|
Ellobius Lutescens
The Transcaucasian mole vole (''Bramus lutescens'') is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Iran, and Turkey. Reproduction Transcaucasian mole vole, they reproduce during the months of April to October, breeding in march-April and October-November, in which the females would gestate their young for 26 days( almost a month). After birth the pups of the Transcaucasian mole vole, they would stay with their mother for about two months. During the pups 1-4 week of their life it would be just feeding with their mother, and developing their motor functions and being able to be weaned off milk and be able to eat solid food. The final and fifth week the pups would be able to be weaned off the milk and eat vegetables by themselves and be able to walk by themselves without difficulty. Chromosomes The karyotype has a low, odd, diploid number, 2n = 17,X. Transcaucasian mole voles have no ''SRY'' gene or Y chromosome; both sexes have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oldfield Thomas
Michael Rogers Oldfield Thomas (21 February 1858 – 16 June 1929) was a British zoologist. Career Thomas worked at the Natural History Museum, London, Natural History Museum on mammals, describing about 2,000 new species and subspecies for the first time. He was appointed to the museum secretary's office in 1876, transferring to the zoological department in 1878. In 1891, Thomas married Mary Kane, daughter of Sir Andrew Clark, 1st Baronet, Sir Andrew Clark, heiress to a small fortune, which gave him the finances to hire mammal collectors and present their specimens to the museum. He also did field work himself in Western Europe and South America. His wife shared his interest in natural history, and accompanied him on collecting trips. In 1896, when William Henry Flower took control of the department, he hired Richard Lydekker to rearrange the exhibitions, allowing Thomas to concentrate on these new specimens. Thomas viewed his taxonomy efforts from the scope of British impe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
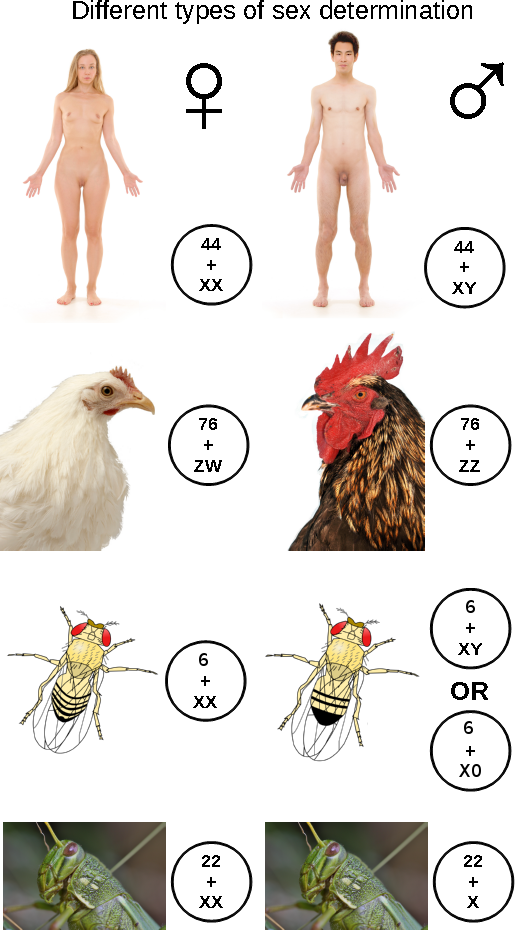
Sex-determination System
A sex-determination system is a biological system that determines the development of sexual characteristics in an organism. Most organisms that create their offspring using sexual reproduction have two common sexes, males and females, and in other species, there are hermaphrodites, organisms that can function reproductively as either female or male, or both. There are also some species in which only one sex is present, temporarily or permanently. This can be due to parthenogenesis, the act of a female reproducing without fertilization. In some plants or algae the gametophyte stage may reproduce itself, thus producing more individuals of the same sex as the parent. In some species, sex determination is genetic: males and females have different alleles or even different genes that specify their sexual morphology. In animals this is often accompanied by chromosomal differences, generally through combinations of XY, ZW, XO, ZO chromosomes, or haplodiploidy. The sexual di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Oldfield Thomas
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based (" Linnaean") nomenclature (much less so under phylogenetic nomenclature). If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were presumably set forth in prehistoric times by hunter-gatherers, as suggested by the fairly sophisticated folk taxonomies. Much later, Aristotle, and later still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Described In 1897
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including cats, dogs, and seals). Mammals are the only living members of Synapsida; this clade, together with Sauropsida (reptiles and birds), constit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and West Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, Georgia (country), Georgia, and Azerbaijan, which are sometimes collectively known as the Caucasian States. The total area of these countries measures about . The South Caucasus and the North Caucasus together comprise the larger Caucasus geographical region that divides Eurasia. The South Caucasus is a dynamic and complex region where the three countries have pursued distinct geopolitical pathways. Geography The South Caucasus spans the southern portion of the Caucasus Mountains and their lowlands, straddling the border between the continents of Europe and Asia, and extending southwards from the southern part of the Main Caucasian Range of southwestern Russia to the Turkey, Turkish and Armenian borders, and from the Black Sea in the west ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna Of Iran
The wildlife of Iran include the fauna and flora of Iran. One of the most famous animals of Iran is the critically endangered Asiatic cheetah (''Acinonyx jubatus venaticus''), which today survives only in Iran. Another notable species is the Iranian ground jay (''Podoces pleskei''), the only bird endemic to Iran. History The animals of Iran were described by Hamdallah Mustawfi in the 14th century. In the 18th and 19th centuries, Samuel Gottlieb Gmelin and Édouard Ménétries explored the Caspian Sea area and the Talysh Mountains to document Caspian fauna. Several naturalists followed in the 19th century, including Filippo de Filippi, William Thomas Blanford, and Nikolai Zarudny who documented mammal, bird, reptile, amphibian and fish species. The Complete Fauna of Iran by Eskandar Firouz, documents a wide range of species across the country’s ecosystems Flora More than one-tenth of the country is forested. The most extensive forest is found on the mountain slopes risin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Of Azerbaijan
This list shows the IUCN Red List status of mammal species occurring in Azerbaijan. One species is endangered, five are vulnerable, and 11 are near threatened. The following tags are used to highlight each species' global conservation status as assessed on the respective IUCN Red List published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature: Order: Artiodactyla * Family: Bovidae ** Genus: ''Bison'' ***European bison, ''B. bonasus'' reintroduced ****Caucasian wisent, ''B. b. caucasicus'' ** Genus: '' Capra'' ***Wild goat, ''C. aegagrus'' *** East Caucasian tur, ''C. cylindricornis'' ** Genus: ''Gazella'' *** Goitered gazelle, ''G. subgutturosa'' ** Genus: ''Ovis'' ***Mouflon, ''O. gmelini'' **** Armenian mouflon, ''O. g. gmelini'' ** Genus: '' Rupicapra'' ***Chamois, ''R. rupicapra'' * Family: Cervidae ** Genus: '' Capreolus'' *** Roe deer, ''C. capreolus'' ** Genus: ''Cervus'' ***Red deer, ''C. elaphus'' ***Sika deer, ''C. nippon'' introduced * Family: Suidae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Of West Asia
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including cats, dogs, and seals). Mammals are the only living members of Synapsida; this clade, together with Sauropsida (reptiles and birds), constitutes the larger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodents Of Asia
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/ricochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Once included with rodents, rabbits, hares, and pikas, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokudaia Tokunoshimensis
The Tokunoshima spiny rat (''Tokudaia tokunoshimensis'') is a rodent found only on the island of Tokunoshima in the Satsunan Islands of Japan. Due to its small habitat, it is considered endangered. It is commonly found in the secondary and primary subtropical moist broadleaf forests of this island. The karyotype has an odd diploid number, 2n = 45. Like its relative '' T. osimensis'', it is one of the few mammals that lack a Y chromosome and ''SRY'' gene. The species is threatened by deforestation Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ... and predation by feral cats and dogs. See also * '' Ellobius lutescens'' * '' Ellobius tancrei'' References Tokudaia Endemic mammals of Japan Endemic fauna of the Ryukyu Islands Mammals described in 2006 {{Murinae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokudaia Osimensis
The Ryukyu spiny rat (''Tokudaia osimensis'') is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. Endemic to Amami Ōshima island in the Amami Islands of the Ryukyu archipelago of Japan, its natural habitat is subtropical moist broadleaf forest. The karyotype has an odd diploid number, 2n = 25. Like its relative '' T. tokunoshimensis'', it has lost its Y chromosome and ''SRY'' gene. The species is threatened by habitat destruction and fragmentation, predation by feral cats and dogs and introduced mongooses, and competition with introduced black rat The black rat (''Rattus rattus''), also known as the roof rat, ship rat, or house rat, is a common long-tailed rodent of the stereotypical rat genus ''Rattus'', in the subfamily Murinae. It likely originated in the Indian subcontinent, but is n ...s. See also * '' Ellobius lutescens'' * '' Ellobius tancrei'' References Y-chromosome - Will it or will it not, hold on? Rats of Asia Endemic mammals of Japan Endemic fauna of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaisan Mole Vole
The Zaisan mole vole (''Ellobius tancrei''), or eastern mole vole, is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in central Asia. Description The Zaisan mole vole is highly adapted to life underground. It grows to a head and body length of with a short tail long and weighs between . The coat is dense, soft and velvety. The face and the crown of the head are dark brown and the external ears are reduced to a fleshy ridge. The incisors are pure white, straight and long and project forward in front of the snout. The dorsal surface of the body varies in colour from sandy brown to dark greyish brown and the underparts vary from white to greyish brown. The tail is sandy brown and is tipped with a tuft of greyish-white hair. The hands and feet are broad, have small claws and are covered with white hairs. Chromosomes The karyotype is variable, with 2n = 32-54. The Y chromosome has been lost, similar to the case of '' E. lutescens''; however, unlike in ''E. lutescens'', b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |