|
Expanded Genetic Code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 common naturally-encoded proteinogenic amino acids. The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: * the non-standard amino acid to encode, * an unused codon to adopt, * a tRNA that recognizes this codon, and * a tRNA synthetase that recognizes only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid. Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science. In May 2019, researchers, in a milestone effort, reported the creation of a new synthetic (possibly artificial) form of viable life, a variant of the bacteria ''Escherichia coli'', by reducing the natural number of 64 codons in the bacterial genome to 61 c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthogonal Pair To Extend Code
In mathematics, orthogonality (mathematics), orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of ''perpendicularity''. Although many authors use the two terms ''perpendicular'' and ''orthogonal'' interchangeably, the term ''perpendicular'' is more specifically used for lines and planes that intersect to form a right angle, whereas ''orthogonal'' is used in generalizations, such as ''orthogonal vectors'' or ''orthogonal curves''. ''Orthogonality'' is also used with various meanings that are often weakly related or not related at all with the mathematical meanings. Etymology The word comes from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning "upright", and ('), meaning "angle". The Ancient Greek (') and Classical Latin ' originally denoted a rectangle. Later, they came to mean a right triangle. In the 12th century, the post-classical Latin word ''orthogonalis'' came to mean a right angle or something related to a right angle. Mathematics Physics Optics In optics, polarization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stop Codon
In molecular biology, a stop codon (or termination codon) is a codon (nucleotide triplet within messenger RNA) that signals the termination of the translation process of the current protein. Most codons in messenger RNA correspond to the addition of an amino acid to a growing polypeptide chain, which may ultimately become a protein; stop codons signal the termination of this process by binding release factors, which cause the ribosomal subunits to disassociate, releasing the amino acid chain. While start codons need nearby sequences or initiation factors to start translation, a stop codon alone is sufficient to initiate termination. Properties Standard codons In the standard genetic code, there are three different termination codons: Alternative stop codons There are variations on the standard genetic code, and alternative stop codons have been found in the mitochondrial genomes of vertebrates, '' Scenedesmus obliquus'', and '' Thraustochytrium''. Reassigned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoserine
Phosphoserine (abbreviated as SEP or J) is an ester of serine and phosphoric acid. Phosphoserine is a component of many proteins as the result of posttranslational modifications. The phosphorylation of the alcohol functional group in serine to produce phosphoserine is catalyzed by various types of kinases. Through the use of technologies that utilize an expanded genetic code, phosphoserine can also be incorporated into proteins during translation. It is a normal metabolite In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism. The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, c ... found in human biofluids. Phosphoserine has three potential coordination sites (carboxyl, amine and phosphate group) Determination of the mode of coordination between phosphorylated ligands and metal ions occurring in an organism is a first step to explain the fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminotransferase
Transaminases or aminotransferases are enzymes that catalyze a transamination reaction between an amino acid and an α- keto acid. They are important in the synthesis of amino acids, which form proteins. Function and mechanism An amino acid contains an amino (NH2) group. A keto acid contains a keto (=O) group. In transamination, the NH2 group on one molecule is exchanged with the =O group on the other molecule. The amino acid becomes a keto acid, and the keto acid becomes an amino acid. Transaminases require the coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate, which is converted into pyridoxamine in the first half-reaction, when an amino acid is converted into a keto acid. Enzyme-bound pyridoxamine in turn reacts with pyruvate, oxaloacetate, or alpha-ketoglutarate, giving alanine, aspartic acid, or glutamic acid, respectively. Many transamination reactions occur in tissues, catalysed by transaminases specific for a particular amino/keto acid pair. The reactions are readily reversible, the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
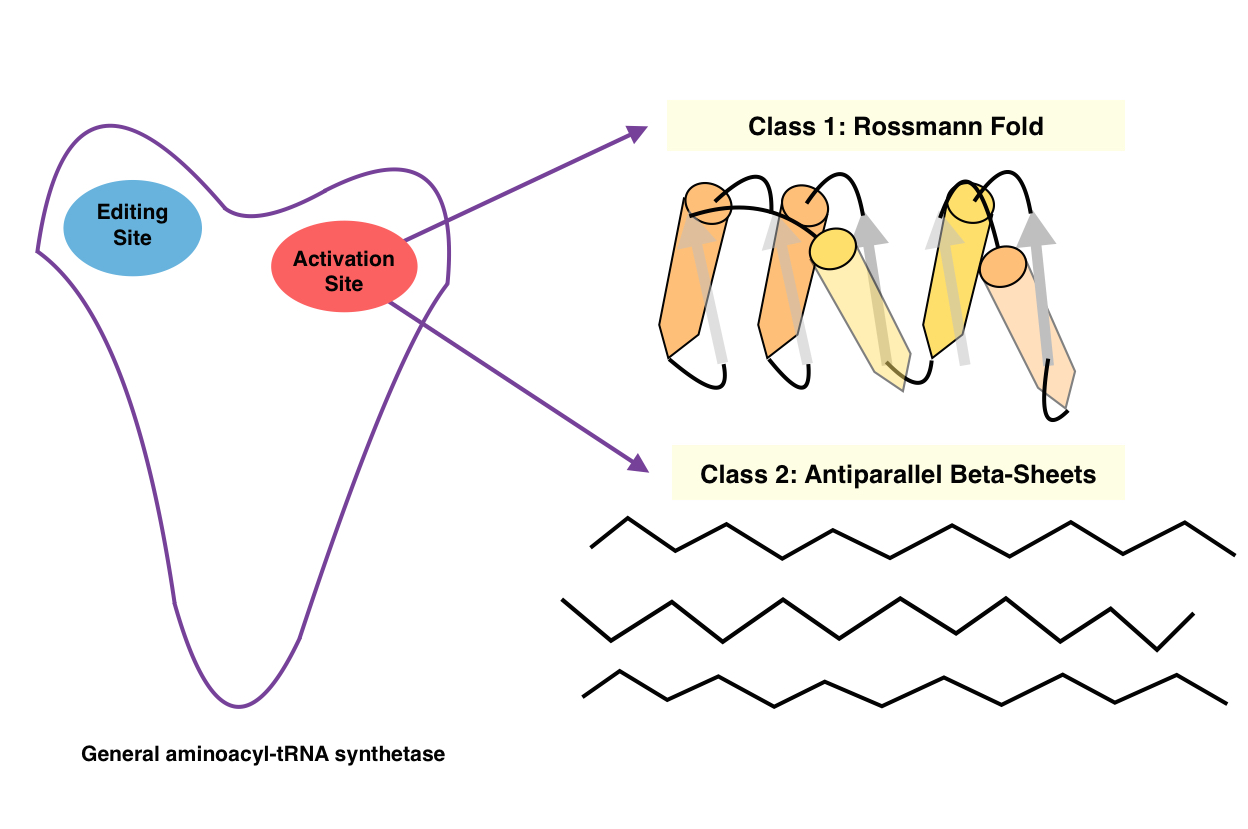
Aminoacyl TRNA Synthetase
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS or ARS), also called tRNA-ligase, is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA. It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its precursor to one of all its compatible cognate tRNAs to form an aminoacyl-tRNA. In humans, the 20 different types of aa-tRNA are made by the 20 different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, one for each amino acid of the genetic code. This is sometimes called "charging" or "loading" the tRNA with an amino acid. Once the tRNA is charged, a ribosome can transfer the amino acid from the tRNA onto a growing peptide, according to the genetic code. Aminoacyl tRNA therefore plays an important role in RNA Translation (biology), translation, the expression of genes to create proteins. Mechanism The synthetase first binds Adenosine triphosphate, ATP and the corresponding amino acid (or its Amino acid synthesis, precursor) to form an aminoacyl-adenylate, relea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticodon
Transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA), formerly referred to as soluble ribonucleic acid (sRNA), is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes). In a cell, it provides the physical link between the genetic code in messenger RNA (mRNA) and the amino acid sequence of proteins, carrying the correct sequence of amino acids to be combined by the protein-synthesizing machinery, the ribosome. Each three-nucleotide codon in mRNA is complemented by a three-nucleotide anticodon in tRNA. As such, tRNAs are a necessary component of translation, the biological synthesis of new proteins in accordance with the genetic code. Overview The process of translation starts with the information stored in the nucleotide sequence of DNA. This is first transformed into mRNA, then tRNA specifies which three-nucleotide codon from the genetic code corresponds to which amino acid. Each mRNA codon is recognized by a particular type of tRNA, which docks to it along a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complementarity (molecular Biology)
In molecular biology, complementarity describes a relationship between two structures each following the lock-and-key principle. In nature complementarity is the base principle of DNA replication and transcription as it is a property shared between two DNA or RNA sequences, such that when they are aligned antiparallel to each other, the nucleotide bases at each position in the sequences will be complementary, much like looking in the mirror and seeing the reverse of things. This complementary base pairing allows cells to copy information from one generation to another and even find and repair damage to the information stored in the sequences. The degree of complementarity between two nucleic acid strands may vary, from complete complementarity (each nucleotide is across from its opposite) to no complementarity (each nucleotide is not across from its opposite) and determines the stability of the sequences to be together. Furthermore, various DNA repair functions as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polypeptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. Peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides have an N-terminal (amine group) and C-terminal (ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribonucleic Acid
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins ( messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) are nucleic acids. The nucleic acids constitute one of the four major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the nitrogenous bases of guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine, denoted by the letters G, U, A, and C) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome. Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function in which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transfer RNA
Transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA), formerly referred to as soluble ribonucleic acid (sRNA), is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes). In a cell, it provides the physical link between the genetic code in messenger RNA (mRNA) and the amino acid sequence of proteins, carrying the correct sequence of amino acids to be combined by the protein-synthesizing machinery, the ribosome. Each three-nucleotide codon in mRNA is complemented by a three-nucleotide anticodon in tRNA. As such, tRNAs are a necessary component of translation, the biological synthesis of new proteins in accordance with the genetic code. Overview The process of translation starts with the information stored in the nucleotide sequence of DNA. This is first transformed into mRNA, then tRNA specifies which three-nucleotide codon from the genetic code corresponds to which amino acid. Each mRNA codon is recognized by a particular type of tRNA, which docks to it along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA molecules and many ribosomal proteins (). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA (mRNA) chain. Ribosomes bind to the messenger RNA molecules and use the RNA's sequence of nucleotides to determine the sequence of amino acids needed to generate a protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which enter the riboso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |