|
Ebora Liberalitas Julia
Ebora Liberalitas Julia is the name of a Roman empire, Roman ''municipium'' that gave rise to the Portuguese district capital Évora in the Alentejo region. While the name "Ebora" indicates a Celts, Celtiberian hill top fortification in the area of the later ''municipia'' or in its vicinity the first archaeological evidence of a settlement is from the History of the Roman Empire, Early Roman Empire. Early Roman activities on the Iberian peninsula were limited to the areas previously partially populated by Greeks and Punics, Punic areas along the south and east coast. The area of today's Alentejo probably did not come under Roman control until the middle of the 2nd century BC. The name addition "Iulia" in the Roman name Évoras infers the emergence of the ''municipium'' under the Julians and their representative Gaius Iulius Caesar. But since clear traces of extensive infrastructures from this time and in the surrounding area are missing, it is considered more probable that É ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
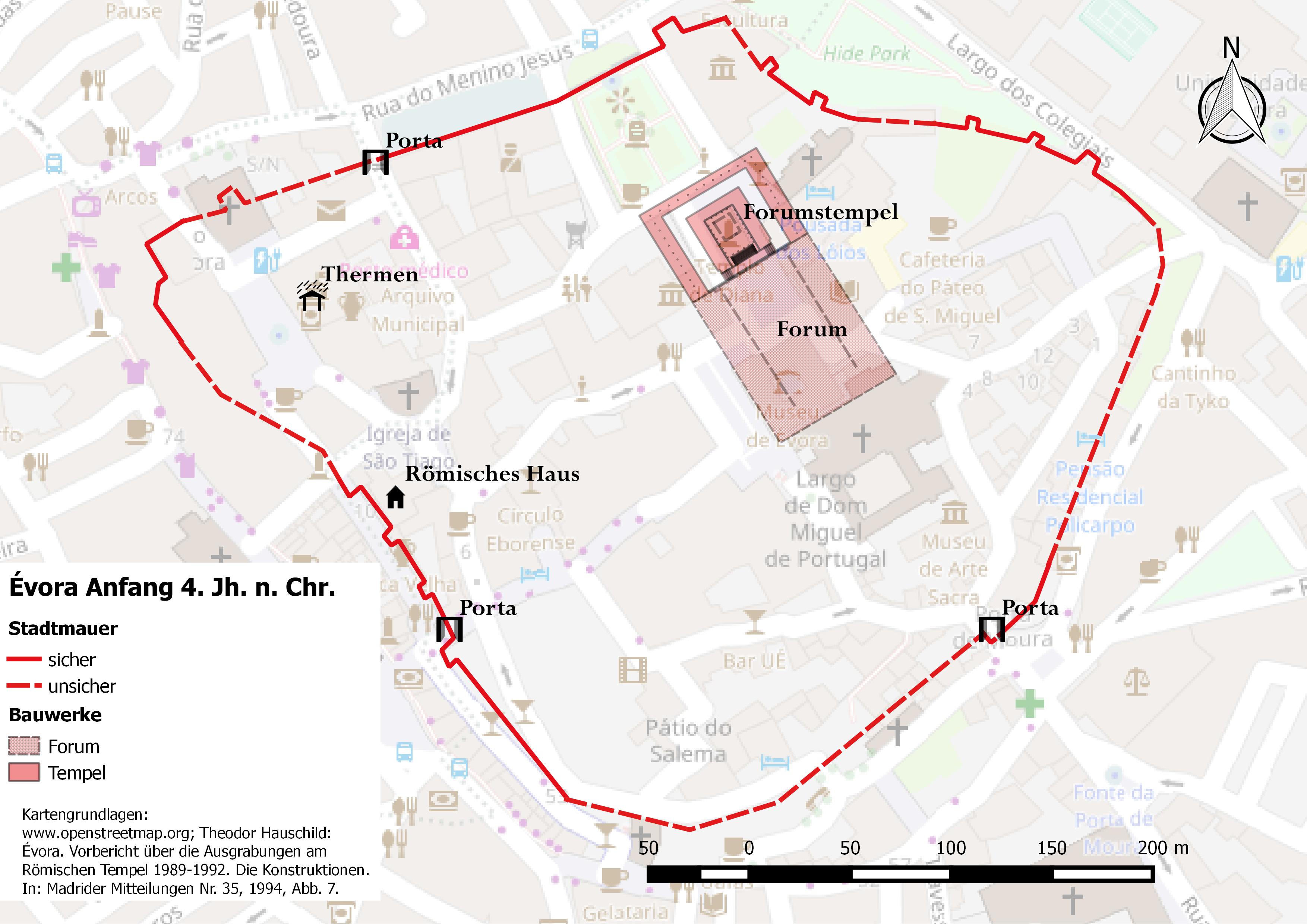
Plan Evora 4
A plan is typically any diagram or list of steps with details of timing and resources, used to achieve an Goal, objective to do something. It is commonly understood as a modal logic, temporal set (mathematics), set of intended actions through which one expects to achieve a goal. For space, spatial or Plane (geometry), planar topology, topologic or topography, topographic sets see map. Plans can be formal or informal: * Structured and formal plans, used by multiple people, are more likely to occur in projects, diplomacy, careers, economic development, military campaigns, combat, sports, games, or in the conduct of other business. In most cases, the absence of a well-laid plan can have adverse effects: for example, a non-robust project plan can cost the organization time and money. * Informal or ad hoc plans are created by individuals in all of their pursuits. The most popular ways to describe plans are by their breadth, time frame, and specificity; however, these planning clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opus Signinum
''Opus signinum'' ('cocciopesto' in modern Italian) is a building material used in ancient Rome. It is made of tiles broken up into very small pieces, mixed with mortar, and then beaten down with a rammer. Pliny the Elder in his '' Natural History'' describes its manufacture: "Even broken pottery has been utilized; it being found that, beaten to powder, and tempered with lime, it becomes more solid and durable than other substances of a similar nature; forming the cement known as the "Signine" composition, so extensively employed for even making the pavements of houses." Pliny's use of the term "signine" references "Signia (modern Segni), the name of a town in Latium which was famous for its tiles." Origins, spread, disuse The technique, most probably invented by the Phoenicians, is documented in the early 7th cent. BC at Tell el-Burak (Lebanon), then in Phoenician colonies in North Africa, some time before 256 BC, and spread north from there to Sicily and finally to the Itali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sao Domingos Mine
The São Domingos Mine is a deserted open-pit mine in Corte do Pinto, Alentejo, Portugal. This site is one of the volcanogenic massive sulfide ore deposits in the Iberian Pyrite Belt, which extends from the southern Portugal into Spain. It was the first place in Portugal to have electric lighting. History The Romans mined in the São Domingos area for gold and silver for about 400 years. Mining stopped here when the Romans left. In 1854 Nicolau Biava, an Italian miner from Piedmont, Italy, staked a claim to the mine; ownership then passed to a French syndicate. In 1855 mining was resumed, as the international demand for copper grew during the Industrial Revolution. In 1859 the mining concession was leased for 50 years to an English mining company, Mason and Barry, run by Sir Francis Barry, 1st Baronet and his brother-in-law James Mason, because of their industrial mining expertise. The nearby port of Pomarão was inaugurated the same year. Known as Pomaron in England, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome And Wine
Ancient Rome played a pivotal role in the history of wine. The earliest influences on the viticulture of the Italian peninsula can be traced to ancient Greeks and the Etruscans. The rise of the Roman Empire saw both technological advances in and burgeoning awareness of winemaking, which spread to all parts of the empire. Rome's influence has had a profound effect on the histories of today's major winemaking regions in France, Germany, Italy, Portugal and Spain. The Roman belief that wine was a daily necessity made the drink "democratic" and ubiquitous; in various qualities, it was available to slaves, peasants and aristocrats, men and women alike. To ensure the steady supply of wine to Roman soldiers and colonists, viticulture and wine production spread to every part of the empire. The economic opportunities presented by trading in wine drew merchants to do business with tribes native to Gaul and Germania, bringing Roman influences to these regions even before the arrival of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Roman Cuisine
The cuisine of ancient Rome changed greatly over the duration of the civilization's existence. Dietary habits were affected by the political changes from kingdom to republic to empire, and the empire's enormous expansion, which exposed Romans to many new provincial culinary habits and cooking methods. In the beginning, dietary differences between Roman social classes were not great, but disparities developed with the empire's growth. Archaeology Most organic foods decay under ordinary conditions, but ashes and animal bones offer some archaeological details about the Ancient Roman diet. Phytoliths have been found at a cemetery in Tarragona, Spain. Imported figs were among the charred foods preserved when Boudica and her army burned down a Roman shop in Colchester. Chickpeas and bowls of fruit are known from Herculaneum, preserved since Vesuvius destroyed the town in 79 AD. Remains of small fish bones, sea urchin spines and mineralized plants have survived in the city's sewe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Agriculture
Roman agriculture describes the farming practices of ancient Rome, during a period of over 1000 years. From humble beginnings, the Roman Republic (509 BC to 27 BC) and the Roman Empire (27 BC to 476 AD) expanded to rule much of Europe, northern Africa, and the Middle East and thus comprised many agricultural environments of which the Mediterranean climate of dry, hot summers and cool, rainy winter was the most common. Within the Mediterranean area, a triad of crops were most important: grains, olives, and grapes. The great majority of the people ruled by Rome were engaged in agriculture. From a beginning of small, largely self-sufficient landowners, rural society became dominated by latifundium, large estates owned by the wealthy and utilizing mostly slave labor. The growth in the urban population, especially of the city of Rome, required the development of commercial markets and long-distance trade in agricultural products, especially grain, to supply the people in the cities w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alentejo
Alentejo ( , ) is a geographical, historical, and cultural region of south–central and southern Portugal. In Portuguese, its name means "beyond () the Tagus river" (''Tejo''). Alentejo includes the regions of Alto Alentejo and Baixo Alentejo. It corresponds to the districts of Beja, Évora, Portalegre, and Alentejo Litoral. Its main cities are Évora, Beja, Sines, Serpa, Estremoz, Elvas, and Portalegre. It has borders with Beira Baixa in the north, with Spain (Andalucia and Extremadura) in the east, Algarve in the south, and the Atlantic Ocean, Ribatejo, and Estremadura in the west. Alentejo is a region known for its traditional polyphonic singing groups, similar to those found in Tuscany, Corsica, and elsewhere. History The comarca of the Alentejo became the Alentejo Province, divided into upper ( Alto Alentejo Province) and lower ( Baixo Alentejo Province) designations. The modern NUTS statistical region, Alentejo Region, was expropriated from the mediev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages. Moors are not a distinct or self-defined people. The 1911 ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' observed that the term had "no real ethnological value." Europeans of the Middle Ages and the early modern period variously applied the name to Arabs and North African Berbers, as well as Muslim Europeans. The term has also been used in Europe in a broader, somewhat derogatory sense to refer to Muslims in general,Menocal, María Rosa (2002). ''Ornament of the World: How Muslims, Jews and Christians Created a Culture of Tolerance in Medieval Spain''. Little, Brown, & Co. , p. 241 especially those of Arab or Berber descent, whether living in Spain or North Africa. During the colonial era, the Portuguese introduced the names " Ceylon Moors" and " Indian Moors" in South Asia and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is known as the Migration Period. The Visigoths emerged from earlier Gothic groups, including a large group of Thervingi, who had moved into the Roman Empire beginning in 376 and had played a major role in defeating the Romans at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Relations between the Romans and the Visigoths varied, with the two groups making treaties when convenient, and warring with one another when not. Under their first leader, Alaric I, the Visigoths invaded Italy and sacked Rome in August 410. Afterwards, they began settling down, first in southern Gaul and eventually in Hispania, where they founded the Visigothic Kingdom and maintained a presence from the 5th to the 8th centuries AD. The Visigoths first settled in southern Gaul as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Roman Units Of Measurement
The ancient Roman units of measurement were primarily founded on the Hellenic system, which in turn was influenced by the Egyptian system and the Mesopotamian system. The Roman units were comparatively consistent and well documented. Length The basic unit of Roman linear measurement was the ''pes'' or Roman foot (plural: ''pedes''). Investigation of its relation to the English foot goes back at least to 1647, when John Greaves published his ''Discourse on the Romane foot''. Greaves visited Rome in 1639, and measured, among other things, the foot measure on the tomb of Titus Statilius Aper, that on the statue of Cossutius formerly in the gardens of Angelo Colocci, the congius of Vespasian previously measured by Villalpandus, a number of brass measuring-rods found in the ruins of Rome, the paving-stones of the Pantheon and many other ancient Roman buildings, and the distance between the milestones on the Appian Way. He concluded that the Cossutian foot was the "true" Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opus Quadratum
''Opus quadratum'' ("squared work") is an ancient Roman construction technique, in which squared blocks of stone of the same height were set in parallel courses, most often without the use of mortar. The Latin author Vitruvius describes the technique. Technique This technique was used by the Romans from about the 6th century BC, and over time the precision and accuracy of the block cutting improved. The technique continued to be used throughout the age of the Roman Empire, even after the introduction of mortar, and was often used in addition to other techniques. The type of stone, the size of the blocks, and the way the blocks were put together can all be used to help archaeologists date structures that display the technique. Etruscan way In early usage (often called the " Etruscan way"), the joints between the block introduce discontinuities, making the blocks uneven. Examples of such construction can be found in reservoirs, basements, terrace walls, and temple podiums in E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Portugal
The history of Portugal can be traced from circa 400,000 years ago, when the region of present-day Portugal was inhabited by Homo heidelbergensis. The Roman invasion in the 3rd century BC lasted several centuries, and developed the Roman provinces of Lusitania in the south and Gallaecia in the north. Following the fall of Rome, Germanic tribes controlled the territory between the 5th and 8th centuries, including the Kingdom of the Suebi centred in Braga and the Visigothic Kingdom in the south. The 711–716 invasion by the Islamic Umayyad Caliphate conquered the Visigoth Kingdom and founded the Islamic State of Al-Andalus, gradually advancing through Iberia. In 1095, Portugal broke away from the Kingdom of Galicia. Henry's son Afonso Henriques proclaimed himself king of Portugal in 1139. The Algarve (the southernmost province in Portugal) conquered from the Moors in 1249, and in 1255 Lisbon became the capital. Portugal's land boundaries have remained almost unchanged sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_01.jpg)




.jpg)
_01.jpg)