|
En Sof
Ein Sof, or Eyn Sof (, '; meaning "infinite", ), in Kabbalah, is understood as God before any self-manifestation in the production of any spiritual realm, probably derived from Solomon ibn Gabirol's (1021ŌĆō1070) term, "the Endless One" ( ''┼Īe╩Š─ōn lo tiql─ü''). It is important to note that Kabbalah (Mystical Elevation of Hidden Knowledge) was developed after exile through exposure to Babylonian and later Greek mystical thought. Many devoted Torah scholars acknowledge this practice as divination which The Torah explicitly prohibits in Deuteronomy 18:10-12. ''Ein Sof'' may be translated as "unending", "(there is) no end", or infinity. It was first used by Azriel of Gerona ( 1160 ŌĆō 1238), who, sharing the Neoplatonic belief that God can have no desire, thought, word, or action, emphasized by the negation of any attribute. This is the origin of the Ohr Ein Sof or "Infinite Light" of paradoxical divine self-knowledge, nullified within the Ein Sof before creation. In Lurianic Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabbalah
Kabbalah or Qabalah ( ; , ; ) is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. It forms the foundation of Mysticism, mystical religious interpretations within Judaism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal (). List of Jewish Kabbalists, Jewish Kabbalists originally developed transmissions of the primary texts of Kabbalah within the realm of Jewish tradition and often use classical Jewish scriptures to explain and demonstrate its mystical teachings. Kabbalists hold these teachings to define the inner meaning of both the Hebrew Bible and traditional rabbinic literature and their formerly concealed transmitted dimension, as well as to explain the significance of Jewish religious observances. Historically, Kabbalah emerged from earlier forms of Jewish mysticism, in 12th- to 13th-century Golden age of Jewish culture in Spain, al-Andalus (Spain) and in Hakhmei Provence, and was reinterpreted during the Jewish mystical renaissance in 16th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Kadmon
In Kabbalah, Adam Kadmon (, ''╩Š─üßĖÅ─üm qaßĖÅm┼Źn'', "Primordial Man") also called Adam Elyon (, ''╩Š─üßĖÅ─üm ╩┐ely┼Źn'', "Most High Man"), or Adam Ila'ah (, ''╩Š─üßĖÅ─üm ╩┐─½ll─ü╩Š─ü'' "Most High Adam" in Aramaic), sometimes abbreviated as A"K (, ''╩ŠA.Q.''), is the first of Four Worlds that came into being after the contraction of God's infinite light. ''Adam Kadmon'' is not the same as the physical ''Adam Ha-Rishon'' (ūÉųĖūōųĖūØ ūöųĖū©ų┤ūÉū®ūüūĢų╣ū¤). In Lurianic Kabbalah, the description of ''Adam Kadmon'' is anthropomorphic. Nonetheless, ''Adam Kadmon'' is divine light without vessels, i.e., pure potential. In the human psyche, ''Adam Kadmon'' corresponds to the yechidah, the collective essence of the soul. In Judaism Philo The first to use the expression "original man," or "heavenly man," was Philo, in whose view this or , "as being born in the image of God, has no participation in any corruptible or earthlike essence; whereas the earthly man is made of loose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
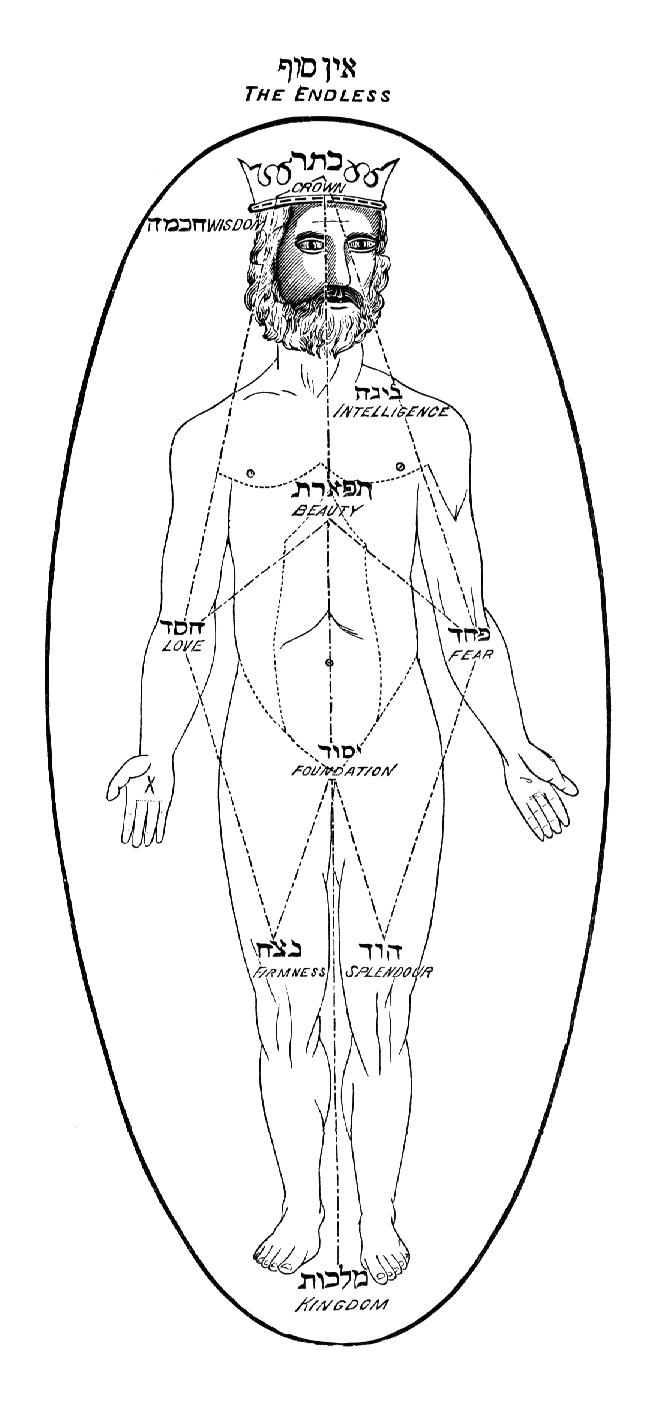
Keter
Keter or Kether (; ) is the first of the ten sefirot in the Kabbalistic Tree of Life, symbolizing the divine will and the initial impulse towards creation from the '' Ein Sof'', or infinite source. It represents pure consciousness and transcends human understanding, often referred to as "Nothing" or the "Hidden Light". Keter is associated with the divine name "'' Ehyeh Asher Ehyeh''" (), meaning "I Am that I Am", which was revealed to Moses from the burning bush, and it embodies the qualities of absolute compassion and humility. Its meaning is "crown", and it is interpreted as both the "topmost" of the Sefirot and the " regal crown" thereof. Keter is positioned at the top of the Tree of Life, sitting above and between Chokmah on the right and Binah on the left, and above Tiferet. It is often depicted with three primary paths: one leading to Chokmah, another to Binah, and the third to Tiferet. This positioning highlights its role as the source from which wisdom (Chokmah) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tzimtzum
The ''tzimtzum'' or ''tsimtsum'' () is a term used in Lurianic Kabbalah to explain Isaac Luria's doctrine that God began the process of creation by limiting the Ohr Ein Sof (infinite light) of the Godhead in order to allow for a conceptual space in which the Four Worlds, or finite realms, could exist. This primordial initial contraction, forming a "vacant space" () into which new creative light could beam, is denoted by general reference to the ''tzimtzum''. In Kabbalistic interpretation, ''tzimtzum'' gives rise to the paradox of simultaneous divine presence and absence within the vacuum and resultant Creation. Various approaches exist as to how the paradox may be resolved, and as to the nature of ''tzimtzum'' itself. Function Because the tzimtzum results in the space in which the spiritual and physical worlds and, ultimately, free will, can exist, God is often referred to as " Ha-Makom" ( lit. "the Place", "the Omnipresent") in rabbinic literature. ''Olam'', the Hebrew t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Of Days
Ancient of Days is a name for God in the Book of Daniel. The title "Ancient of Days" has been used as a source of inspiration in art and music, denoting the creator's aspects of eternity combined with perfection. William Blake's watercolour and relief etching entitled '' The Ancient of Days'' is one such example. Judaism This term appears three times in the Book of Daniel (7:9, 13, 22), and is used in the sense of God being eternal. "In contrast with all earthly kings, his days are past reckoning." Kabbalah In the Zohar, the seminal document of Kabbalah that emerged in 13th-century Spain, there is mention of the Ancient of Ancients, and the Holy Ancient One – Atika Kadisha, variably interpreted as synonymous with the Ein Sof, the unmanifested Godhead. The Ancient of Days is the manifestation of the Ancient of Ancients within Creation. It refers to the most primary ("ancient") source of creation in the divine will Keter ("Crown"). In 16th-century Lurianic Kabbalah, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emanationism
Emanationism is a speculative theory in the cosmology or cosmogony of certain religious and philosophical systems, that posits the concept of ''emanation''. According to this theory, emanation, from the Latin ''emanare'' meaning "to flow from" or "to pour forth or out of", is the mode by which all existing things are derived from a 'first reality', or first principle. In the emanationist concept all things are derived from this first reality or perfect God, by consecutive steps of degradation, to a lower degree of this first reality or God: at every consecutive step the emanating beings are less pure, less perfect, less divine. Emanationism posits a transcendent principle from which everything is derived, as opposed to creationism, that considers the universe to be created by a sentient God who is separate from creation, and to materialism, which posits no underlying subjective and/or ontological nature behind phenomena, all phenomena being considered immanent. Origins Ema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sefirot
Sefirot (; , plural of ), meaning '' emanations'', are the 10 attributes/emanations in Kabbalah, through which Ein Sof ("infinite space") reveals itself and continuously creates both the physical realm and the seder hishtalshelut (the chained descent of the metaphysical Four Worlds). The term is alternatively transliterated into English as ''sephirot/sephiroth'', singular ''sefira/sephirah''. As revelations of the creator's will (, ''r─üß╣Żon''), the sefirot should not be understood as ten gods, but rather as ten different channels through which the one God reveals His will. In later Jewish literature, the ten sefirot refer either to the ten manifestations of God; the ten powers or faculties of the soul; or the ten structural forces of nature. Alternative configurations of the sefirot are interpreted by various schools in the historical evolution of Kabbalah, with each articulating differing spiritual aspects. The tradition of enumerating 10 is stated in the ''Sefer Yetzirah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gershom Scholem
Gershom Scholem (; 5 December 1897 ŌĆō 21 February 1982) was an Israeli philosopher and historian. Widely regarded as the founder of modern academic study of the Kabbalah, Scholem was appointed the first professor of Jewish mysticism at Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Scholem and the Kabbalah Scholem is acknowledged as the single most significant figure in the recovery, collection, annotation, and registration into rigorous Jewish scholarship of the canonical bibliography of mysticism and scriptural commentary that runs through its primordial phase in the ''Sefer Yetzirah,'' its inauguration in the '' Bahir,'' its exegesis in the ''Pardes'' and the ''Zohar'' to its cosmogonic, apocalyptic climax in Isaac Luria's '' Ein Sof'' that is known collectively as Kabbalah. After generations of demoralization and assimilation in the European Enlightenment, the disappointment of messianic hopes, the famine of 1916 in Palestine, and in the midst of the catastrophe of the Final Solution i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azriel (Jewish Mystic)
Azriel ibn Menahem ibn Ibrahim al-Tar─üs (Arabic: ž╣ž▓ž▒┘Ŗ┘ä ž©┘å ┘ģ┘垦žŁ┘Ŗ┘ģ ž©┘å ž¦ž©ž▒ž¦┘ć┘Ŗ┘ģ ž¦┘䞬ž¦ž▒ž¦ž│ ''Azr─ōyl bin Min─üßĖź─½m ben Ibr─ühim ─ül-T─ür─üs''; Hebrew: ūóū¢ū©ūÖūÉū£ ūæū¤ ū×ūĀūŚūØ ūæū¤ ūÉūæū©ūöūØ ūÉū£ū¬ū©ūÉūĪ ''╩┐├üzr─½y╩Š─ōl ben M╔Ön├ĪßĖź─ōm ben ╩ŠAßĖćr─üh─üm al-Taras''; ŌĆō ) also known as Azriel of Girona was the founder of speculative Kabbalah and the Gironian Kabbalist school. He is known for implementing Neoplatonic thought into mainstream kabbalistic tradition. Biography Azriel ibn Menahem ibn Ibrahim al-Tar─üs was born around 1160 in Girona, Catalonia to the al-Taras family. His father Menahem was a minor rabbi in Girona. In his early years, Azriel moved to southern France, where he studied under Isaac the Blind. Azriel later travelled across Spain, preaching his kabbalistic views, however this proved to be unsuccessful, with Azriel later stating that "''the philosophers believe in nothing that can not be demonstrated logically''." He later return ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac The Blind
Isaac the Blind ( ''Rabb─½ Y─½ß╣ŻßĖźaq Sagg─½ N╔Öh┼Źr'', literally "Rabbi Isaac, of much light"; c. 1160ŌĆō1235 in Provence, France), was a French rabbi and a famous writer on Kabbalah (Jewish mysticism). The Aramaic epithet "Saggi Nehor" means "of Much Light" in the sense of having excellent eyesight, an ironic euphemism A euphemism ( ) is when an expression that could offend or imply something unpleasant is replaced with one that is agreeable or inoffensive. Some euphemisms are intended to amuse, while others use bland, inoffensive terms for concepts that the u ... for being blind. Some historians suspect him to be the author of the '' Book of the Bahir'', an important early text of Kabbalah. Others (especially Gershom Scholem, see his Origins of the Kabbalah, p. 253) characterize this view as an "erroneous and totally unfounded hypothesis". Isaac was the son of the famous talmudist, Abraham ben David of Posqui├©res (Raavad). The ''Bahir'' first appeared in the Middl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle EastŌĆöonce part of the Byzantine EmpireŌ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |