|
Electroosmotic Pump
An electroosmotic pump is used for generating flow or pressure by use of an electric field. One application of this is removing liquid flooding water from channels and gas diffusion layers and direct hydration of the proton exchange membrane in the membrane electrode assembly (MEA) of the proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Additionally, electroosmotic pumps have gained significant attention due to their potential applications in microfluidic channels, lab-on-a-chip devices, and biomedical engineering. Principle Electroosmotic pumps are fabricated from silica nanospheres or hydrophilic porous glass, the pumping mechanism is generated by an external electric field applied on an electric double layer (EDL), generates high pressures (e.g., more than 340 atm (34 MPa) at 12 kV applied potentials) and high flow rates (e.g., 40 ml/min at 100 V in a pumping structure less than 1 cm3 in volume). EO pumps are compact, have no moving parts, and scale favorably with fuel cell desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, , indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. In liquid form, is also called "water" at standard temperature and pressure. Because Earth's environment is relatively close to water's triple point, water exists on Earth as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, Voltage#Galvani potential vs. electrochemical potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units, International System of Units (SI). Definition One volt is defined as the electric potential between two points of a electrical conductor, conducting wire when an electric current of one ampere dissipates one watt of power (physics), power between those points. It can be expressed in terms of SI base units (metre, m, kilogram, kg, second, s, and ampere, A) as : \text = \frac = \frac = \frac = \text\text^2\text^. Equivalently, it is the potential difference between two points that will impart one joule of energy per coulomb of charge that passes through it. It can be expressed in terms of SI base units (metre, m, kilogram, kg, second, s, and ampere, A) as : \text = \frac = \frac = \frac = \text\text^2\text^. It can also be expressed as amperes times ohms (curre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Technologies
Hydrogen technologies are technologies that relate to the production and use of hydrogen as a part hydrogen economy. Hydrogen technologies are applicable for many uses. Some hydrogen technologies are carbon neutral and could have a role in preventing climate change and a possible future hydrogen economy. Hydrogen is a chemical widely used in various applications including ammonia production, oil refining and energy. The most common methods for producing hydrogen on an industrial scale are: Steam reforming, oil reforming, coal gasification, water electrolysis. Hydrogen is not a primary energy source, because it is not naturally occurring as a fuel. It is, however, widely regarded as an ideal energy storage medium, due to the ease with which electricity can convert water into hydrogen and oxygen through electrolysis and can be converted back to electrical power using a fuel cell or hydrogen turbine. There are a wide number of different types of fuel and electrolysis ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micropump
Micropumps are devices that can control and manipulate small fluid volumes. Although any kind of small pump is often referred to as a micropump, a more accurate definition restricts this term to pumps with functional dimensions in the micrometer range. Such pumps are of special interest in microfluidic research, and have become available for industrial product integration in recent years. Their miniaturized overall size, potential cost and improved dosing accuracy compared to existing miniature pumps fuel the growing interest for this innovative kind of pump. Note that the below text is very incomplete in terms of providing a good overview of the different micropump types and applications, and therefore please refer to good review articles on the topic. Introduction and history First true micropumps were reported in the mid-1970s, but attracted interest only in the 1980s, when Jan Smits and Harald Van Lintel developed Microelectromechanical systems, MEMS micropumps. Most of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
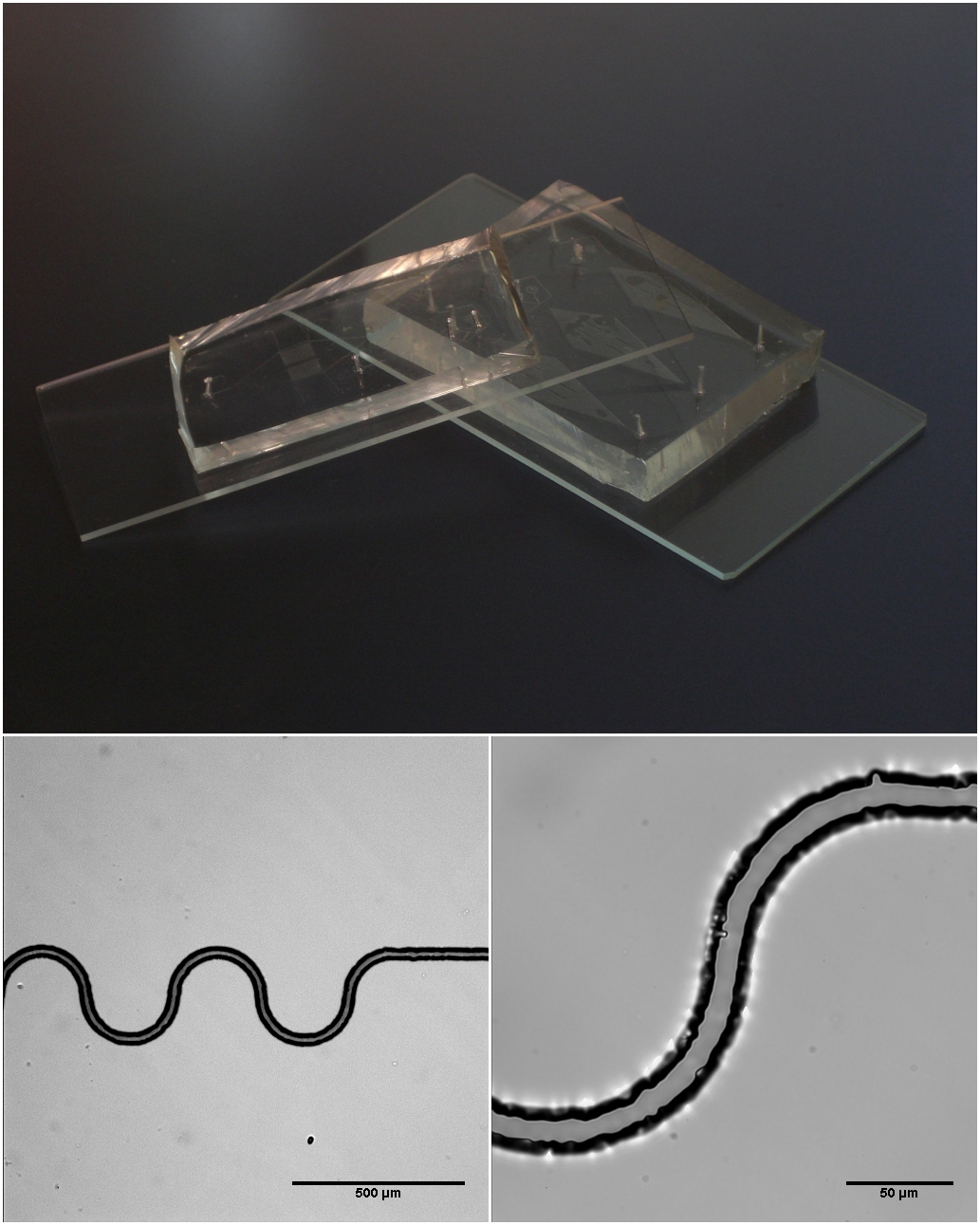
Microfluidics
Microfluidics refers to a system that manipulates a small amount of fluids (10−9 to 10−18 liters) using small channels with sizes of ten to hundreds of micrometres. It is a multidisciplinary field that involves molecular analysis, molecular biology, and microelectronics. It has practical applications in the design of systems that process low volumes of fluids to achieve multiplexing, automation, and high-throughput screening. Microfluidics emerged in the beginning of the 1980s and is used in the development of inkjet printheads, DNA chips, lab-on-a-chip technology, micro-propulsion, and micro-thermal technologies. Typically, micro means one of the following features: * Small volumes (μL, nL, pL, fL) * Small size * Low energy consumption * Microdomain effects Typically microfluidic systems transport, mix, separate, or otherwise process fluids. Various applications rely on passive fluid control using capillary forces, in the form of capillary flow modifying elements, akin to f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Fuel Cell Terms
The Glossary of fuel cell terms lists the definitions of many terms used within the fuel cell industry. The terms in this fuel cell glossary may be used by fuel cell industry associations, in education material and fuel cell codes and standards to name but a few. A ; Activation loss : See overpotential ; Adsorption : Adsorption is a process that occurs when a gas or liquid solute accumulates on the surface of a solid or a liquid (adsorbent), forming a film of molecules or atoms (the adsorbate). ; Alkali : In chemistry, an alkali is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or alkaline earth metal element. ; Alkali anion exchange membrane : An alkali anion exchange membrane (AAEM) is a semipermeable membrane generally made from ionomers and designed to conduct anions while being impermeable to gases such as oxygen or hydrogen. ; Alkaline fuel cell : Alkaline fuel cell (AFC) also known as the Bacon fuel cell. ; Alloy : An alloy is a solid solution or homogeneous mix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroosmotic Flow
In chemistry, electro-osmotic flow (EOF, hyphen optional; synonymous with electro-osmosis or electro-endosmosis) is the motion of liquid induced by an applied potential across a porous material, capillary tube, membrane, microchannel, or any other fluid conduit. Because electro-osmotic velocities are independent of conduit size, as long as the electrical double layer is much smaller than the characteristic length scale of the channel, electro-osmotic flow will have little effect. Electro-osmotic flow is most significant when in small channels, and is an essential component in chemical separation techniques, notably capillary electrophoresis. Electro-osmotic flow can occur in natural unfiltered water, as well as buffered solutions. History Electro-osmotic flow was first reported in 1807 by Ferdinand Friedrich Reuss (18 February 1778 (Tübingen, Germany) – 14 April 1852 (Stuttgart, Germany)) in an unpublished lecture before the Physical-Medical Society of Moscow; Reuss firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capillary Electrophoresis
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) is a family of electrokinetic separation methods performed in submillimeter diameter capillaries and in micro- and nanofluidic channels. Very often, CE refers to capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE), but other electrophoresis, electrophoretic techniques including capillary gel electrophoresis (CGE), capillary isoelectric focusing (CIEF), capillary isotachophoresis and micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC) belong also to this class of methods. In CE methods, analytes migrate through electrolyte solutions under the influence of an electric field. Analytes can be separated according to ionic mobility and/or partitioning into an alternate phase via non-covalent interactions. Additionally, analytes may be concentrated or "focused" by means of gradients in Electrical resistivity and conductivity, conductivity and pH. Instrumentation The instrumentation needed to perform capillary electrophoresis is relatively simple. A basic schematic of a capil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microchannel (microtechnology)
Microchannel in microtechnology is a channel with a hydraulic diameter below 1 mm, usually 1–99 μm. Microchannels are used in fluid control (see Microfluidics), heat transfer (see Micro heat exchanger) and cell migration observation. They are more efficient than their 'macro' counterparts, because of a high surface-area to volume ratio yet pose a multitude of challenges due to their small size. Materials Different types of materials are required for the different uses of microchannels. These are the three main categories. Polymeric and glass substrates Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is used as a solution to a wide range of microfluidic devices due to its low cost and easier fabricating methods. Silicon elastomers can be used for situations in which elasticity and deformation is necessary. Metallic substrates Metallic substrates are often chosen for their advantageous metallic properties, such as withstanding high temperatures and transferring heat faster. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Chemistry
Surface science is the study of physics, physical and chemistry, chemical phenomena that occur at the interface (chemistry), interface of two phase (matter), phases, including solid–liquid interfaces, solid–gas interfaces, solid–vacuum interfaces, and liquid–gas interfaces. It includes the fields of ''surface chemistry'' and ''surface physics''. Some related practical applications are classed as surface engineering. The science encompasses concepts such as heterogeneous catalysis, semiconductor device fabrication, fuel cells, self-assembled monolayers, and adhesives. Surface science is closely related to interface and colloid science. Interfacial chemistry and physics are common subjects for both. The methods are different. In addition, interface and colloid science studies macroscopic phenomena that occur in heterogeneous systems due to peculiarities of interfaces. History The field of surface chemistry started with heterogeneous catalysis pioneered by Paul Sabatier (che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sintered Glass
Fritted glass is finely porous glass through which gas or liquid may pass, made by sintering together glass particles into a solid but porous body. This porous glass body can also be called a frit. Applications in laboratory glassware include use in fritted glass filter items, scrubbers, or spargers. Other laboratory applications of fritted glass include packing in chromatography columns and resin beds for special chemical synthesis. In a fritted glass filter, a disc or pane of fritted glass is used to filter out solid particles, precipitate, or residue from a fluid, similar to a piece of filter paper. The fluid can go through the pores in the fritted glass, but the frit will often stop a solid from going through. A fritted filter is often part of a glassware item, so fritted glass funnels and fritted glass crucibles are available. Laboratory scale spargers (also known as gas diffusing stones or diffusors) as well as scrubber Scrubber systems (e.g. chemical scrubbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |