|
Exon Junction Complex
An exon junction complex (EJC) is a protein complex which forms on a pre-messenger RNA strand at the junction of two exons which have been joined together during RNA splicing. The EJC has major influences on translation, surveillance, localization of the spliced mRNA, and m6A methylation. It is first deposited onto mRNA during splicing and is then transported into the cytoplasm. There it plays a major role in post-transcriptional regulation of mRNA. It is believed that exon junction complexes provide a position-specific memory of the splicing event. The EJC consists of a stable heterotetramer core, which serves as a binding platform for other factors necessary for the mRNA pathway. The core of the EJC contains the protein eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-III ( eIF4A-III; a DEAD-box RNA helicase) bound to an adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) analog, as well as the additional proteins Magoh and Y14. The binding of these proteins to nuclear speckled domains has been measured recently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiprotein Complex
A protein complex or multiprotein complex is a group of two or more associated polypeptide chains. Protein complexes are distinct from multidomain enzymes, in which multiple catalytic domains are found in a single polypeptide chain. Protein complexes are a form of quaternary structure. Proteins in a protein complex are linked by non-covalent protein–protein interactions. These complexes are a cornerstone of many (if not most) biological processes. The cell is seen to be composed of modular supramolecular complexes, each of which performs an independent, discrete biological function. Through proximity, the speed and selectivity of binding interactions between enzymatic complex and substrates can be vastly improved, leading to higher cellular efficiency. Many of the techniques used to enter cells and isolate proteins are inherently disruptive to such large complexes, complicating the task of determining the components of a complex. Examples of protein complexes include the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Y14 (gene)
RNA-binding protein 8A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RBM8A'' gene. This gene encodes a protein with a conserved RNA-binding motif. The protein is found predominantly in the nucleus, although it is also present in the cytoplasm. It is preferentially associated with mRNAs produced by splicing, including both nuclear mRNAs and newly exported cytoplasmic mRNAs. It is thought that the protein remains associated with spliced mRNAs as a tag to indicate where introns had been present, thus coupling pre- and post-mRNA splicing events. Previously, it was thought that two genes encode this protein, RBM8A and RBM8B; it is now thought that the RBM8B locus is a pseudogene. Two alternative start codons result in two forms of the protein, and this gene also uses multiple polyadenylation sites. Interactions RBM8A has been shown to interact with IPO13, MAGOH and UPF3A. Related gene problems *TAR syndrome TAR syndrome (thrombocytopenia with absent radius) is a rare genetic di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Bridge (protein And Supramolecular)
In chemistry, a salt bridge is a combination of two non-covalent interactions: hydrogen bonding and ionic bonding (Figure 1). Ion pairing is one of the most important noncovalent forces in chemistry, in biological systems, in different materials and in many applications such as ion pair chromatography. It is a most commonly observed contribution to the stability to the entropically unfavorable folded conformation of proteins. Although non-covalent interactions are known to be relatively weak interactions, small stabilizing interactions can add up to make an important contribution to the overall stability of a conformer. Not only are salt bridges found in proteins, but they can also be found in supramolecular chemistry. The thermodynamics of each are explored through experimental procedures to access the free energy contribution of the salt bridge to the overall free energy of the state. Salt bridges in chemical bonding In water, formation of salt bridges or ion pairs is mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Sheet
The beta sheet (β-sheet, also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A β-strand is a stretch of polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformation. The supramolecular association of β-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the fibrils and protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, Alzheimer's disease and other proteinopathies. History The first β-sheet structure was proposed by William Astbury in the 1930s. He proposed the idea of hydrogen bonding between the peptide bonds of parallel or antiparallel extended β-strands. However, Astbury did not have the necessary data on the bond geometry of the amino acids in order to build accurate models, especially since he did not then know that the peptide bond was planar. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallization
Crystallization is a process that leads to solids with highly organized Atom, atoms or Molecule, molecules, i.e. a crystal. The ordered nature of a crystalline solid can be contrasted with amorphous solids in which atoms or molecules lack regular organization. Crystallization can occur by various routes including Precipitation (chemistry), precipitation from solution, freezing of a liquid, or Deposition (phase transition), deposition from a gas. Attributes of the resulting crystal can depend largely on factors such as temperature, air pressure, cooling rate, or Solution (chemistry), solute concentration. Crystallization occurs in two major steps. The first is nucleation, the appearance of a crystalline phase from either a Supercooling, supercooled liquid or a supersaturation, supersaturated solvent. The second step is known as crystal growth, which is the increase in the size of particles and leads to a crystal state. An important feature of this step is that loose particles fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in reinforcing the DNA during cell division, preventing DNA repair#DNA damage, DNA damage, and regulating gene expression and DNA replication. During mitosis and meiosis, chromatin facilitates proper segregation of the chromosomes in anaphase; the characteristic shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage are the result of DNA being coiled into highly condensed chromatin. The primary protein components of chromatin are histones. An octamer of two sets of four histone cores (Histone H2A, Histone H2B, Histone H3, and Histone H4) bind to DNA and function as "anchors" around which the strands are wound.Maeshima, K., Ide, S., & Babokhov, M. (2019). Dynamic chromatin organization without the 30 nm fiber. ''Current opinion in cell biolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DEK (gene)
The human ''DEK'' gene encodes the DEK protein. Function This gene encodes a protein with one SAP domain. The protein binds to cruciform DNA and DNA coiled into a superhelix, thereby inducing positive supercoils into closed circular DNA. It is also involved in splice site selection during mRNA In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein. mRNA is ... processing. Chromosomal aberrations involving this region increased expression of this gene and the presence of antibodies against this protein are all associated with various diseases. Interactions ''DEK'' interacts with TFAP2A. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links PDBe-KBprovides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human Protein D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UAP56
Spliceosome RNA helicase BAT1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''BAT1'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the DEAD box family of RNA-dependent ATPases that mediate ATP hydrolysis during pre-mRNA splicing. The encoded protein is an essential splicing factor required for association of U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein with pre-mRNA, and also plays an important role in mRNA export from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. A cluster of genes, BAT1-BAT5, is localized in the vicinity of the genes for TNF alpha and TNF beta. These genes are all within the human major histocompatibility complex class III region. Mutations in this gene may be associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants Alternative splicing, alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to produce different splice variants. For example, some exons of a gene may be included ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
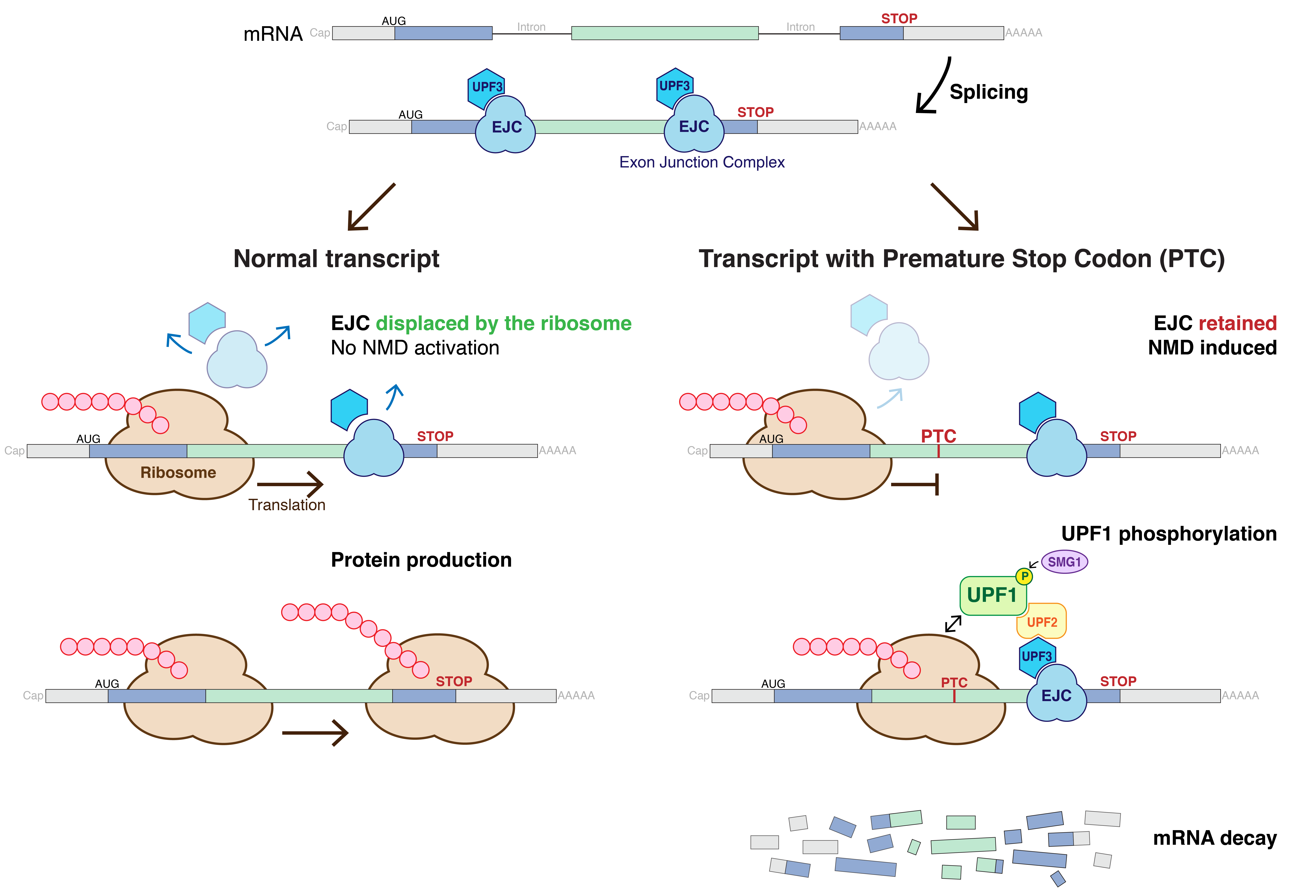
Nonsense Mediated Decay
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) is a surveillance pathway that exists in all eukaryotes. Its main function is to reduce errors in gene expression by eliminating mRNA transcripts that contain premature stop codons. Translation of these aberrant mRNAs could, in some cases, lead to deleterious gain-of-function or dominant-negative activity of the resulting proteins. NMD was first described in human cells and in yeast almost simultaneously in 1979. This suggested broad phylogenetic conservation and an important biological role of this intriguing mechanism. NMD was discovered when it was realized that cells often contain unexpectedly low concentrations of mRNAs that are transcribed from alleles carrying nonsense mutations. Nonsense mutations code for a premature stop codon which causes the protein to be shortened. The truncated protein may or may not be functional, depending on the severity of what is not translated. In human genetics, NMD has the possibility to not only limit the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coactivator
A coactivator is a type of transcriptional coregulator that binds to an activator (a transcription factor) to increase the rate of transcription of a gene or set of genes. The activator contains a DNA binding domain that binds either to a DNA promoter site or a specific DNA regulatory sequence called an enhancer. Binding of the activator-coactivator complex increases the speed of transcription by recruiting general transcription machinery to the promoter, therefore increasing gene expression. The use of activators and coactivators allows for highly specific expression of certain genes depending on cell type and developmental stage. Some coactivators also have histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity. HATs form large multiprotein complexes that weaken the association of histones to DNA by acetylating the N-terminal histone tail. This provides more space for the transcription machinery to bind to the promoter, therefore increasing gene expression. Activators are found in all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ALYREF
Aly/REF export factor, also known as THO complex subunit 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ALYREF'' gene. The ALYREF gene encodes Aly/REF export factor (ALY; THO complex subunit 4, Tho4; RNA and export factor binding protein 1, Refbp1), a ubiquitously expressed nuclear protein that functions as a molecular chaperone and export adapter involved in nuclear export of spliced and unspliced mRNA. The TRanscription-EXport (TREX) complex, a key player in mRNA export, includes the THO subcomplex, the RNA helicase UAP56, and the RNA-binding protein ALY. In yeast, TREX is recruited co-transcriptionally; in human cells it is recruited during a late step of splicing. The human TREX complex is recruited to a region near the 5' end of mRNA by interaction of ALY and THO with the nuclear cap-binding complex. As a chaperone, ALY promotes dimerization of transcription factors containing basic leucine zipper (bZIP bzip2 is a free and open-source file compression program tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SRm160
Serine/arginine repetitive matrix protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SRRM1'' gene. Interactions SRRM1 has been shown to interact with CDC5L Cell division cycle 5-like protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CDC5L'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene shares a significant similarity with '' Schizosaccharomyces pombe'' cdc5 gene product, which is a cell .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * * {{gene-1-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |