|
Engine Computer
An engine control unit (ECU), also called an engine control module (ECM), is a device that controls various subsystems of an internal combustion engine. Systems commonly controlled by an ECU include the fuel injection and ignition systems. The earliest ECUs (used by aircraft engines in the late 1930s) were mechanical-hydraulic units; however, most 21st-century ECUs operate using digital electronics. Functions The main functions of the ECU are typically: * Fuel injection system * Ignition system * Idle speed control (typically either via an idle air control valve or the electronic throttle system) * Variable valve timing and/or variable valve lift systems The sensors used by the ECU include: * accelerator pedal position sensor * camshaft position sensor * coolant temperature sensor * crankshaft position sensor * knock sensors * inlet manifold pressure sensor (MAP sensor) * intake air temperature * intake air mass flow rate sensor ( MAF sensor) * oxygen (lambda) sensor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inlet Manifold
An inlet manifold or intake manifold (in American English) is the part of an internal combustion engine that supplies the fuel/ air mixture to the cylinders. The word ''manifold'' comes from the Old English word ''manigfeald'' (from the Anglo-Saxon ''manig'' anyand ''feald'' epeatedly and refers to the multiplying of one (pipe) into many.manifold, (adv.) "in the proportion of many to one, by many times". AD1526 ''Oxford English Dictionary'', In contrast, an exhaust manifold collects the exhaust gases from multiple cylinders into a smaller number of pipes – often down to one pipe. The primary function of the intake manifold is to ''evenly'' distribute the combustion mixture (or just air in a direct injection engine) to each intake port in the cylinder head(s). Even distribution is important to optimize the efficiency and performance of the engine. It may also serve as a mount for the carburetor, throttle body, fuel injectors and other components of the engine. Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camless Piston Engine
A camless or free-valve piston engine is an engine that has poppet valves operated by means of electromagnetic, hydraulic, or pneumatic actuators instead of conventional cams. Actuators can be used to both open and close valves, or to open valves closed by springs or other means. Camshafts normally have one lobe per valve, with a fixed valve duration and lift. Although many modern engines use camshaft phasing, adjusting the lift and valve duration in a working engine is more difficult. Some manufacturers use systems with more than one cam lobe, but this is still a compromise as only a few profiles can be in operation at once. This is not the case with the camless engine, where lift and valve timing can be adjusted freely from valve to valve and from cycle to cycle. It also allows multiple lift events per cycle and, indeed, no events per cycle—switching off the cylinder entirely. Camless development Camless valve trains have long been investigated by several companies, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immobiliser
An immobiliser or immobilizer is an electronic security device fitted to a motor vehicle that prevents the engine from being started unless the correct key (transponder or smart key) is present. This prevents the vehicle from being "Hotwiring, hot wired" after entry has been achieved and thus reduces motor vehicle theft. Research shows that the uniform application of immobilisers reduced the rate of car theft by 40%. Description The electric immobiliser/alarm system was invented by St. George Evans and Edward Birkenbeuel and patented in 1919. They developed a 3x3 grid of double-contact Electric switchboard, switches on a panel mounted inside the car so when the ignition switch was activated, current from the battery (or magneto) went to the spark plugs allowing the engine to start, or immobilizing the vehicle and Car alarm, sounding the Vehicle horn, horn. The system settings could be changed each time the car was driven. Modern immobiliser systems are automatic, meaning the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-lag
The anti-lag system (ALS) is a method of reducing turbo lag or effective compression used on turbocharged engines to minimize turbo lag on racing or performance cars. It works by retarding the ignition timing and adding extra fuel (and sometimes air) to balance an inherent loss in combustion efficiency with increased pressure at the charging side of the turbo. This is achieved as an excess amount of fuel/air mixture escapes through the exhaust valves and combusts in the hot exhaust manifold spooling the turbocharger creating higher usable pressure. Overview ALS was first used in the early days of turbocharged cars in Formula One racing circa mid to late 1980s, until fuel restrictions made its use unsuitable. Later it became a common feature in rally cars because of the increased turbo lag from the mandated restrictors at the intake manifold inlet. Due to the pressure drop across the restriction, the pressure ratio for a given boost level is much higher and the turbocharger must ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wastegate
A wastegate is a valve that controls the flow of exhaust gases to the turbine wheel in a turbocharged engine system.Robson, D. (2018). Aircraft General Knowledge. Aviation Theory Centre Pty Ltd. . Diversion of exhaust gases regulates the turbine speed, which in turn regulates the rotating speed of the compressor. The primary function of the wastegate is to regulate the maximum boost pressure in turbocharger systems, to protect the engine and the turbocharger. One advantage of installing a remote mount wastegate to a free-float (or non-wastegate) turbo includes an allowance for a smaller area over radius (A/R) turbine housing, resulting in less lag time before the turbo begins to spool and create boost. One of the earliest usage of a modern wastegate was in the Saab 99 Turbo 1978, presented in 1977. Wastegate types External An external wastegate is a separate self-contained mechanism typically used with turbochargers that do not have internal wastegates. An external wastegate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rev Limiter
A rev limiter is a device fitted in modern vehicles that have internal combustion engines. They are intended to protect an engine by restricting its maximum rotational speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM). Rev limiters are Engine control unit, pre-set by the engine manufacturer. There are also aftermarket units where a separate controller is installed using a custom RPM setting. A limiter prevents a vehicle's engine from being pushed beyond the manufacturer's limit, known as the ''redline'' (literally the red line marked on the tachometer). At some point beyond the redline, engine damage may occur. Operation Limiters usually work by shutting off a component necessary for the combustion processes to occur, whether it be fuel, air or spark. Internal combustion engine#Compression ignition process, Compression-ignition engines use mechanical Governor (device), governors or limiters to shut off electronic fuel injectors. A Internal combustion engine#Spark ignition process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Pressure Regulator
A pressure regulator is a valve that controls the pressure of a fluid to a desired value, using negative feedback from the controlled pressure. Regulators are used for gases and liquids, and can be an integral device with a pressure setting, a restrictor and a sensor all in the one body, or consist of a separate pressure sensor, controller and flow valve. Two types are found: The pressure reduction regulator and the back-pressure regulator. *A pressure reducing regulator is a control valve that reduces the input pressure of a fluid to a desired value at its output. It is a normally-open valve and is installed upstream of pressure sensitive equipment. *A back-pressure regulator, back-pressure valve, pressure sustaining valve or pressure sustaining regulator is a control valve that maintains the set pressure at its inlet side by opening to allow flow when the inlet pressure exceeds the set value. It differs from an over-pressure relief valve in that the over-pressure valve is on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
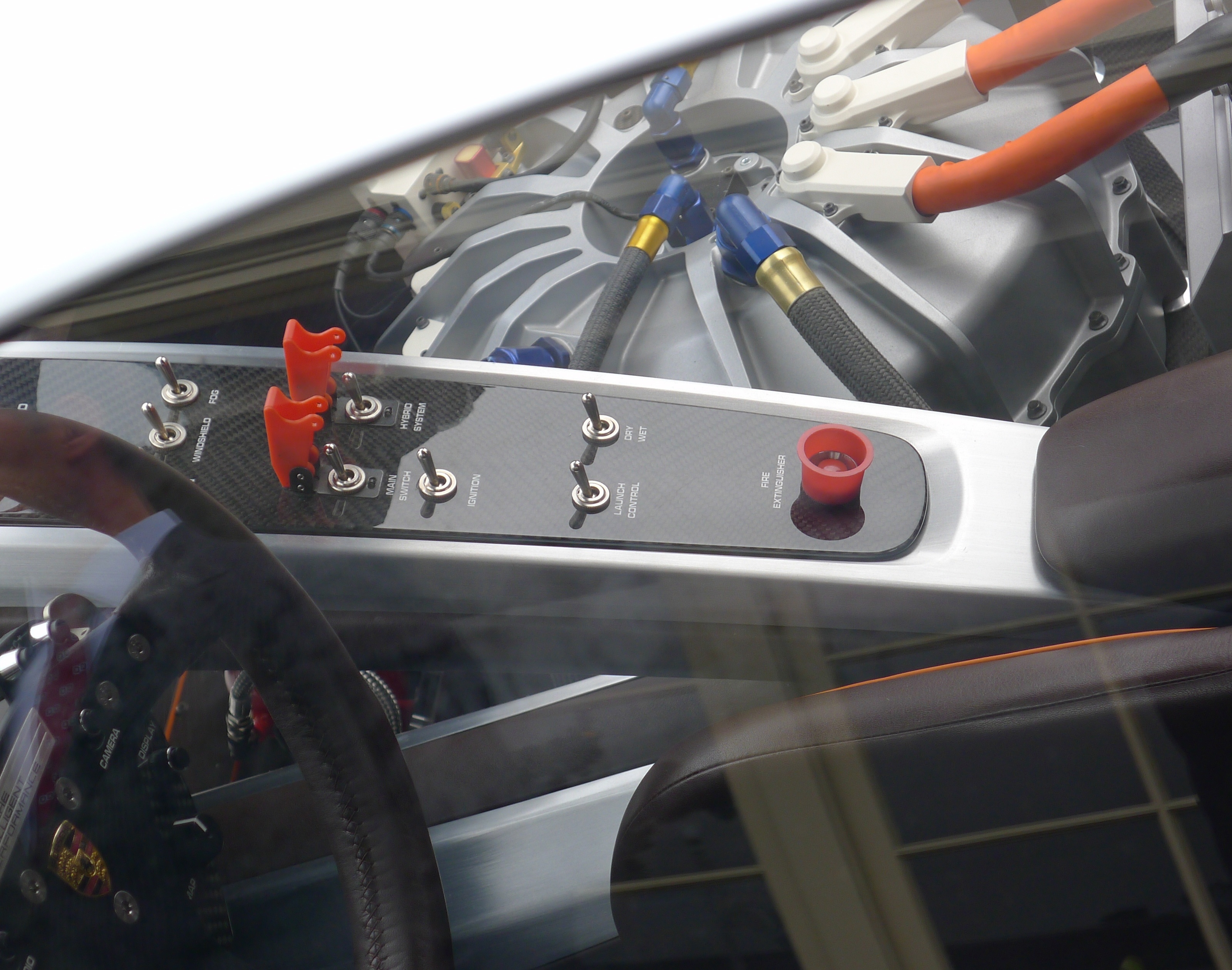
Launch Control (automotive)
Launch control is an electronic aid to assist drivers of both racing and street cars to accelerate from a standing start. Motorcycles have been variously fitted with mechanical and electronic devices for both street and race. Popular automobiles with launch control include the BMW M series, certain marques of the Volkswagen Group with Direct-Shift Gearbox (most notably the Bugatti Veyron), Porsche 911 (sport+ mode), Panamera Turbo, Alfa Romeo with TCT gearbox and certain General Motors products. Mitsubishi also incorporated launch control into their Twin Clutch SST gearbox, on its "S-Sport" mode, but the mode is only available in the Evolution X MR and MR Touring (USDM). The Jaguar F-Type includes launch control. The Nissan GT-R has electronics to control launch but the company does not use the term "launch control" since some owners have equated the term with turning off the stability control to launch the car, which may void the warranty of the drivetrain. One version of Nissa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheel Speed Sensor
A wheel speed sensor (WSS) or vehicle speed sensor (VSS) is a type of tachometer. It is a sender device used for reading the speed of a vehicle's wheel rotation. It usually consists of a toothed ring and pickup. Automotive wheel speed sensor Purpose The wheel speed sensor was initially used to replace the mechanical linkage from the wheels to the speedometer, eliminating cable breakage and simplifying the gauge construction by eliminating moving parts. These sensors also produce data that allows automated driving aids like ABS to function. Construction The most common wheel speed sensor system consists of a ferromagnetic toothed reluctor ring and a sensor (which can be passive or active). The tone wheel is typically made of steel and may be an open-air design, or sealed (as in the case of unitized bearing assemblies). The number of teeth is chosen as a trade-off between low-speed sensing/accuracy and high-speed sensing/cost. Greater numbers of teeth will require more ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen Sensor
An oxygen sensor is an electronic component that detects the concentration of oxygen molecules in the air or a gas matrix such as in a combustion engine exhaust gas. For automotive applications, an oxygen sensor is referred to as a lambda sensor, where lambda refers to the air–fuel equivalence ratio, usually denoted by λ). It was developed by Robert Bosch GmbH during the late 1960s under the supervision of Günter Bauman. The original sensing element is made with a thimble-shaped zirconia ceramic coated on both the exhaust and reference sides with a thin layer of platinum and comes in both heated and unheated forms. The planar-style sensor entered the market in 1990 and significantly reduced the mass of the ceramic sensing element, as well as incorporating the heater within the ceramic structure. This resulted in a sensor that started sooner and responded faster. The most common application is to measure the exhaust-gas concentration of oxygen for internal combustion engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |