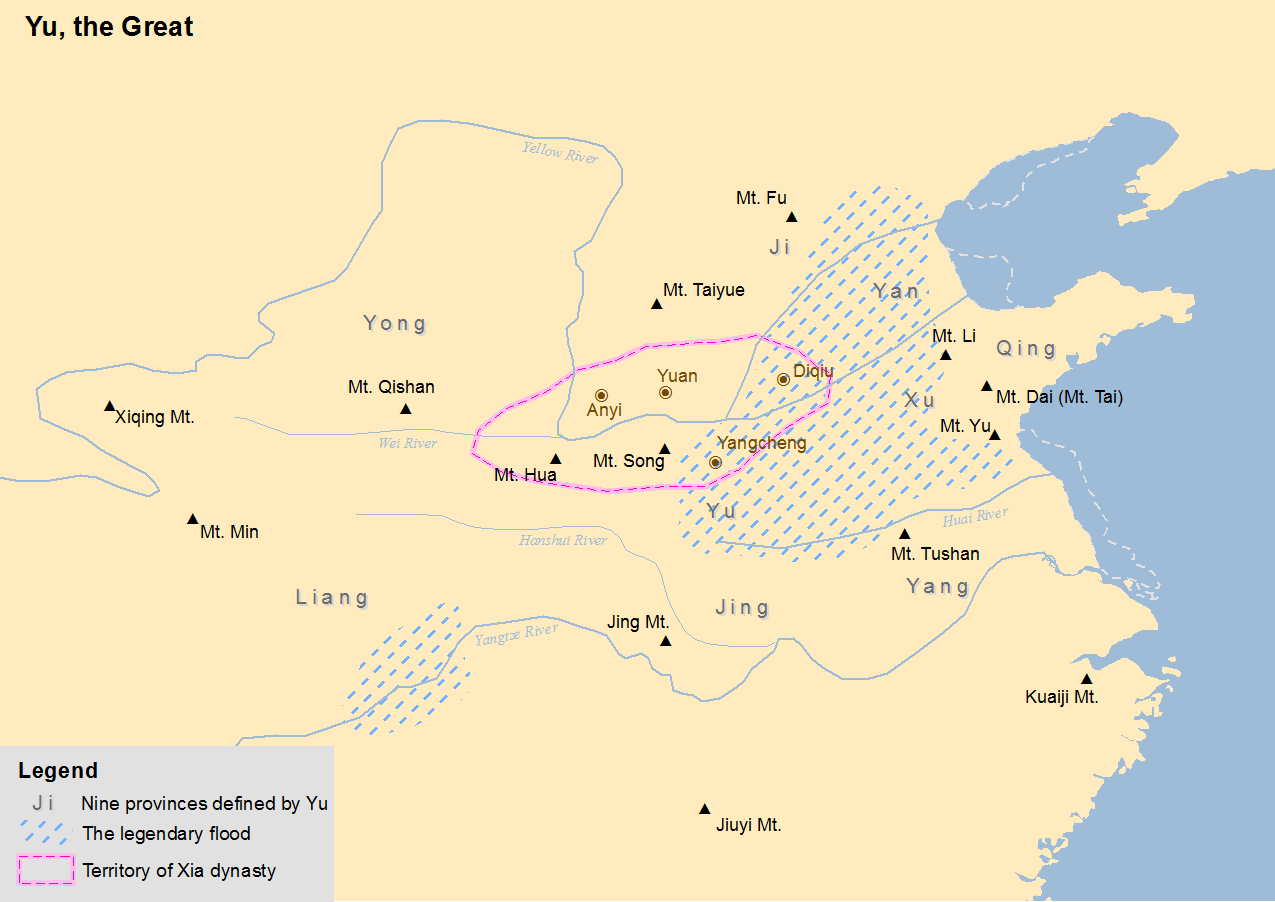
Xia Dynasty
The Xia dynasty () is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, the Xia dynasty was established by the legendary Yu the Great, after Shun, the last of the Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In traditional historiography, the Xia was later succeeded by the Shang dynasty. There are no contemporaneous records of the Xia, who are not mentioned in the oldest Chinese texts, since the earliest oracle bone inscriptions date from the late Shang period (13th century BC). The earliest mentions occur in the oldest chapters of the '' Book of Documents'', which report speeches from the early Western Zhou period and are accepted by most scholars as dating from that time. The speeches justify the Zhou conquest of the Shang as the passing of the Mandate of Heaven and liken it to the succession of the Xia by the Shang. That political philosophy was promoted by the Confucian school in the Eastern Zhou period. The succession of dynasties was incorpor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dongyi
The Dongyi or Eastern Yi () was a collective term for ancient peoples found in Chinese records. The definition of Dongyi varied across the ages, but in most cases referred to inhabitants of eastern China, then later, the Korean peninsula, and Japan. As such, the name "Yí" was something of a catch-all and was applied to different groups over time. According to the earliest Chinese record, the '' Zuo Zhuan'', the Shang Dynasty was attacked by King Wu of Zhou while attacking the Dongyi and collapsed afterward. Ancient inhabitants of Eastern China Oracle bone inscriptions from the early 11th century BCE refer to campaigns by the late Shang king Di Yi against the ''Rénfāng'' (), a group occupying the area of southern Shandong and Jianghuai (northern Anhui and Jiangsu). Many Chinese archaeologists apply the historical name "Dongyi" to the archaeological Yueshi culture (1900–1500 BCE). Other scholars, such as Fang Hui, consider this identification problematic because of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fu Sinian
Fu Ssu-nien (; 26 March 1896 – 20 December 1950), was a Chinese historian, linguist, and writer. He was one of the leaders of the May Fourth Movement in 1919. He was also one of the creators of the Academia Sinica, and was named director of the Institute of History and Philology upon its founding in 1928. Early years Fu was born on 26 March 1896 in Shandong, immediately after the First Sino-Japanese War, a time when the traditional systems were being challenged and revolutions were about to happen. In 1909, Fu entered the secondary school set up by Tianjin government, excelling in mathematics, English, and Chinese. In 1913, Fu was accepted by the preparatory school of Peking University where he ranked first upon graduation in humanities division.Wang, Fan-shen, ''Fu Ssu-nien: A life in Chinese history and politics.'' New York: Cambridge University Press, 2000 In 1916, Fu went on to the Chinese Department of Peking University to pursue his bachelor's degree. During his time at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liang Siyong
Liang Siyong (; 13 November 1904 2 April 1954) was a Chinese anthropologist and archaeologist. He was deputy director of the Institute of Archaeology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences. One of the first scholars to introduce the discipline of archaeology to China, Liang is regarded as one of China's "first-generation archaeologists". He was the second son of the scholar Liang Qichao. Liang was married to Li Fuman, with whom he had one daughter. He died of a heart attack on 2 April 1954, at the age of 49. Life and career Liang was born on 13 November 1904 in Macau, the fourth child and second son of journalist and scholar Liang Qichao. He had eight siblings four brothers ( Sicheng, Sizhong, Sida, and Sili) and four sisters (Sishun, Sizhuang, Siyi, and Sining). He completed his primary education in Yokohama, where his family had been exiled to, and graduated from Tsinghua University in 1924. He was enrolled into Harvard University, at which he studied archaeology and picked up E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yangshao Culture
The Yangshao culture (仰韶文化, pinyin: Yǎngsháo wénhuà) was a Neolithic culture that existed extensively along the middle reaches of the Yellow River in China from around 5000 BC to 3000 BC. The culture is named after the Yangshao site, the first excavated site of this culture, which was discovered in 1921 in Yangshao town, Mianchi County, Sanmenxia, western Henan Province by the Swedish geologist Johan Gunnar Andersson (1874–1960). The culture flourished mainly in the provinces of Henan, Shaanxi and Shanxi. Recent research indicates a common origin of the Sino-Tibetan languages with the Cishan, Yangshao and/or the Majiayao cultures. Economy Subsistence The main food of the Yangshao people was millet, with some sites using foxtail millet and others proso millet, though some evidence of rice has been found. The exact nature of Yangshao agriculture, small-scale slash-and-burn cultivation versus intensive agriculture in permanent fields, is currently a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longshan Culture
The Longshan (or Lung-shan) culture, also sometimes referred to as the Black Pottery Culture, was a late Neolithic culture in the middle and lower Yellow River valley areas of northern China from about 3000 to 1900 BC. The first archaeological find of this culture took place at the Chengziya Archaeological Site in 1928, with the first excavations in 1930 and 1931. The culture is named after the nearby modern town of Longshan (lit. "Dragon Mountain") in Zhangqiu, Shandong. The culture was noted for its highly polished black pottery (or egg-shell pottery). The population expanded dramatically during the 3rd millennium BC, with many settlements having rammed earth walls. It decreased in most areas around 2000 BC until the central area evolved into the Bronze Age Erlitou culture. The Longshan culture has been linked to the early Sinitic (of the Sino-Tibetan languages). According to the area and cultural type, the Longshan culture can be divided into two types: Shandong Longs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yinxu
Yinxu (modern ; ) is the site of one of the ancient and major historical capitals of China. It is the source of the archeological discovery of oracle bones and oracle bone script, which resulted in the identification of the earliest known Chinese writing. The archeological remnants (or ruins) known as Yinxu represent the ancient city of Yin, the last capital of China's Shang dynasty which existed through eight generations for 255 years, and through the reign of 12 kings. Yinxu was discovered, or rediscovered, in 1899. It is now one of China's oldest and largest archeological sites, and was selected as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2006. Yinxu is located in northernmost Henan province near the modern city of Anyang, and near the Hebei and Shanxi province borders. Public access to the site is permitted. Traditional history According to the 2nd century ''Shuowen Jiezi'' dictionary (說文解字), the Chinese character "" (''yīn'') originally referred to "vibrant music-ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erligang Culture
The Erligang culture () is a Bronze Age urban civilization and archaeological culture in China that existed from approximately 1600 to 1400 BC. The primary site, Zhengzhou Shang City, was discovered at Erligang, within the modern city of Zhengzhou, Henan, in 1951. Major sites The culture was centered in the Yellow River valley. In its early years, it expanded rapidly, reaching the Yangtze River. The culture then gradually shrank from its early peak. Zhengzhou Later investigations showed that the Erligang site was part of an ancient city surrounded by a roughly rectangular wall with a perimeter of about . The walls were of rammed earth construction, a technique dating back to Chinese Neolithic sites of the Longshan culture (c. 3000–1900 BC). It has been estimated that the walls would have been wide at the base, rising to a height of . Large workshops were located outside the city walls, including a bone workshop, a pottery workshop and two bronze vessel workshops. The moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhongyuan
Zhongyuan (), the Central Plain(s), also known as Zhongtu (, lit. 'central land') and Zhongzhou (, lit. 'central region'), commonly refers to the part of the North China Plain surrounding the lower and middle reaches of the Yellow River, centered on the region between Luoyang and Kaifeng. It has been perceived as the birthplace of the Chinese civilization. Historically, the Huaxia people viewed Zhongyuan as 'the center of the world'. Human activities in the Zhongyuan region can be traced back to the Palaeolithic period. In prehistoric times, Huaxia, a confederation of tribes that later developed into the Han ethnicity, lived along the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River. The term 'Zhongguo' (Central State) was used to distinguish themselves from the Siyi tribes that were perceived as 'barbaric'. For a large part of Chinese history, Zhongyuan had been the political, economic, and cultural center of the Chinese civilization, as over 20 dynasties had located their capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erlitou Culture
The Erlitou culture was an early Bronze Age urban society and archaeological culture that existed in the Yellow River valley from approximately 1900 to 1500 BC. A 2007 study of radiocarbon dating proposed a narrower date range of 1750 to 1530 BC. The culture was named after the site discovered at Erlitou in Yanshi, Henan. The culture was widely spread throughout Henan and Shanxi and later appeared in Shaanxi and Hubei. Chinese archaeologists generally identify the Erlitou culture as the site of the Xia dynasty, but there is no firm evidence, such as writing, to substantiate such a linkage, as the earliest evidence of Chinese writing dates to the late Shang dynasty. Erlitou site The Erlitou culture may have evolved from the matrix of Longshan culture. Originally centered around Henan and Shanxi province, the culture spread to Shaanxi and Hubei provinces. After the rise of the Erligang culture, the site at Erlitou diminished in size but remained inhabited. Discovered in 1959 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yueshi Culture
The Yueshi culture () was an archaeological culture in the Shandong region of eastern China, dated from 1900 to 1500 BC. It spanned the period from the Late Neolithic to the early Bronze Age. In the Shandong area, it followed the Longshan culture period (c. 2600–1900 BC) and was later replaced by the Erligang culture (identified with the historical Shang dynasty). Geographical range Yueshi culture sites have been found in Shandong, eastern Henan, and north Jiangsu province. It is named after the type site at Dongyueshi (East Yueshi) Village in Pingdu, Shandong. More than 340 Yueshi sites have been identified in Shandong, but this was still a considerable decline from the previous Shandong Longshan culture. Yueshi was contemporary with the Erlitou culture and the early Erligang culture, both located to its west. The Tai-Yi Mountains ( 泰沂山脉) region in central Shandong is the core area of Yueshi, but as the Erligang state (commonly identified with the early Shang dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_and_%22弓%22_(meaning_bow).jpg)


