|
Expedition One
Expedition 1 was the first long-duration expedition to the International Space Station (ISS). The three-person crew stayed aboard the station for 136 days, from 2 November 2000 to 19 March 2001. It was the beginning of an uninterrupted human presence on the station which continues as of . The official start of the expedition occurred when the crew docked to the station on 2 November 2000, aboard the Russian spacecraft Soyuz TM-31, which had launched on 31 October 2000 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. During their mission, the Expedition 1 crew activated various systems on board the station, unpacked equipment that had been delivered, and hosted three visiting Space Shuttle crews and two uncrewed Russian Progress resupply vehicles. The crew was very busy throughout the mission, which was declared a success. The three visiting Space Shuttles brought equipment, supplies, and key components of the space station. The first of these, STS-97, docked in early Decem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-97
STS-97 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle '' Endeavour''. The crew installed the first set of solar arrays to the ISS, prepared a docking port for arrival of the Destiny Laboratory Module, and delivered supplies for the station's crew. It was the last human spaceflight of the 20th century. Crew Spacewalks ;EVA 1 – Tanner and Noriega *EVA 1 Start: 3 December 2000 – 18:35 UTC *EVA 1 End: 4 December 2000 – 02:08 UTC *Duration: 7 hours, 33 minutes ;EVA 2 – Tanner and Noriega *EVA 2 Start: 5 December 2000 – 17:21 UTC *EVA 2 End: 5 December 2000 – 23:58 UTC *Duration: 6 hours, 37 minutes ;EVA 3 – Tanner and Noriega *EVA 3 Start: 7 December 2000 – 16:13 UTC *EVA 3 End: 7 December 2000 – 21:23 UTC *Duration: 5 hours, 10 minutes Crew seat assignments Mission highlights During the 11-day mission, the primary objective was completed, which was to deliver and connect the first set of U.S.-provided sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
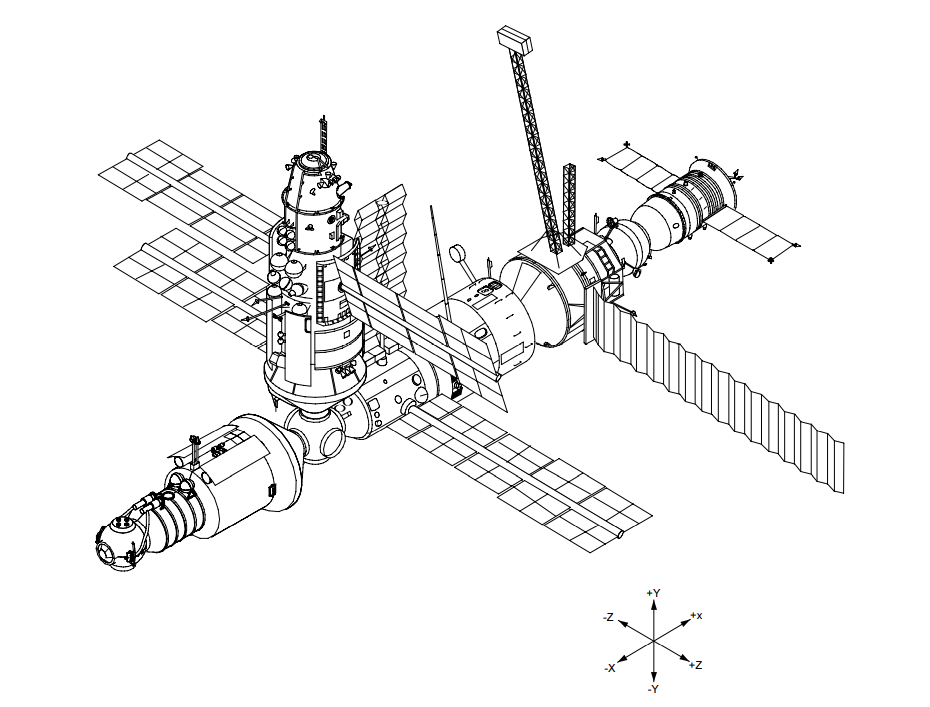
Integrated Truss Structure
The Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) of the International Space Station (ISS) consists of a linear arranged sequence of connected trusses on which various unpressurized components are mounted such as logistics carriers, radiators, ISS Solar Arrays, solar arrays, and other equipment. It supplies the ISS with a Spacecraft bus, bus architecture. It is approximately 110 meters long and is made from aluminium and stainless steel. Truss components All truss components were named after their planned end-positions: Z for zenith, S for starboard and P for port, with the number indicating the sequential position. The S0 truss might be considered a misnomer, as it is mounted centrally on the zenith position of ''Destiny'' and is neither starboard nor port side. Manufacturing ISS truss segments were Manufacturing of the International Space Station, fabricated by Boeing in its facilities at Huntington Beach, California (formerly McDonnell Douglas), Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orlean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Dezhurov
Vladimir Nikolayevich Dezhurov (; born July 30, 1962) is a Russian former cosmonaut who resides in Star City, Moscow. He is a veteran of two spaceflights, to the Mir and International Space Stations. During his career, Dezhurov also conducted nine spacewalks before his retirement on July 12, 2004. Personal Dezhurov was born on July 30, 1962, in the settlement of Yavas, Zubovo-Polyansky District, Mordovia, Russia. He is married to Elena Valentinovna Dezhurova (née Suprina). They have two daughters, Anna, born in 1983, and Svetlana, born in 1987. His father, Nikolai Serafimovich Dezhurov and mother, Anna Vasilevna Dezhurova reside in Yavas settlement, Zubovo-Polyansk district, Mordovia, Russia. Education Dezhurov attended and graduated from the S.I. Gritsevits Kharkov Higher Military Aviation School in 1983 with a pilot engineer's diploma. Experience After graduating, Dezhurov served as a pilot and senior pilot in the Russian Air Force. Awards Dezhurov was awarded the He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenneth Bowersox
Kenneth Dwane "Sox" Bowersox (born November 14, 1956) is a United States Navy officer and former NASA astronaut. He is a veteran of five Space Shuttle launches and an extended stay aboard the International Space Station. When he launched on STS-73 at the age of 38 years and 11 months, he became the youngest person to command a Space Shuttle. Early life and education Bowersox was born November 14, 1956, in Portsmouth, Virginia, but considers Bedford, Indiana his home town. As a young boy, his family lived in Oxnard, California for seven years and he attended Rio Real Elementary School. Bowersox was active in the Boy Scouts of America, and is an Eagle Scout (Boy Scouts of America), Eagle Scout. He earned a Bachelor of Science degree in aerospace engineering from the United States Naval Academy in Annapolis, Maryland, before receiving his commission in 1978. A year later, in 1979, he received a Master of Science degree in mechanical engineering from Columbia University in New York C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Federal Space Agency
The State Corporation for Space Activities "Roscosmos", commonly known simply as Roscosmos (), is a state corporation of the Russian Federation responsible for space flights, cosmonautics programs, and aerospace research. Originating from the Soviet space program founded in the 1950s, Roscosmos emerged following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It initially began as the Russian Space Agency,, ''Rossiyskoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', or RKA (). which was established on 25 February 1992 and restructured in 1999 and 2004 as the Russian Aviation and Space Agency, ''Rossiyskoye aviatsionno-kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', commonly known as (), established on 25 May 1999. and the Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), (Роскосмос), ''Federalnoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo (Roskosmos)''. respectively. In 2015, the Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) was merged with the United Rocket and Space Corporation, a government corporation, to re-nationalize the space industr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz TM-21
Soyuz TM-21 was a crewed Soyuz (spacecraft), Soyuz spaceflight to ''Mir''. The mission launched from Baikonur Cosmodrome, atop a Soyuz-U2 carrier rocket, at 06:11:34 UTC on 14 March 1995. The flight marked the first time thirteen humans were flying in space simultaneously, with three aboard the Soyuz, three aboard ''Mir'' and seven aboard Space Shuttle Endeavour, Space Shuttle ''Endeavour'', flying STS-67. The spacecraft carried expedition EO-18 to the space station. This included the first American astronaut to launch on a Soyuz spacecraft and board ''Mir'', Norman Thagard, for the American Thagard Increment aboard the station, which was the first Shuttle-Mir Program#Increments, Increment of the Shuttle-Mir program. The three crew members it launched were relieved by Space Shuttle Atlantis, Space Shuttle ''Atlantis'' during STS-71, when they were replaced by expedition EO-19. The crew returned to earth aboard Soyuz TM-21 on 11 September 1995. Crew Mir Principal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Thagard
Norman Earl Thagard (born July 3, 1943; Capt, USMC, Ret.) is an American scientist and former U.S. Marine Corps officer and naval aviator and NASA astronaut. On March 14, 1995, he became the first American to ride to space on board a Russian vehicle, the Soyuz TM-21 spacecraft for the Russian Mir-18 mission. Therefore, Thagard was the first American cosmonaut. Experience Thagard held a number of research and teaching posts while completing the academic requirements for various earned degrees. In September 1966 he entered active duty with the United States Marine Corps Reserve. He achieved the rank of captain in 1967, was designated a Naval Aviator in 1968 and was subsequently assigned to duty flying F-4 Phantom IIs with VMFA-333 at Marine Corps Air Station Beaufort, South Carolina. He flew 163 combat missions in Vietnam while assigned to VMFA-115 from January 1969 to 1970. He returned to the United States and an assignment as aviation weapons division officer with VMFA-251 at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-88
STS-88 was the first Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS). It was flown by Space Shuttle Space Shuttle Endeavour, ''Endeavour'', and took the first American module, the Unity (ISS module), ''Unity'' node, to the station. The seven-day mission was highlighted by the mating of the U.S.-built ''Unity'' node to the Zarya (ISS module), Functional Cargo Block (''Zarya'' module) already in orbit, and three spacewalks to connect power and data transmission cables between the Node and the FGB. ''Zarya'', built by Boeing and the Russian Space Agency, was launched on a Russian Proton (rocket), Proton rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan in November 1998. Other payloads on the STS-88 mission included the IMAX Cargo Bay Camera (ICBC), the Argentine Scientific Applications Satellite-S (SAC-A), the MightySat 1 Hitchhiker payload, the Space Experiment Module (SEM-07) and Getaway Special G-093 sponsored by the University of Michigan. Crew Launch attempts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zarya (ISS Module)
''Zarya'' (), also known as the ''Functional Cargo Block'' (), is the inaugural component of the International Space Station (ISS). Launched on 20 November 1998 atop a Proton-K rocket, the module would serve as the ISS's primary source of power, propulsion, and guidance during its early years. As the station has grown, ''Zarya''s role has transitioned primarily to storage, both internally and in its external fuel tanks. A descendant of the TKS spacecraft used in the ''Salyut'' programme, ''Zarya'' was built in Russia but its construction was financed by the United States. Its name, meaning "sunrise," symbolizes the beginning of a new era of international space cooperation. Construction The Zarya design was originally intended as a module for the Russian '' Mir'' space station, but was not flown as of the end of the Mir program. A FGB cargo block was incorporated as an upper stage engine into the Polyus spacecraft, flown (unsuccessfully) on the first Energia launch.B. Hen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaceflight
Spaceflight (or space flight) is an application of astronautics to fly objects, usually spacecraft, into or through outer space, either with or without humans on board. Most spaceflight is uncrewed and conducted mainly with spacecraft such as satellites in orbit around Earth, but also includes space probes for flights beyond Earth orbit. Such spaceflights operate either by telerobotic or autonomous control. The first spaceflights began in the 1950s with the launches of the Soviet Sputnik satellites and American Explorer and Vanguard missions. Human spaceflight programs include the Soyuz, Shenzhou, the past Apollo Moon landing and the Space Shuttle programs. Other current spaceflight are conducted to the International Space Station and to China's Tiangong Space Station. Spaceflights include the launches of Earth observation and telecommunications satellites, interplanetary missions, the rendezvouses and dockings with space stations, and crewed spaceflights on sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy SEALs
The United States Navy Sea, Air, and Land (SEAL) Teams, commonly known as Navy SEALs, are the United States Navy's primary special operations force and a component of the United States Naval Special Warfare Command. Among the SEALs' main functions are conducting small-unit special operation missions in maritime, jungle, urban, arctic, mountainous, and desert environments. SEALs are typically ordered to capture or kill high-level targets, or to gather intelligence behind enemy lines. SEAL team personnel are hand-selected, highly trained, and highly proficient in unconventional warfare (UW), direct action (DA), and special reconnaissance (SR), among other tasks like sabotage, demolition, intelligence gathering, and hydrographic reconnaissance, training, and advising friendly militaries or other forces. All active SEALs are members of the U.S. Navy. History Origins Although not formally founded until 1962, the modern-day U.S. Navy SEALs trace their roots to World War II. The U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expedition 1 Crew Poster
Expedition may refer to: * An exploration, journey, or voyage undertaken by a group of people especially for discovery and scientific research Places * Expedition Island, a park in Green River, Wyoming, US * Expedition Range, a mountain range in Queensland, Australia Arts, entertainment, and media Games *Expedition, included in the List of Pokémon Trading Card Game sets *''Expeditions'', a sequel to the board game ''Scythe'' *'' Expeditions: Conquistador'', a 2013 video game, the first game in the ''Expeditions'' series Literature * ''Expeditions'' (poetry collection), a collection of poetry by Margaret Atwood * ''Expedition'' (book), a science-fiction novel by Wayne Douglas Barlowe *''Expedition Magazine'', published by Penn Museum *''L'Expédition'', a volume of the French science fiction comic series '' Les Mondes d'Aldébaran'', part of the ''Bételgeuse'' graphic novel *''L'expédition'', a novel by Agnès Desarthe Music *"Expedition", a song by Sara Groves fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |