|
Elisachar
Helisachar (died between 837 and 840) was a churchman and statesman in the Carolingian Empire. He served as the chancellor of Aquitaine from 808 to 814 and archchancellor of the empire from 814 until 819. He remained an influential figure at court into the 830s and was entrusted with military responsibilities in 824 and 827. He was rewarded with multiple abbacies and composed an antiphonary. Life Helisachar was a Goth originally from Septimania. He may have begun his career as a notary. He is first recorded as the chancellor of King Louis the Pious of Aquitaine in April 808. When Louis succeeded his father as emperor in 814, Helisachar accompanied him to Aachen and became archchancellor of the empire, an office in which he continued until at least August 819. According to Amalarius, he was "first among the first" in Louis's palace. According to Ermold the Black, Louis granted Helisachar the abbey of Saint-Aubin in the summer of 818. Although he was a canon at the time, he was not a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis The Pious
Louis the Pious (; ; ; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and Holy Roman Emperor, co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aquitaine from 781. As the only surviving son of Charlemagne and Hildegard (queen), Hildegard, he became the sole ruler of the Franks after his father's death in 814, a position that he held until his death except from November 833 to March 834, when he was deposed. During his reign in Aquitaine, Louis was charged with the defence of the empire's southwestern frontier. He Siege of Barcelona (801), conquered Barcelona from the Emirate of Córdoba in 801 and asserted Frankish authority over Pamplona and the Basques south of the Pyrenees in 812. As emperor, he included his adult sons, Lothair I, Lothair, Pepin I of Aquitaine, Pepin and Louis the German, Louis, in the government and sought to establish a suitable division of the realm among them. The first decade of his reig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Franks, Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as List of Frankish kings, kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lombards in Italy from 774. In 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne as Roman emperor in return for political protection, disregarding the universalist claims of the weakened Byzantine Empire. The Carolingian Empire is sometimes considered the first phase in the history of the Holy Roman Empire. After a Carolingian civil war, civil war from 840 to 843 following the death of Emperor Louis the Pious, the empire was divided into autonomous kingdoms, with one king still recognised as emperor, but with little authority outside his own kingdom. The unity of the empire and the hereditary right of the Carolingians continued to be acknowledged. In 884, Charles the Fat reunited all the Carolingian kingdoms f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hariulf Of Oudenburg
Hariulf ( – 1143) was a Benedictine monk, hagiographer and historian. He was born in Ponthieu and given by his parents to the abbey of Saint-Riquier as a child oblate. In 1105, he was elected abbot of Saint Peter's in Oudenburg,where he served until his death.Theodore Evergates, "Historiography and Sociology in Early Feudal Society: The Case of Hariulf and the ''milites'' of Saint-Riquier", ''Viator'' 6 (1975): 35–49. During his time at Saint-Riquier, Hariulf wrote a chronicle of the abbey at the request of his fellow monks. The original ''Chronicon Centulense'' (also called ''Gesta ecclesiae Centulensis'') cover the years 625–1088. He later extended it down to the end of the abbacy of in 1096. He used a wide variety of written and oral sources. His work preserves information lost with the destruction of Saint-Riquier's archives in 1131.Brigitte Meijns"Hariulf" in G. Dunphy (ed.), '' Encyclopedia of the Medieval Chronicle Online'' (Brill, 2016). An English translation was pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maine (province)
Maine () is one of the traditional provinces of France. It corresponds to the former County of Maine, whose capital was also the city of Le Mans. The area, now divided into the departments of Sarthe and Mayenne, has about 857,000 inhabitants. History Antiquity The Gallic tribe Aulerci Cenomani lived in the region during the Iron Age and Roman period. The province of Maine was named after them, in the 6th century AD as ''in Cinomanico'' (''in'' ''pago Celmanico'' in 765, ''*Cemaine'', then ''Le Maine'' from the 12th century). Early Middle Ages In the 8th and 9th centuries, there existed a Duchy of Cénomannie (ducatus Cenomannicus), which several of the Carolingian kings used as an appanage. This duchy was a march that may have included several counties including Maine, and extended into Lower Normandy, all the way to the Seine. In 748, Pepin the Short, then Mayor of the Palace and thus the most powerful man in Francia after the king, gave this duchy to his half-brother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missus Dominicus
A ''missus dominicus'' (plural ''missi dominici''), Latin for "envoy of the lord uler, also known in Dutch as Zendgraaf ( German: ''Sendgraf''), meaning "sent Graf", was an official commissioned by the Frankish king or Holy Roman Emperor to supervise the administration, mainly of justice, in parts of his dominions too remote for frequent personal visits. As such, the ''missus'' performed important intermediary functions between royal and local administrations. There are superficial points of comparison with the original Roman ''corrector'', except that the ''missus'' was sent out on a regular basis. Four points made the ''missi'' effective as instruments of the centralized monarchy: the personal character of the ''missus'', yearly change, isolation from local interests and the free choice of the king. Reign of Charlemagne Based on Merovingian ''ad hoc'' arrangements, using the form ''missus regis'' (the "king's envoy") and sending a layman and an ecclesiastic in pairs, the use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lothair I
Lothair I (9th. C. Frankish: ''Ludher'' and Medieval Latin: ''Lodharius''; Dutch and Medieval Latin: ''Lotharius''; German: ''Lothar''; French: ''Lothaire''; Italian: ''Lotario''; 795 – 29 September 855) was a 9th-century emperor of the Carolingian empire (817–855, with his father until 840) and king of Italy (818–855) and Middle Francia (843–855). Lothair I was the eldest son of the Carolingian emperor Louis I and his wife Ermengarde of Hesbaye, daughter of Ingerman the duke of Hesbaye. On several occasions, Lothair led his full-brothers Pepin I of Aquitaine and Louis the German in revolt against their father to protest against attempts to make their half-brother Charles the Bald a co-heir to the Frankish domains. Upon the father's death, Charles and Louis joined forces against Lothair in a three-year dynastic war (840–843). The struggles between the brothers led directly to the breakup of the Frankish Empire assembled by their grandfather Charlemagne, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breton March
The Marches of Neustria (; ; Norman: ''Maurches de Neûtrie'') were two marches created in 861 by the Carolingian king of West Francia Charles the Bald. They were ruled by officials appointed by the Monarchy of France (or the Crown), known as wardens, prefects or margraves (). One march (the Breton March) was created as a buffer against the Bretons and the other (the Norman March) against the Norsemen. Ultimately, for the Breton March alone, some 29 strongholds across several 'provinces' were constructed or fortified and designated to serve as fortresses of the march. In 911, Robert I of France, the incumbent margrave of Breton March, was affirmed/appointed margrave of both marches by king Charles the Simple, and took the title ''demarchus''. His family, the later Capetians, ruled the whole of Neustria until 987, when Hugh Capet was elected King of the Franks. The subsidiary counts of Neustria had exceeded the margrave in power by that time and the peak of Viking and Breton ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nithard
Nithard (c. 795–844), a Frankish historian, was the son of Charlemagne's daughter Bertha. His father was Angilbert. Life Nithard was born sometime around the year Charlemagne was crowned '' Imperator Augustus'' in December 800. He was probably raised either at the imperial palace, where his mother continued to live until the death of the emperor, or at the monastery of St. Riquier, where his father was lay abbot. He would have been educated most likely at the imperial ''schola'', which offered the kind of high-quality instruction in both military and literary training he is known to have received. Nithard himself later became lay abbot of St Riquier '' in commendam''. He served his cousin Charles the Bald in both war and peace, fighting at his side during the Carolingian civil war and at the battle of Fontenoy in June 841. It is probable that he died as the result of wounds received whilst fighting for him against the Northmen near Angoulême. The date of his death is disp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thegan Of Trier
Thegan of Trier (or Degan of Treves) (before 800 – ca. 850) was a Frankish Roman Catholic prelate and the author of ''Gesta Hludowici imperatoris'' which is a principal source for the life of the Holy Roman Emperor Louis the Pious, the son and successor of Charlemagne. Biography Very little is known of Thegan's life; he appears to have come from a noble Frankish family in the middle Rhine-Moselle region. He may have been educated at Lorsch. All that is certain is that by 825 he was auxiliary bishop of Trier and probably '' praepositus'' of the monastery of St. Cassius in Bonn. He was also a warm friend of Walafrid Strabo, who was the earliest editor of Thegan's ''Gesta'' and divided it into chapters, just as he did with Einhard's '' Vita Karoli''. Walafrid also gave it the name by which it is known: ''Gesta et Laudes'' ("Deeds and Praise"), which he mentions in his prologue. Some poetry and a single letter from Thegan survive. This letter is written to one Hatto who was a count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notre-Dame-sur-Orbieu
The Abbey of St. Mary of Lagrasse (French: ''Abbaye Sainte-Marie de Lagrasse'' or ''Abbaye Sainte-Marie-d'Orbieu'') is a Romanesque abbey in Lagrasse, southern France, whose origins date to the 7th century. It is located in Languedoc, near the Corbières Massif, about 35 km from Carcassonne. It was originally a Benedictine monastery, but since 2004 has been home to a community of canons regular. History The monastic community was founded in the 7th century by the abbot of Narbonne, Nimphridius, who adopted the Rule of Saint Benedict. It was elevated to the rank of abbey in 779 and enriched quickly thanks to donations from lords from the neighbourhood and the county of Barcelona, acquiring lands, castles, priories and other assets. During the 12th century it ruled over a large territory encompassing the dioceses of Toulouse and Béziers and the county of Urgell. During the 13th to 15th centuries, it was reinforced and fortified due to the numerous wars, and there was a declin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oliba I Of Carcassonne
Oliba I of Carcassonne (died 837) was a count of Carcassonne in the 9th century. He was the son of Bello of Carcassonne, and brother (or cousin) of Sunifred I of Barcelona. He succeeded to the county of Carcassonne (as well as to the county of Razès) after his brother Guisclafred had died without heirs. Oliba married to Elmetruda and Richelda, with whom he had three sons: Oliba II, Sunifred (who was abbot of Lagrasse) and Acfred. After his death the county of Carcassonne was ruled by Bernard of Septimania Bernard (or Bernat) of Septimania (795–844), son of William of Gellone and cousin of Charlemagne, was the Duke of Septimania and Count of Barcelona from 826 to 832 and again from 835 until his execution, and also Count of Carcassonne from 837. H .... {{DEFAULTSORT:Oliba 01 Of Carcassonne 9th-century births 9th-century deaths Counts of Carcassonne Nobility of the Carolingian Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
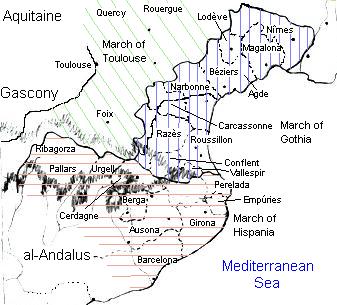
Marca Hispanica
The Spanish March or Hispanic March was a march or military buffer zone established c. 795 by Charlemagne in the eastern Pyrenees and nearby areas, to protect the new territories of the Christian Carolingian Empire—the Duchy of Gascony, the Duchy of Aquitaine, and Septimania—from the Muslim Umayyad Emirate of Córdoba in al-Andalus. In its broader meaning, the ''Spanish March'' sometimes refers to a group of early Iberian and trans-Pyrenean lordships or counts coming under Frankish rule. As time passed, these lordships merged or gained independence from Frankish imperial rule. Geographical context The area of the Spanish March broadly corresponds to the eastern regions between the Pyrenees and the Ebro. The local population of the march was diverse. It included Basques in its northwestern valleys, the Jews of Occitania, and a large Occitano-Romance-speaking population governed by the Visigothic Code, all of them under the influence of al-Andalus since their lords had v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |