|
Elementary Entities
In chemistry and physics, a molecular entity, or chemical entity, is "any constitutionally or isotopically distinct atom, molecule, ion, ion pair, radical, radical ion, complex, conformer, etc., identifiable as a separately distinguishable entity". A molecular entity is any singular entity, irrespective of its nature, used to concisely express any type of chemical particle that can exemplify some process: for example, atoms, molecules, ions, etc. can all undergo a chemical reaction. Chemical species is the macroscopic equivalent of molecular entity and refers to sets or ensembles of molecular entities. According to IUPAC, "The degree of precision necessary to describe a molecular entity depends on the context. For example 'hydrogen molecule' is an adequate definition of a certain molecular entity for some purposes, whereas for others it is necessary to distinguish the electronic state and/or vibrational state and/or nuclear spin, etc. of the hydrogen molecule." See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during chemical reaction, reactions with other chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
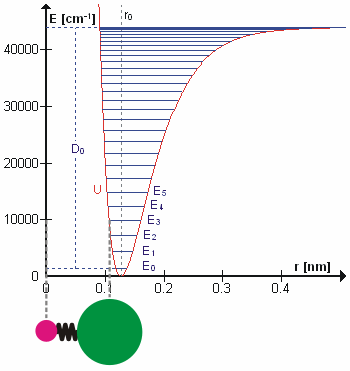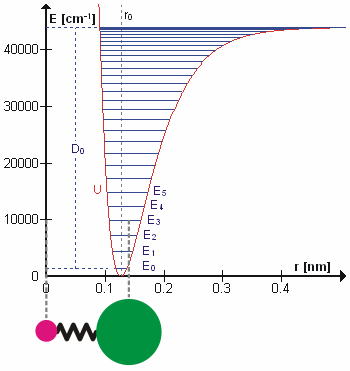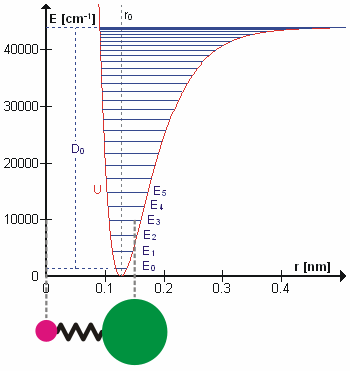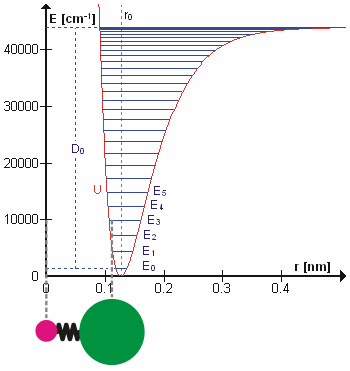
Energy Level
A quantum mechanics, quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound state, bound—that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy, called energy levels. This contrasts with classical mechanics, classical particles, which can have any amount of energy. The term is commonly used for the energy levels of the electrons in atoms, ions, or molecules, which are bound by the electric field of the atomic nucleus, nucleus, but can also refer to energy levels of nuclei or molecular vibration, vibrational or rotational energy levels in molecules. The energy spectrum of a system with such discrete energy levels is said to be Quantization (physics), quantized. In chemistry and atomic physics, an electron shell, or principal energy level, may be thought of as the orbit of one or more electrons around an atom's atomic nucleus, nucleus. The closest shell to the nucleus is called the "1 shell" (also called "K shell"), followed by the "2 shell" (or "L shell"), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ChEBI
Chemical Entities of Biological Interest, also known as ChEBI, is a chemical database and ontology of molecular entities focused on "small" chemical compounds, that is part of the Open Biomedical Ontologies (OBO) effort at the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI). The term "molecular entity" refers to any "constitutionally or isotopically distinct atom, molecule, ion, ion pair, radical, radical ion, complex, conformer, etc., identifiable as a separately distinguishable entity". The molecular entities in question are either products of nature or synthetic products which have potential bioactivity. Molecules directly encoded by the genome, such as nucleic acids, proteins and peptides derived from proteins by proteolytic cleavage, are not as a rule included in ChEBI. ChEBI uses nomenclature, symbolism and terminology endorsed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and nomenclature committee of the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Chemical Entity
A new chemical entity (NCE) is, according to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, a novel, small, chemical molecule drug that is undergoing clinical trials or has received a first approval (not a new use) by the FDA in any other application submitted under section 505(b) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. A new molecular entity (NME) is a broader term that encompasses both an NCE or an NBE (New Biological Entity). Definition An active moiety is a molecule or ion, excluding those appended portions of the molecule that cause the drug to be an ester, salt (including a salt with hydrogen or coordination bonds), or other noncovalent derivative (such as a complex, chelate, or clathrate) of the molecule, responsible for the physiological or pharmacological action of the drug substance. An NCE is a molecule developed by the innovator company in the early drug discovery stage, which after undergoing clinical trials could translate into a drug that could be a treatment fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avogadro Constant
The Avogadro constant, commonly denoted or , is an SI defining constant with an exact value of when expressed in reciprocal moles. It defines the ratio of the number of constituent particles to the amount of substance in a sample, where the particles in question are any designated elementary entity, such as molecules, atoms, ions, ion pairs. The numerical value of this constant is known as the Avogadro number, commonly denoted . The Avogadro ''number'' is an exact number equal to the number of constituent particles in one mole of any substance (by definition of the mole), historically derived from the experimental determination of the number of atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12 (12C) before the 2019 revision of the SI. Both the constant and the number are named after the Italian physicist and chemist Amedeo Avogadro. The Avogadro constant is used as a proportionality factor in relating the ''amount of substance'' , in a sample of a substance , to the corresponding n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mole (unit)
The mole (symbol mol) is a unit of measurement, the base unit in the International System of Units (SI) for ''amount of substance'', an SI base quantity proportional to the number of elementary entities of a substance. One mole is an aggregate of exactly elementary entities (approximately 602 sextillion or 602 billion times a trillion), which can be atoms, molecules, ions, ion pairs, or other particles. The number of particles in a mole is the Avogadro number (symbol ) and the numerical value of the '' Avogadro constant'' (symbol ) expressed in mol−1. The relationship between the mole, Avogadro number, and Avogadro constant can be expressed in the following equation:1\text = \frac = \frac The current SI value of the mole is based on the historical definition of the mole as the amount of substance that corresponds to the number of atoms in 12 grams of 12C, which made the molar mass of a compound in grams per mole, numerically equal to the average molecular mass or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amount Of Substance
In chemistry, the amount of substance (symbol ) in a given sample of matter is defined as a ratio () between the particle number, number of elementary entities () and the Avogadro constant (). The unit of amount of substance in the International System of Units is the Mole (unit), mole (symbol: mol), a SI base unit, base unit. p. 134 Since 2019, the mole has been defined such that the value of the Avogadro constant is exactly , defining a macroscopic unit convenient for use in laboratory-scale chemistry. The elementary entities are usually molecules, atoms, ions, or Ion pair, ion pairs of a specified kind. The particular chemical substance, substance sampled may be specified using a subscript or in parentheses, e.g., the amount of sodium chloride (NaCl) could be denoted as or . Sometimes, the amount of substance is referred to as the chemical amount or, informally, as the "number of moles" in a given sample of matter. The amount of substance in a sample can be calculated from mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin (physics)
Spin is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic form of angular momentum carried by elementary particles, and thus by List of particles#Composite particles, composite particles such as hadrons, atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei, and atoms. Spin is quantized, and accurate models for the interaction with spin require relativistic quantum mechanics or quantum field theory. The existence of electron spin angular momentum is inferred from experiments, such as the Stern–Gerlach experiment, in which silver atoms were observed to possess two possible discrete angular momenta despite having no orbital angular momentum. The relativistic spin–statistics theorem connects electron spin quantization to the Pauli exclusion principle: observations of exclusion imply half-integer spin, and observations of half-integer spin imply exclusion. Spin is described mathematically as a vector for some particles such as photons, and as a spinor or bispinor for other particles such as electrons. Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Vibration
A molecular vibration is a Periodic function, periodic motion of the atoms of a molecule relative to each other, such that the center of mass of the molecule remains unchanged. The infrared spectroscopy correlation table, typical vibrational frequencies range from less than 1013 hertz, Hz to approximately 1014 Hz, corresponding to wavenumbers of approximately 300 to 3000 cm−1 and wavelengths of approximately 30 to 3 μm. Vibrations of polyatomic molecules are described in terms of normal modes, which are independent of each other, but each normal mode involves simultaneous vibrations of parts of the molecule. In general, a non-linear molecule with ''N'' atoms has vibrational mode, normal modes of vibration, but a ''linear'' molecule has modes, because rotation about the molecular axis cannot be observed. A diatomic molecule has one normal mode of vibration, since it can only stretch or compress the single bond. A molecular vibration is excited when the mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Pure And Applied Chemistry
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. IUPAC's executive director heads this administrative office, currently Greta Heydenrych. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national chemistry societies, national academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organizations. IUPAC's Inter-divisional Committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Species
Chemical species are a specific form of chemical substance or chemically identical molecular entities that have the same molecular energy level at a specified timescale. These entities are classified through bonding types and relative abundance of isotopes. Types of chemical species can be classified based on the type of molecular entity and can be either an atomic, molecular, ionic or radical species. Classification Generally, a chemical species is defined as a chemical identity that has the same set of molecular energy levels in a defined timescale (i.e. an experiment). These energy levels determine the way the chemical species will interact with others through properties such as bonding or isotopic compositions. The chemical species can be an atom, molecule, ion, or radical, with a specific chemical name and chemical formula. In supramolecular chemistry, chemical species are structures created by forming or breaking bonds between molecules, such as hydrogen bonding, dipole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |