|
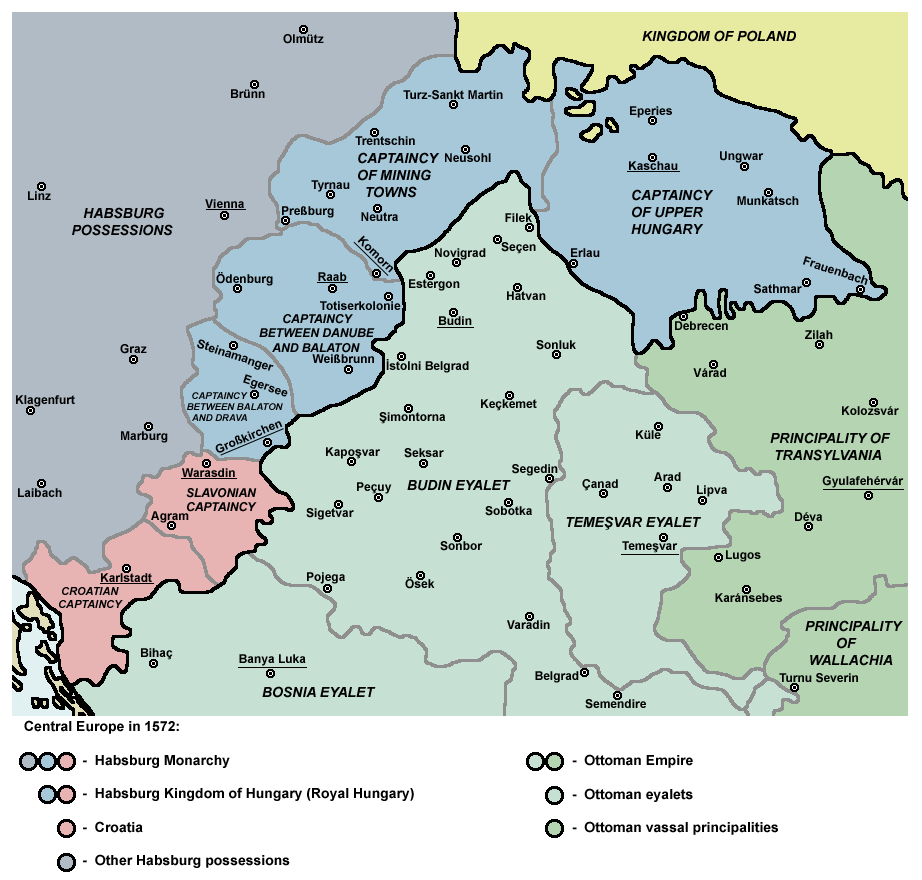
Eparchy Of Marča
The Eparchy of Marča (, sr-Cyrl, Марчанска епархија) was an Eastern Christian ecclesiastical entity taking two forms in the 17th century: an Eastern Orthodox eparchy and an Eastern Catholic vicariate. The term was derived from the name of the monastery at Marča (today Stara Marča) near Ivanić-Grad, Habsburg monarchy (present-day Zagreb County, Republic of Croatia). Although Serbian Orthodox bishop Simeon Vratanja traveled to Rome in 1611 and formally accepted jurisdiction of the Pope over this bishopric, until 1670 Serb bishops continued to recognize the jurisdiction of the Serbian Patriarchate of Peć and struggled against conversion attempts by Roman Catholic bishops from Zagreb. This semi-union existed until the 1670 appointment of Pavle Zorčić as bishop. All Serb Orthodox clergy who objected to the union were arrested and sentenced to life in prison in Malta, where they died. The bishopric eventually became the Eastern Catholic Eparchy of Križevci. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habsburg Monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is also referred to as the Austrian monarchy, the Austrian Empire () or the Danubian monarchy. The history of the Habsburg monarchy can be traced back to the election of Rudolf I of Germany, Rudolf I as King of the Romans, King of Germany in 1273 and his acquisition of the Duchy of Austria for the Habsburgs in 1282. In 1482, Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, Maximilian I acquired the Habsburg Netherlands, Netherlands through marriage. Both realms passed to his grandson and successor, Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V, who also inherited the Monarchy of Spain, Spanish throne and Spanish Empire, its colonial possessions, and thus came to rule the Habsburg empire at its greatest territorial extent. The abdication of Charles V in 1556 led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smederevo Fortress
The Smederevo Fortress () is a medieval fortified city in Smederevo, Serbia, which was the temporary capital of Serbia in the Middle Ages. It was built between 1427 and 1430 on the order of Despot Đurađ Branković, the ruler of the Serbian Despotate. It was further fortified by the Ottoman Empire, which had taken the city in 1459. The fortress withstood several sieges by Ottomans and Serbs, surviving relatively unscathed. During World War II it was heavily damaged by explosions and bombing, despite which the fortress remained "one of the rare preserved courts of medieval Serbian rulers." As of 2009, it was in the midst of extensive restoration and conservation work, Smederevo Fortress was declared a national Monument of Culture of Exceptional Importance in 1979. In 2010, the fortress was placed on the tentative list for possible nomination as a World Heritage Site (UNESCO). Location Smederevo Fortress, 45 kilometers southeast of Belgrade, covers 11.3 hectares ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacred Congregation For The Propagation Of The Faith
The Congregation for the Evangelization of Peoples (CEP; ) was a congregation of the Roman Curia of the Catholic Church in Rome, responsible for missionary work and related activities. It is also known by its former title, the Sacred Congregation for the Propagation of the Faith (), or simply the ''Propaganda Fide''. On 5 June 2022, it was merged with the Pontifical Council for Promoting the New Evangelization into the Dicastery for Evangelization. It was responsible for Latin Church pre-diocesan missionary jurisdictions: missions sui iuris, apostolic prefectures (neither entitled to a titular bishop) and apostolic vicariates. Eastern Catholic equivalents like apostolic exarchate are the responsibility of the Dicastery for the Eastern Churches. However many former missionary jurisdictions – mainly in the Third World – remain, after promotion to diocese of (Metropolitan) Archdiocese, under the Propaganda Fide instead of the normally competent Congregation for Bishops, notab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand III, Holy Roman Emperor
Ferdinand III (Ferdinand Ernest; 13 July 1608 – 2 April 1657) was Archduke of Austria, Kingdom of Hungary, King of Hungary and Kingdom of Croatia (Habsburg), Croatia from 1625, Kingdom of Bohemia, King of Bohemia from 1627 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1637 to his death. Ferdinand ascended the throne at the beginning of the last decade of the Thirty Years' War and introduced lenient policies to depart from the old ideas of Divine right of kings, divine right held by his father, as he wished to end the war quickly. After military defeats and against a background of declining power, Ferdinand was compelled to abandon the political stances of his Habsburg predecessors in many respects to open the long road towards the much-delayed Peace of Westphalia. Although his authority as emperor was weakened after the war, his position in Bohemia, Hungary and Austria was stronger than that of his predecessors before 1618. Ferdinand was the first Habsburg monarch to be recognised as a musical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benedikt Vinković
Benedikt Benko Vinković () (1581 – 2 December 1642) was a Croatian prelate of the Catholic Church who served as the bishop of Pécs from 1630 to 1637 and the bishop of Zagreb from 1637 to his death in 1642. Early life Vinković was born in 1581 in Jastrebarsko. While some contemporary sources say his parents, Petar and Magdalena, were free peasants, others, including Toma Kovačević, claim they were serfs. During his early years, Vinković was educated by Jesuits in seminaries in Erdelj, Zagreb, and Vienna. In 1606 Vinković became rector of the Ilyrian College in Bologne, and in 1608 he received a PhD in philosophy. In 1610, Vinković became a canon of the Diocese of Zagreb and organised the foundation of the Croatian College in Vienna. As a representative at the Diet of Hungary in Pressburg, he staunchly defended the interests of Croatia. In 1611, he became archdeacon in Čazma; in 1612, he became archdeacon of Komarnica. In 1619, Vinković served as an envoy of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julian Calendar
The Julian calendar is a solar calendar of 365 days in every year with an additional leap day every fourth year (without exception). The Julian calendar is still used as a religious calendar in parts of the Eastern Orthodox Church and in parts of Oriental Orthodox Churches, Oriental Orthodoxy as well as by the Amazigh, Amazigh people (also known as the Berbers). The Julian calendar was proposed in 46 BC by (and takes its name from) Julius Caesar, as a reform of the earlier Roman calendar, which was largely a lunisolar calendar, lunisolar one. It took effect on , by his edict. Caesar's calendar became the predominant calendar in the Roman Empire and subsequently most of the Western world for more than 1,600 years, until 1582 when Pope Gregory XIII promulgated a revised calendar. Ancient Romans typically designated years by the names of ruling consuls; the ''Anno Domini'' system of numbering years was not devised until 525, and became widespread in Europe in the eighth cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavonian Military Frontier
The Slavonian Military Frontier ( or ; ; ; ) was a district of the Military Frontier, a territory in the Habsburg monarchy, first during the period of the Austrian Empire and then during the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy. It was formed out of territories the Habsburgs conquered from the Ottoman Empire and included southern parts of Slavonia and Syrmia; today the area it covered is mostly in eastern Croatia, with its easternmost parts in northern Serbia (mostly in Vojvodina region.) Divisions The Slavonian Military Frontier was divided between three regiments: Regiment N°VII, based at Vinkovci; Regiment N°VIII, based at Nova Gradiška and Regiment N°IX, based at Petrovaradin. Other important towns in the area included Sremski Karlovci, Stara Pazova, Zemun, and Sremska Mitrovica. History During the history, name Slavonian Military Frontier referred to different territories. It was first located in what is now Central Croatia and was known as the Varaždin generalat. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatian Military Frontier
The Croatian Military Frontier ( or ') was a district of the Military Frontier, a territory in the Habsburg monarchy, first during the period of the Austrian Empire and then during Austria-Hungary. History Founded in the late 16th century out of lands of the Habsburg Kingdom of Croatia, it was initially a nominal part of that Kingdom, to be transferred in 1627 to direct imperial rule as part of the Military Frontier. The Frontier was located on the border with the Ottoman Empire. In the Frontier zone, the king-emperors promised free land and freedom of religion to people who came to the area with the majority of the population being Croats, Serbs and Vlachs. In exchange, the people who lived in the area had an obligation to fight for the Empire, and to protect the land. In 1630 Emperor Ferdinand II enacted the '' Statuta Valachorum'' laws. It was known that the soldiers had to fulfill military service between the ages of 16 and 66. At the end of the 17th century, Habsburg Kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vlachs In The History Of Croatia
The term ''Vlachs'' () was initially used in medieval Croatian and Venetian history for a Romance-speaking pastoralist community, called "Vlachs" and " Morlachs", inhabiting the mountains and lands of the Croatian Kingdom and the Republic of Venice ( Venetian Dalmatia) from the early 14th century. By the end of the 15th century they were highly assimilated with the Slavs and lost their language or were at least bilingual, while some communities managed to preserve and continue to speak their language (Istro-Romanians). Later in the 16th and 17th century with the Ottoman conquest and mass migrations, the term was primarily used for a socio-cultural and professional segment of the population rather than to an ethnicity, and referred to the mostly Slavic-speaking emigrants and refugees from Ottoman-held territories to the Habsburg Empire (such as Croatia) and the Republic of Venice (Dalmatia), mostly of Eastern Orthodox faith, and to a lesser degree, Catholic. With the nation-bui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Dobrović
Martin Dobrović or Martin Dubravić (1599–1621) was a Catholic priest. After finishing his education in Graz, he became a parson of Ivanić Grad and later became a priest in the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Zagreb. Early life and education Born in a Serbian Orthodox Christian family, Dobrović was born to parents who had migrated from Bosnia to what is now modern-day Croatia. Later, his family converted to Catholicism. With a recommendation from the Bishop of Ljubljana, Thomas Chrön, the Catholic church educated him as a priest at a school in Graz. He studied there from 1599 to 1608. As a student of literature, he wrote a song entitled ''Eidem,'' () which was published in 1601. After graduating, Dobrović became parson of Ivanić and chaplain of the German Military Garrison in Ivanić. Conversion of Orthodox Serbians to Catholicism As parson of Ivanić Grad, Dobrović actively tried to convert Orthodox Serbians, who had migrated from the Ottoman Empire to Catholicism. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Florence
The Council of Florence is the seventeenth ecumenical council recognized by the Catholic Church, held between 1431 and 1445. It was convened in territories under the Holy Roman Empire. Italy became a venue of a Catholic ecumenical council after a gap of about 2 centuries (the last ecumenical council to be held in Italy was the 4th Council of the Lateran in Rome's Lateran Palace). It was convoked in Basel as the Council of Basel by Pope Martin V shortly before his death in February 1431 and took place in the context of the Hussite Wars in Bohemia and the rise of the Ottoman Empire. At stake was the greater conflict between the conciliar movement and the principle of papal supremacy. The Council entered a second phase after Emperor Sigismund's death in 1437. Pope Eugene IV translated the Council to Ferrara on 8 January 1438, where it became the Council of Ferrara and succeeded in drawing some of the Byzantine ambassadors who were in attendance at Basel to Italy. Some Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Paul V
Pope Paul V (; ) (17 September 1552 – 28 January 1621), born Camillo Borghese, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 16 May 1605 to his death, in January 1621. In 1611, he honored Galileo Galilei as a member of the papal Accademia dei Lincei and supported his discoveries. In 1616, Pope Paul V instructed Cardinal Robert Bellarmine to inform Galileo that the Copernican theory could not be taught as fact, but Bellarmine's certificate allowed Galileo to continue his studies in search for evidence and use the geocentric model as a theoretical device. That same year Paul V assured Galileo that he was safe from persecution so long as he, the Pope, should live. Bellarmine's certificate was used by Galileo for his defense at the trial of 1633. Trained in jurisprudence, Borghese was made Cardinal-Priest of Sant'Eusebio and the Cardinal Vicar of Rome by Pope Clement VIII. He was elected as Pope in 1605, following the death of Pope Leo XI. Pope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |