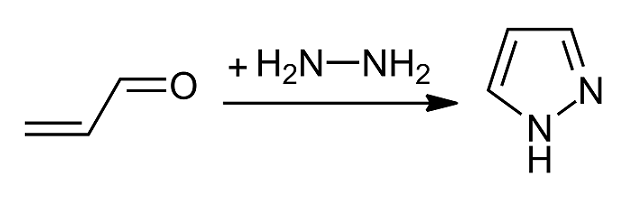|
Emrusolmin
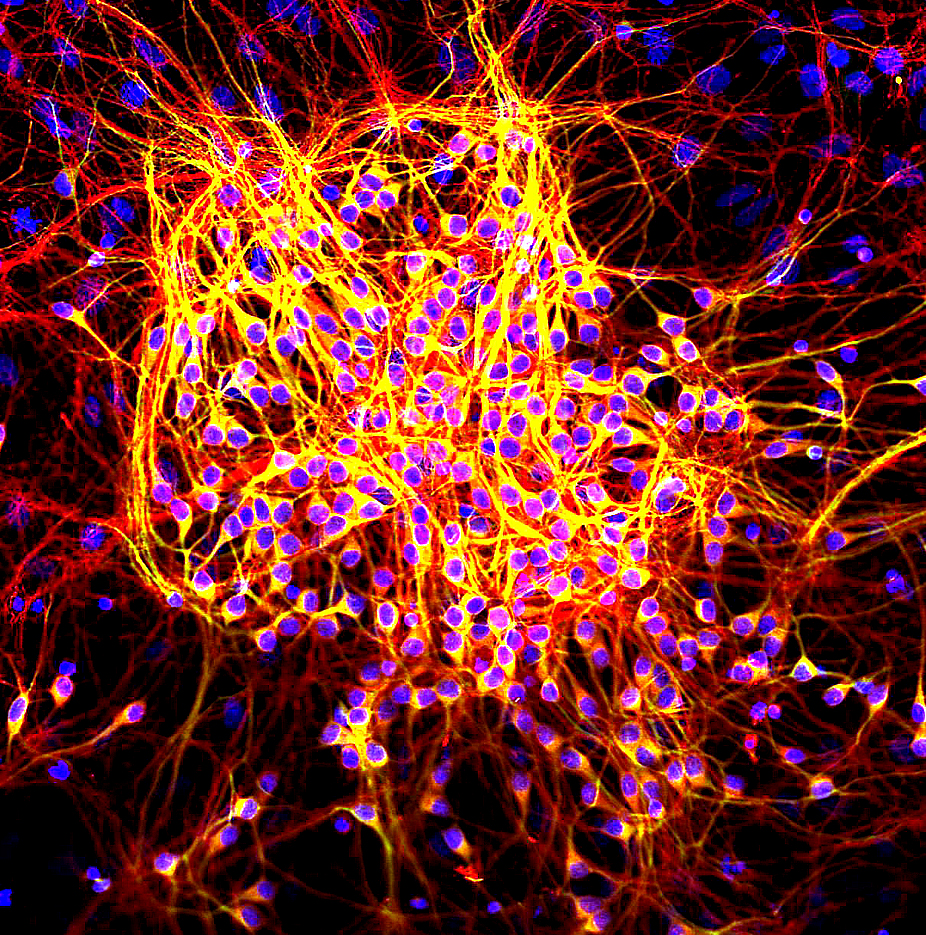
Emrusolmin (development code Anle138b) is an experimental drug for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. It is an inhibitor of protein aggregation, particularly preventing the aggregation of α-synuclein which is implicated in the development of Parkinson's disease. Other proteins it inhibits the aggregation of include tau which is associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and tauopathy, and amyloid beta which is associated with AD. It is currently in clinical trials for Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy Multiple system atrophy (MSA) is a rare neurodegenerative disorder characterized by tremors, slow movement, muscle rigidity, postural instability (collectively known as parkinsonism), autonomic dysfunction and ataxia. This is caused by progr .... References {{Nervous-system-drug-stub Drugs acting on the nervous system Pyrazoles Bromobenzene derivatives Benzodioxoles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
α-synuclein
Alpha-synuclein (aSyn) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SNCA'' gene. It is a neuronal protein involved in the regulation of synaptic vesicle trafficking and the release of neurotransmitters. Alpha-synuclein is abundant in the brain, with smaller amounts present in the heart, muscles, and other tissues. Within the brain, it is primarily localized to the axon terminals of presynaptic neurons. There, it interacts with phospholipids and other proteins. Presynaptic terminals release neurotransmitters from specialized compartments called synaptic vesicles, a process essential for neuronal communication and normal brain function. In Parkinson's disease and related synucleinopathies, abnormal, insoluble forms of alpha-synuclein accumulate within neurons as inclusions known as Lewy bodies. Mutations in the ''SNCA'' gene are linked to familial forms of Parkinson's disease. During the process of seeded nucleation, alpha-synuclein adopts a cross-beta sheet structure charac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become more prevalent as the disease progresses. The motor symptoms are collectively called parkinsonism and include tremors, bradykinesia, spasticity, rigidity as well as postural instability (i.e., difficulty maintaining balance). Non-motor symptoms develop later in the disease and include behavior change (individual), behavioral changes or mental disorder, neuropsychiatric problems such as sleep abnormalities, psychosis, anosmia, and mood swings. Most Parkinson's disease cases are idiopathic disease, idiopathic, though contributing factors have been identified. Pathophysiology involves progressive nerve cell death, degeneration of nerve cells in the substantia nigra, a midbrain region that provides dopamine to the basal ganglia, a system invo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tau Protein
The tau proteins (abbreviated from tubulin associated unit) form a group of six highly soluble protein isoforms produced by alternative splicing from the gene ''MAPT'' (microtubule-associated protein tau). They have roles primarily in maintaining the stability of microtubules in axons and are abundant in the neurons of the central nervous system (CNS), where the cerebral cortex has the highest abundance. They are less common elsewhere but are also expressed at very low levels in CNS astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Pathologies and dementias of the nervous system such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease are associated with tau proteins that have become hyperphosphorylated insoluble aggregates called neurofibrillary tangles. The tau proteins were identified in 1975 as heat-stable proteins essential for microtubule assembly, and since then they have been characterized as intrinsically disordered proteins. Function Microtubule stabilization Tau proteins are found m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the average life expectancy following diagnosis is three to twelve years. The causes of Alzheimer's disease remain poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an allele of apolipoprotein E. Other risk factors include a history of head injury, clinical depression, and high blood pressure. The progression of the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tauopathy
Tauopathies are a class of neurodegenerative diseases characterized by the aggregation of abnormal tau protein. Hyperphosphorylation of tau proteins causes them to dissociate from microtubules and form insoluble aggregates called neurofibrillary tangles. Various neuropathologic phenotypes have been described based on the anatomical regions and cell types involved as well as the unique tau isoforms making up these deposits. The designation 'primary tauopathy' is assigned to disorders where the predominant feature is the deposition of tau protein. Alternatively, diseases exhibiting tau pathologies attributed to different and varied underlying causes are termed 'secondary tauopathies'. Some neuropathologic phenotypes involving tau protein are Alzheimer's disease, frontotemporal dementia, progressive supranuclear palsy, and corticobasal degeneration. Tau protein Tau protein, also called tubulin associated unit or microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT), is a microtubule-associate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyloid Beta
Amyloid beta (Aβ, Abeta or beta-amyloid) denotes peptides of 36–43 amino acids that are the main component of the amyloid plaques found in the brains of people with Alzheimer's disease. The peptides derive from the amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP), which is cleaved by Beta-secretase 1, beta secretase and gamma secretase to yield Aβ in a cholesterol-dependent process and substrate presentation. Both neurons and oligodendrocytes produce and release Aβ in the brain, contributing to formation of amyloid plaques. Aβ molecules can aggregate to form flexible soluble oligomers which may exist in several forms. It is now believed that certain misfolded oligomers (known as "seeds") can induce other Aβ molecules to also take the misfolded oligomeric form, leading to a chain reaction akin to a prion infection. The oligomers are toxic to nerve cells. The other protein implicated in Alzheimer's disease, tau protein, also forms such prion-like misfolded oligomers, and there is some ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple System Atrophy
Multiple system atrophy (MSA) is a rare neurodegenerative disorder characterized by tremors, slow movement, muscle rigidity, postural instability (collectively known as parkinsonism), autonomic dysfunction and ataxia. This is caused by progressive degeneration of neurons in several parts of the brain including the basal ganglia, inferior olivary nucleus, and cerebellum. MSA was first described in 1960 by Milton Shy and Glen Drager and was then known as Shy–Drager syndrome. Many people affected by MSA experience dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, which commonly manifests as orthostatic hypotension, impotence, loss of sweating, dry mouth and urinary retention and incontinence. Palsy of the vocal cords is an important and sometimes initial clinical manifestation of the disorder. A prion of the alpha-synuclein protein within affected neurons may cause MSA. About 55% of MSA cases occur in men, with those affected first showing symptoms at the age of 50–60 ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drugs Acting On The Nervous System
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via inhalation, injection, smoking, ingestion, absorption via a patch on the skin, suppository, or dissolution under the tongue. In pharmacology, a drug is a chemical substance, typically of known structure, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. A pharmaceutical drug, also called a medication or medicine, is a chemical substance used to treat, cure, prevent, or diagnose a disease or to promote well-being. Traditionally drugs were obtained through extraction from medicinal plants, but more recently also by organic synthesis. Pharmaceutical drugs may be used for a limited duration, or on a regular basis for chronic disorders. Classification Pharmaceutical drugs are often classified into drug classes—groups of related drugs that have simila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrazoles
Pyrazole is an organic compound with the formula . It is a heterocycle characterized as an azole with a 5-membered ring of three carbon atoms and two adjacent nitrogen atoms, which are in ortho-substitution. Pyrazoles are also a class of compounds that have the ring C3N2 with adjacent nitrogen atoms. Pyrazole itself has few applications but many substituted pyrazoles are of commercial interest. Notable drugs containing a pyrazole ring are celecoxib (celebrex) and the anabolic steroid stanozolol. Properties Pyrazole is a weak base, with p''K''b 11.5 (p''K''a of the conjugate acid 2.49 at 25 °C). According to X-ray crystallography, the compound is planar. The two C-N distances are similar, both near 1.33 Å History The term pyrazole was given to this class of compounds by German Chemist Ludwig Knorr in 1883. In a classical method developed by German chemist Hans von Pechmann in 1898, pyrazole was synthesized from acetylene and diazomethane. Preparation Pyrazoles are syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromobenzene Derivatives
Bromobenzene is an aryl bromide and the simplest of the bromobenzenes, consisting of a benzene ring substituted with one bromine atom. Its chemical formula is . It is a colourless liquid although older samples can appear yellow. It is a reagent in organic synthesis. Synthesis and reactions Bromobenzene is prepared by the action of bromine on benzene in the presence of Lewis acid catalysts such as aluminium chloride or ferric bromide. Bromobenzene is used to introduce a phenyl group into other compounds. One method involves its conversion to the Grignard reagent, phenylmagnesium bromide. This reagent can be used, e.g. in the reaction with carbon dioxide to prepare benzoic acid. Other methods involve palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions, such as the Suzuki reaction. Bromobenzene is used as a precursor in the manufacture of phencyclidine Phencyclidine or phenylcyclohexyl piperidine (PCP), also known in its use as a street drug as angel dust among other names, is a dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |