|
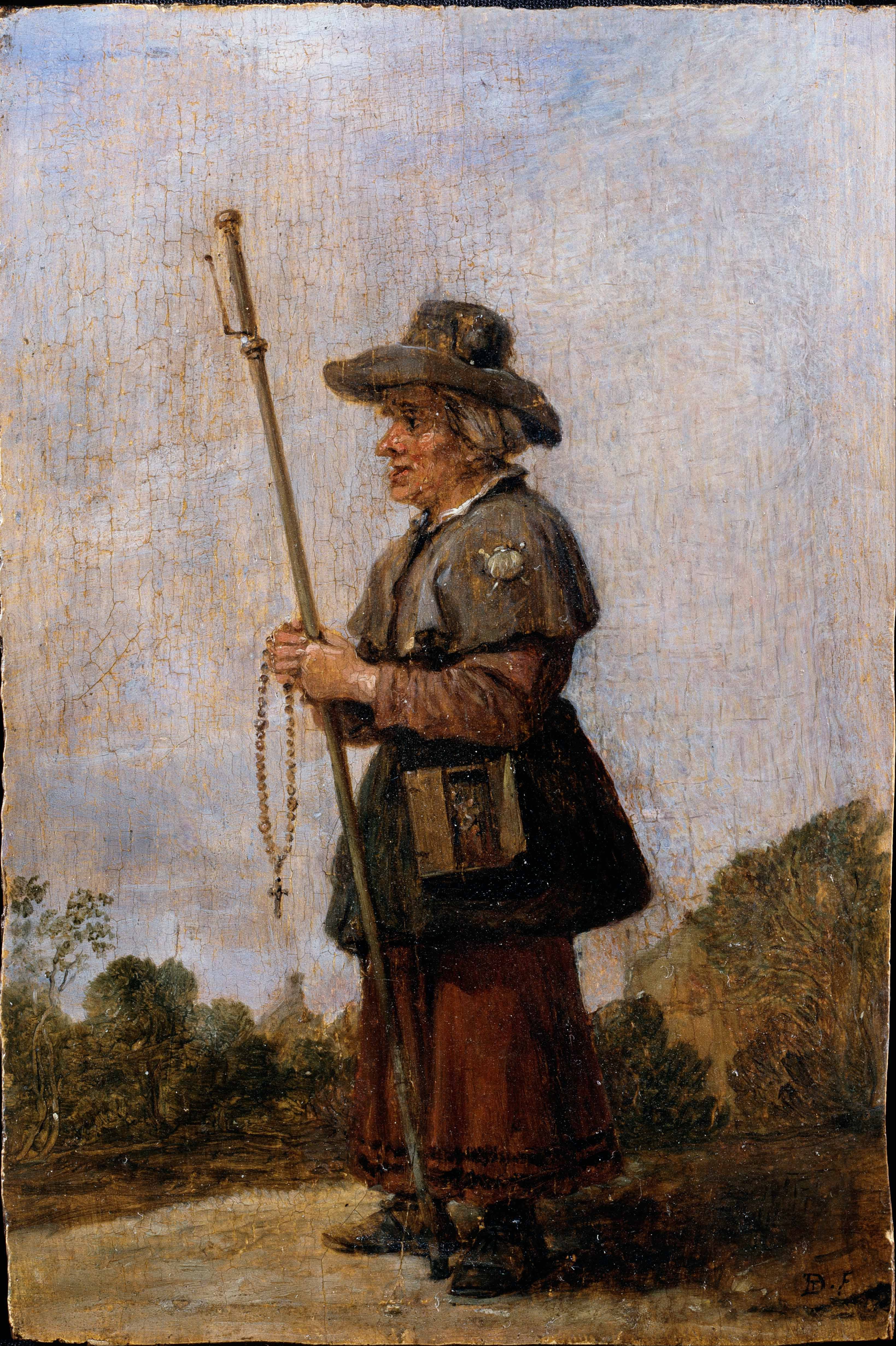
Edigna
Edigna (–1109) is a venerated figure in Puch, and is beatified in the Catholic Church. Her historical existence is debated. Legend According to legend, Edigna was a daughter of Henry I of France and Anne of Kiev, and was born . In 1074, at the age of 19, she fled to Bavaria on a farmer's bullock cart to escape an arranged marriage. The farmer stopped in Puch, Fürstenfeldbruck, where a rooster in the cart crowed and a bell rang. Edigna took this as a sign that she should leave the cart. She remained in Puch until her death on 26 February, 1109, living as a hermit in a hollowed-out linden tree and revered by the people as a miracle worker. She did not reveal her royal background, but it was discovered after her death. When she died, holy oil flowed from the tree, but it dried up when attempts were made to sell it. Edigna has been venerated since her death, and regarded as the patroness saint of Puch. Historical evidence In support In 1347, a document related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry I Of France
Henry I (4 May 1008 – 4 August 1060) was King of the Franks from 1031 to 1060. The royal demesne of France reached its smallest size during his reign, and for this reason he is often seen as emblematic of the weakness of the early Capetians. This is not entirely agreed upon, however, as other historians regard him as a strong but realistic king, who was forced to conduct a policy mindful of the limitations of the French monarchy. Reign A member of the House of Capet, Henry was born in Reims, the son of King Robert II (972–1031) and Constance of Arles (986–1034). In the early-Capetian tradition, he was crowned King of France at the Cathedral of Reims on 14 May 1027, while his father still lived. He had little influence and power until he became sole ruler on his father's death 4 years later. The reign of Henry I, like those of his predecessors, was marked by territorial struggles. Initially, he joined his younger brother Robert, with the support of their mother, in a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Of Kiev
Anne of Kiev or Anna Yaroslavna, Russian: Анна Ярославна (c. 1030 – 1075) was a Rus' princess who became Queen of France in 1051 upon marrying King Henry I. She ruled the kingdom as regent during the minority of their son Philip I from Henry's death in 1060 until her controversial marriage to Count Ralph IV of Valois. Anne founded the Abbey of St. Vincent at Senlis. Childhood Anne was a daughter of Yaroslav the Wise, Grand Prince of Kiev and Prince of Novgorod, and his second wife Ingegerd Olofsdotter of Sweden. Her exact birthdate is unknown; Philippe Delorme has suggested 1027, while Andrew Gregorovich has proposed 1032, citing a mention in a Kievan chronicle of the birth of a daughter to Yaroslav in that year. Anne's exact place in the birth order of her siblings is unknown, although she was almost certainly the youngest daughter. Little is known about Anne's childhood or education. It is assumed that she was literate, at least enough to write her name, bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a journey, often into an unknown or foreign place, where a person goes in search of new or expanded meaning about their self, others, nature, or a higher good, through the experience. It can lead to a personal transformation, after which the pilgrim returns to their daily life. Background Pilgrimages frequently involve a journey or search of moral or spiritual significance. Typically, it is a journey to a shrine or other location of importance to a person's beliefs and faith, although sometimes it can be a metaphorical journey into someone's own beliefs. Many religions attach spiritual importance to particular places: the place of birth or death of founders or saints, or to the place of their "calling" or spiritual awakening, or of their connection (visual or verbal) with the divine, to locations where miracles were performed or witnessed, or locations where a deity is said to live or be "housed", or any site that is seen to have special spiritual power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Louis IV (german: Ludwig; 1 April 1282 – 11 October 1347), called the Bavarian, of the house of Wittelsbach, was King of the Romans from 1314, King of Italy from 1327, and Holy Roman Emperor from 1328. Louis' election as king of Germany in 1314 was controversial, as his Habsburg cousin Frederick the Fair was simultaneously elected king by a separate set of electors. Louis defeated Frederick in the Battle of Mühldorf in 1322, and the two eventually reconciled. Louis was opposed and excommunicated by the French Pope John XXII; Louis in turn attempted to depose the pope and install an anti-pope. Louis IV was Duke of Upper Bavaria from 1294 to 1301 together with his elder brother Rudolf I, was Margrave of Brandenburg until 1323, and Count Palatine of the Rhine until 1329, and became Duke of Lower Bavaria in 1340. He was the last Bavarian to be a king of Germany until 1742. He became Count of Hainaut, Holland, Zeeland, and Friesland in 1345 when his wife Margaret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthew Rader
Matthew Rader (also Matthäus, or Mathaeus) (1561 – 22 December 1634) was a Jesuit philologist and historian. Life Rader was born in Innichen in Tyrol. At the age of twenty he entered the Society of Jesus and subsequently taught the humanities for twenty-one years in different Jesuit institutions. He wrote several school dramas, but was particularly known among Catholics and non-Catholics for his scholarly attainments. He died, aged 73, in Munich. Works In 1599 he published an improved and expurgated edition of Martial, and in 1628 one of Quintus Curtius Rufus. His edition of the Acts of the Eighth Ecumenical Council was incorporated by Philippe L'Abbe and Gabriel Cossart in their collection of the Acts of councils; that of the works of St. John Climacus, published in 1614, was reprinted by Jacques Paul Migne in his ''Patrologia Graeca'' (LXXXVIII, 585 sqq.). More important than the publications just mentioned were his now very rare works: ''Bavaria Sancta'' (Munich, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
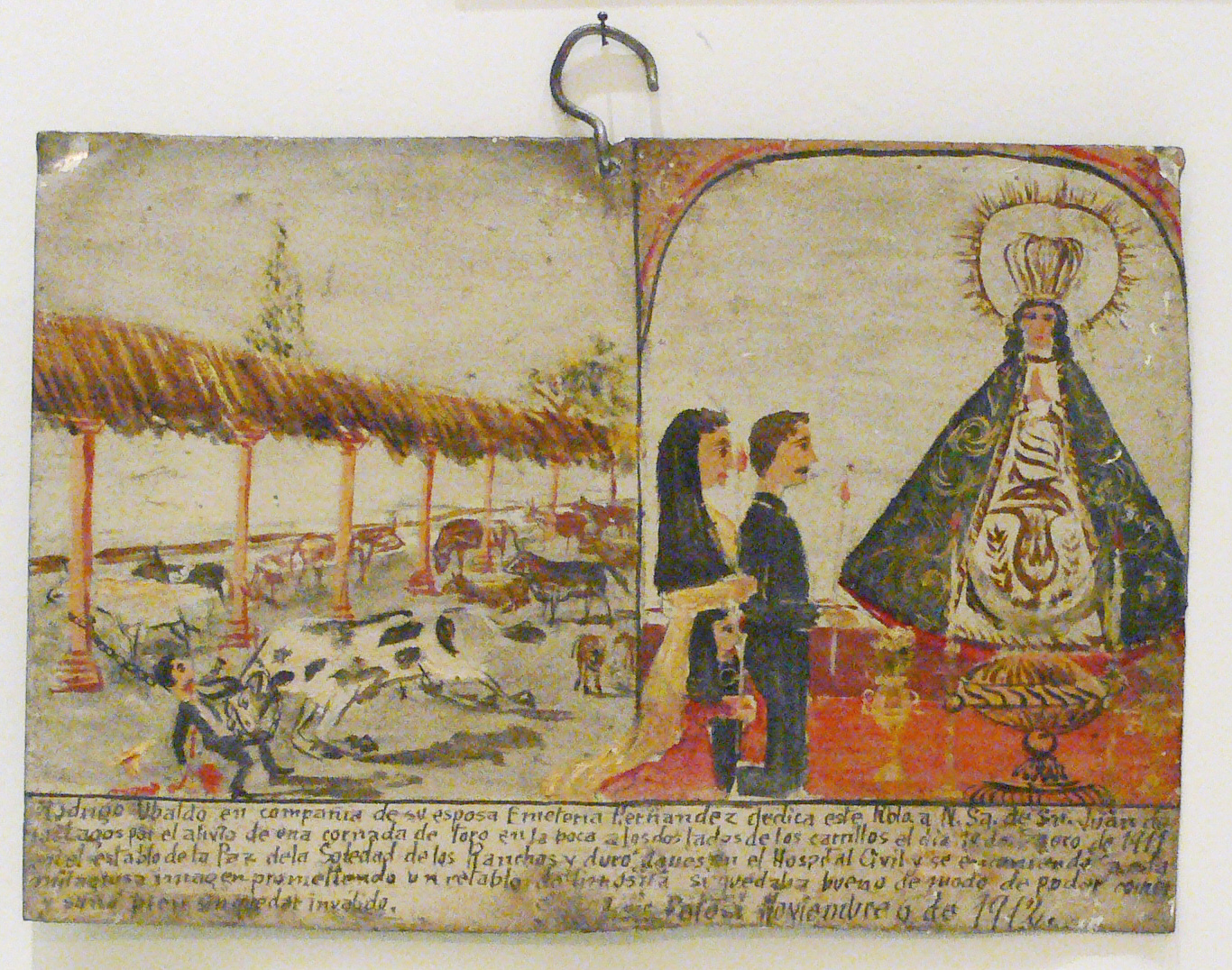
Votive Tablet
An ex-voto is a votive offering to a saint or to a divinity; the term is usually restricted to Christian examples. It is given in fulfillment of a vow (hence the Latin term, short for ''ex voto suscepto'', "from the vow made") or in gratitude or devotion. Definition Ex-votos are placed in a church or chapel where the worshiper seeks grace or wishes to give thanks. The destinations of pilgrimages often include shrines decorated with ex-votos. Ex-votos can take a wide variety of forms. They are not only intended for the helping figure, but also as a testimony to later visitors of the received help. As such they may include texts explaining a miracle attributed to the helper, or symbols such as a painted or modeled reproduction of a miraculously healed body part, or a directly related item such as a crutch given by a person formerly lame. There are places where a very old tradition of depositing ex-votos existed, such as Abydos in ancient Egypt. Ex-voto paintings Especially in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammendorf
Mammendorf is a municipality in Bavaria, Germany. It is located halfway between Munich and Augsburg. Location Mammendorf is part of the district of Fürstenfeldbruck, Upper Bavaria and lies about 6 kilometres northwest of the city of Fürstenfeldbruck. The towns Nannhofen and Peretshofen are part of the municipality of Mammendorf. Geography The Maisach River flows through Mammendorf. Transport Mammendorf-Nannhofen is the last station of the Munich S-Bahn The Munich S-Bahn (german: S-Bahn München) is an electric rail transit system in Munich, Germany. "S-Bahn" is the German abbreviation for ''Stadtschnellbahn'' (literally, "urban rapid rail"), and the Munich S-Bahn exhibits characteristics of bot ... line S3, as well as the terminus of the R1 line of Augsburg's transport system, Augsburger Verkehrsverbund (AVV). Notable people * Gerhard Merz, artist References Fürstenfeldbruck (district) {{Fürstenfeldbruck-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fürstenfeldbruck
Fürstenfeldbruck () is a town in Bavaria, Germany, located 32 kilometres west of Munich. It is the capital of the district of Fürstenfeldbruck. it has a population of 35,494. Since the 1930s, Fürstenfeldbruck has had an air force base. The name of Fürstenfeldbruck is composed of two parts, namely 'Bruck', Bavarian dialect for 'bridge' (meaning the bridge over the Amper river) and after the famous monastery of Fürstenfeld Abbey. Geography Fürstenfeldbruck covers an area of 32.53 km². It is located halfway between Munich and Augsburg, and along the Amper river. Main sights *Cistercian monastery ( Fürstenfeld Abbey), founded in 1266 by Louis II, Duke of Bavaria and closed in 1803. It was one of the favourite monasteries of the Wittelsbach family. *Parish church of St. Magdalene (late 17th century) *Pilgrim church of St. Leonhard. A Gothic building which can be crossed riding a horse. *''Aumühle'', a 14th-century mill now housing the municipal library. Fürst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion En Libertad
Religion is usually defined as a social-cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, transcendental, and spiritual elements; however, there is no scholarly consensus over what precisely constitutes a religion. Different religions may or may not contain various elements ranging from the divine, sacred things, faith,Tillich, P. (1957) ''Dynamics of faith''. Harper Perennial; (p. 1). a supernatural being or supernatural beings or "some sort of ultimacy and transcendence that will provide norms and power for the rest of life". Religious practices may include rituals, sermons, commemoration or veneration (of deities or saints), sacrifices, festivals, feasts, trances, initiations, funerary services, matrimonial services, meditation, prayer, music, art, dance, public service, or other aspects of human culture. Religions have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puch (Fürstenfeldbruck) St
Puch () is a manufacturing company located in Graz, Austria. The company was founded in 1899 by the industrialist Johann Puch and produced automobiles, bicycles, mopeds, and motorcycles. It was a subsidiary of the large Steyr-Daimler-Puch conglomerate. History Foundation From 1889 Johann Puch (1862–1914) worked as an agent for Humber vehicles and manufacturer of ''Styria'' safety bicycles in a small workshop in Graz and in 1890 he founded his first company, Johann Puch & Comp., employing 34 workers. Cyclists like Josef Fischer, winning the first edition of Paris–Roubaix in 1896, popularized ''Styria'' bicycles which were even exported to England and France. By 1895, Puch already employed more than 300 workers producing about 6000 bikes a year. In 1897 Puch left the company after a dispute with his business partners. Two years later he founded the First Styrian Bicycle Factory AG (''Erste Steiermärkische Fahrradfabrik AG'') in Graz. Puch's company became successful thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_St._Sebastian_203.jpg)