|
Electrogram
An electrogram (EGM) is a recording of electrical activity of organs such as the brain and heart, measured by monitoring changes in electric potential. Historically, it also referred to an instrument to measure atmospheric electrical potential. Brain Electroencephalography (EEG) An electroencephalogram (EEG) is an electrical recording of the activity of the brain taken from the scalp. An EEG can be used to diagnose seizures, sleep disorders, and for monitoring of level of anesthesia during surgery. Electrocorticography (ECoG or iEEG) An electrocorticogram is an electrical recording of the brain measured intracranially, that is, from within the brain. Eye Electrooculography (EOG) An electrooculogram (EOG) is an electrical recording of the potential between the cornea and the retina, and does not change with visual stimuli. An EOG can measure movements of the eyes and can help in diagnosis of nystagmus. Electroretinography (ERG) An electroretinogram (ERG) is an elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiology
Radiology ( ) is the medical specialty that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide treatment within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiation), but today it includes all imaging modalities. This includes technologies that use no ionizing electromagnetic radiation, such as medical ultrasound, ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), as well as others that do use radiation, such as x-ray computed tomography, computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually invasiveness of surgical procedures, minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above. The modern practice of radiology involves a team of several different healthcare professionals. A radiologist, who is a medical doctor with specialized post-graduate tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Cardiac Pacemaker
A pacemaker, also known as an artificial cardiac pacemaker, is an implanted medical device that generates electrical pulses delivered by electrodes to one or more of the chambers of the heart. Each pulse causes the targeted chamber(s) to contract and pump blood, thus regulating the function of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The primary purpose of a pacemaker is to maintain an even heart rate Heart rate is the frequency of the cardiac cycle, heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute (''beats per minute'', or bpm). The heart rate varies according to the body's Human body, physical needs, including the nee ..., either because the heart's natural cardiac pacemaker provides an inadequate or irregular heartbeat, or because there is a heart block, block in the heart's electrical conduction system. Modern pacemakers are externally programmable and allow a cardiologist to select the optimal pacing modes for individual patients. Most p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Potential
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of Membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cells, which include animal cells like neurons and myocyte, muscle cells, as well as some plant cells. Certain endocrine cells such as pancreatic beta cells, and certain cells of the anterior pituitary gland are also excitable cells. In neurons, action potentials play a central role in cell–cell interaction, cell–cell communication by providing for—or with regard to saltatory conduction, assisting—the propagation of signals along the neuron's axon toward axon terminal, synaptic boutons situated at the ends of an axon; these signals can then connect wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial Infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is retrosternal Angina, chest pain or discomfort that classically radiates to the left shoulder, arm, or jaw. The pain may occasionally feel like heartburn. This is the dangerous type of acute coronary syndrome. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, presyncope, feeling faint, a diaphoresis, cold sweat, Fatigue, feeling tired, and decreased level of consciousness. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms. Women more often present without chest pain and instead have neck pain, arm pain or feel tired. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an Cardiac arrhythmia, irregular heartbeat, cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. Most MIs occur d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrodiagnosis
Electrodiagnosis (EDX) is a method of medical diagnosis that obtains information about diseases by passively recording the electrical activity of body parts (that is, their natural electrophysiology) or by measuring their response to external electrical stimuli (evoked potentials). The most widely used methods of recording spontaneous electrical activity are various forms of electrodiagnostic testing (electrophysiology#Electrographic modalities by body part, electrography) such as electrocardiography (ECG), electroencephalography (EEG), and electromyography (EMG). Electrodiagnostic medicine (also EDX) is a medical subspecialty of neurology, clinical neurophysiology, cardiology, and physical medicine and rehabilitation. Electrodiagnostic physicians apply electrophysiology, electrophysiologic techniques, including needle electromyography and Nerve conduction study, nerve conduction studies to diagnose, evaluate, and treat people with impairments of the neurologic, neuromuscular syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
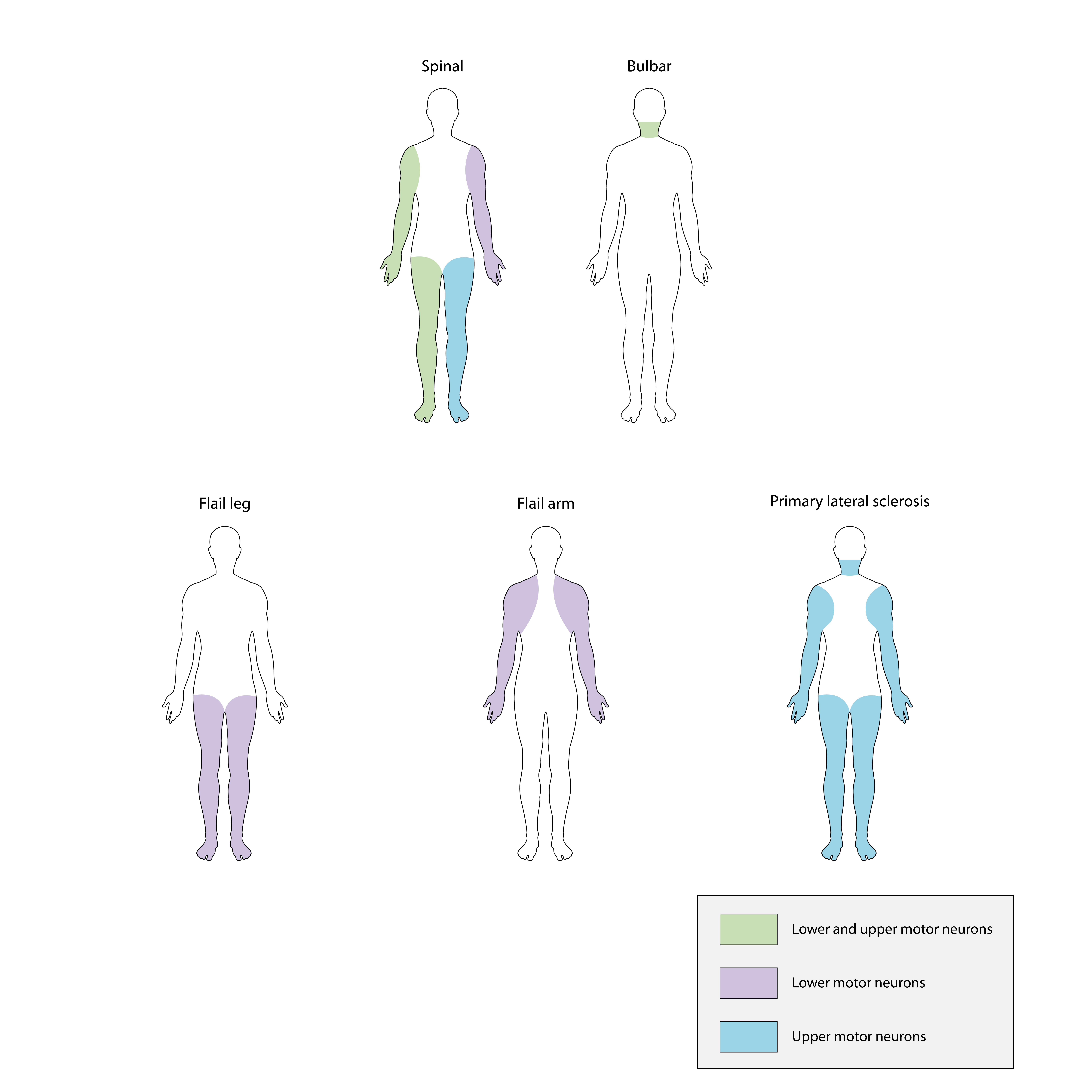
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, Terminal illness, terminal neurodegenerative disease, neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neurons that normally control Skeletal muscle, voluntary muscle contraction. ALS is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle Spasticity, stiffness, Fasciculation, twitches, Muscle weakness, weakness, and Muscle atrophy, wasting. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with cognitive disorder, thinking and behavior. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as ''limb-onset'' (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropathies affecting motor, sensory, or autonomic nerve fibers result in different symptoms. More than one type of fiber may be affected simultaneously. Peripheral neuropathy may be acute (with sudden onset, rapid progress) or chronic (symptoms begin subtly and progress slowly), and may be reversible or permanent. Common causes include systemic diseases (such as diabetes or leprosy), hyperglycemia-induced glycation, vitamin deficiency, medication (e.g., chemotherapy, or commonly prescribed antibiotics including metronidazole and the fluoroquinolone class of antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin)), traumatic injury, ischemia, radiation therapy, excessive alcohol consumption, immune system disease, celiac disease, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Conduction Study
A nerve conduction study (NCS) is a medical test, medical diagnostic test commonly used to evaluate the function, especially the ability of action potential, electrical conduction, of the motor nerve, motor and sensory nerves of the human body. These tests may be performed by Specialty (medicine), medical specialists such as clinical neurophysiology, clinical neurophysiologists, physical therapy, physical therapists, physiatry, physiatrists (physical medicine and rehabilitation physicians), and neurology, neurologists who subspecialize in electrodiagnostic medicine. In the United States, neurologists and physiatrists receive training in electrodiagnostic medicine (performing needle electromyography (EMG and NCSs) as part of residency training and, in some cases, acquire additional expertise during a fellowship in clinical neurophysiology, electrodiagnostic medicine, or neuromuscular medicine. Outside the US, clinical neurophysiologists learn needle EMG and NCS testing. Purpose and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscular System
The muscular system is an organ (anatomy), organ system consisting of skeletal muscle, skeletal, smooth muscle, smooth, and cardiac muscle, cardiac muscle. It permits movement of the body, maintains posture, and circulates blood throughout the body. The muscular systems in vertebrates are controlled through the nervous system although some muscles (such as the cardiac muscle) can be completely autonomous. Together with the Human skeleton, skeletal system in the human, it forms the musculoskeletal system, which is responsible for the movement of the human body, body. Types There are three distinct types of muscle: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, cardiac or heart muscle, and smooth muscle, smooth (non-striated) muscle. Muscles provide strength, balance, posture, movement, and heat for the body to keep warm. There are more than 600 muscles in an adult male human body. A kind of elastic tissue makes up each muscle, which consists of thousands, or tens of thousands, of small musc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophysiology Study
A cardiac electrophysiology study (EP test or EP study) is a Invasiveness of surgical procedures, minimally invasive procedure using catheters introduced through a vein or artery to record electrical activity from within the heart. This electrical activity is recorded when the heart is in a normal rhythm (sinus rhythm) to assess the conduction system of the heart and to look for additional electrical connections (accessory pathways), and during any Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythms that can be induced. EP studies are used to investigate the cause, location of origin, and best treatment for various abnormal heart rhythms, and are often followed by a catheter ablation during the same procedure. Preparation It is important for patients not to eat or drink for up to 12 hours before the procedure. This is to prevent vomiting, which can result in aspiration, and also cause severe bleeding from the insertion site of the catheter. Failure to follow this simple preparation may resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/ os clitoris. All mammals have some hair on their skin, even marine mammals like whales, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by fibrillation, rapid and irregular beating of the Atrium (heart), atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods of abnormal cardiac cycle, beating, which become longer or continuous over time. It may also start as other forms of arrhythmia such as atrial flutter that then transform into AF. Episodes can be asymptomatic. Symptomatic episodes may involve heart palpitations, syncope (medicine), fainting, Presyncope, lightheadedness, Unconsciousness, loss of consciousness, or shortness of breath. Atrial fibrillation is associated with an increased risk of heart failure, dementia, and stroke. It is a type of supraventricular tachycardia. Atrial fibrillation frequently results from bursts of tachycardia that originate in muscle bundles extending from the Atrium (heart), atrium to the pulmonary veins. Pulmonary vein isolation by catheter ablation, trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |