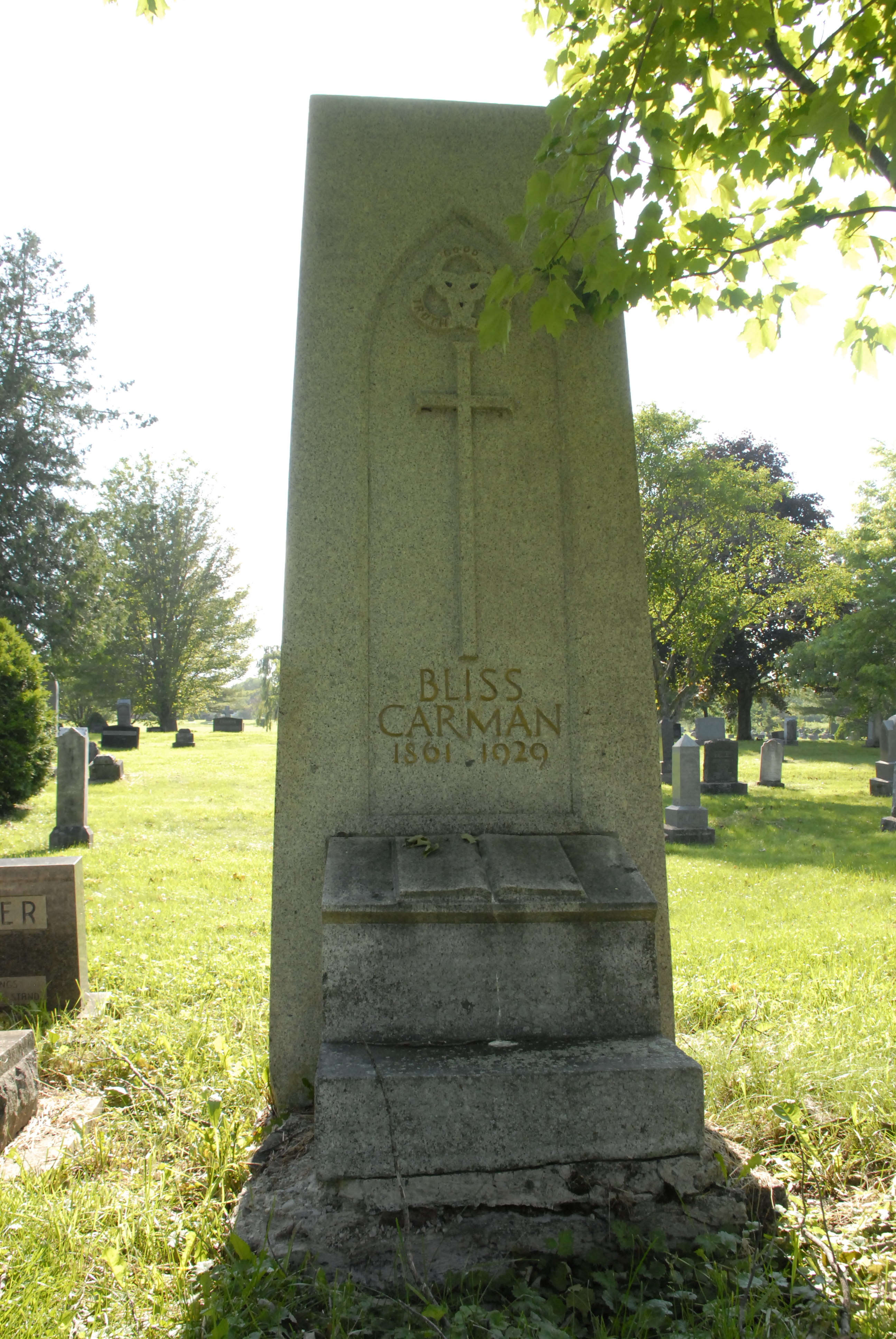|
E.K. Brown
Edward Killoran Brown (August 15, 1905 – April 24, 1951), who wrote as E. K. Brown, was a Canadians, Canadian professor and literary critic. He "influenced Canadian literature primarily through his award-winning book ''On Canadian Poetry'' (1943)," which "established the standards of excellence and many of the subsequent directions of Canadians, Canadian criticism." Northrop Frye called him "the first critic to bring Canadian literature into its proper context". Life E.K. Brown was born in Toronto, the son of Winifred Killoran and Edward David Brown, a businessman.W.H. New, ''Encyclopedia of Literature in Canada'' (McGill-Queen's University Press, 2002), 161–162. He graduated from the University of Toronto in 1926, winning the Governor-General's Medal for Modern Languages and a scholarship to the University of Paris, Sorbonne.Douglas Bush, E.K. Brown and the Evolution of Canadian Poetry" ''Seewanee Review,'' 87:1 (Winter 1979), 186, Web, May 13, 2011. Brown taught at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Template:Infobox Writer/doc
Infobox writer may be used to summarize information about a person who is a writer/author (includes screenwriters). If the writer-specific fields here are not needed, consider using the more general ; other infoboxes there can be found in :People and person infobox templates. This template may also be used as a module (or sub-template) of ; see WikiProject Infoboxes/embed for guidance on such usage. Syntax The infobox may be added by pasting the template as shown below into an article. All fields are optional. Any unused parameter names can be left blank or omitted. Parameters Please remove any parameters from an article's infobox that are unlikely to be used. All parameters are optional. Unless otherwise specified, if a parameter has multiple values, they should be comma-separated using the template: : which produces: : , language= If any of the individual values contain commas already, add to use semi-colons as separators: : which produces: : , ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duncan Campbell Scott
Duncan Campbell Scott (August 2, 1862 – December 19, 1947) was a Canadian civil servant and poet and prose writer. With Charles G.D. Roberts, Bliss Carman, and Archibald Lampman, he is classed as one of Canada's Confederation Poets. A career civil servant, Scott served as deputy superintendent of the Department of Indian Affairs from 1913 to 1932. Life and legacy Scott was born in Ottawa, Ontario, the son of Rev. William Scott, a Methodist preacher, and Janet MacCallum. He was educated at Stanstead Wesleyan College. Early in life, he became an accomplished pianist. Scott wanted to be a doctor, but family finances were precarious, so in 1879 he joined the federal civil service. William Scott might not have money uthe had connections in high places. Among his acquaintances was the prime minister, Sir John A. Macdonald, who agreed to meet with Duncan. As chance would have it, when Duncan arrived for his interview, the prime minister had a memo on his desk from the Indian Bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Canada
The Royal Society of Canada (RSC; french: Société royale du Canada, SRC), also known as the Academies of Arts, Humanities and Sciences of Canada (French: ''Académies des arts, des lettres et des sciences du Canada''), is the senior national, bilingual council of distinguished Canadian scholars, humanists, scientists and artists. The primary objective of the RSC is to promote learning and research in the arts, the humanities and the sciences. The RSC is Canada's National Academy and exists to promote Canadian research and scholarly accomplishment in both official languages, to recognize academic and artistic excellence, and to advise governments, non-governmental organizations and Canadians on matters of public interest. History In the late 1870s, the Governor General of Canada, the Marquis of Lorne, determined that Canada required a cultural institution to promote national scientific research and development. Since that time, succeeding Governor Generals have remained involved w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1943 Governor General's Awards
The 1943 Governor General's Awards for Literary Merit were the eighth rendition of the Governor General's Awards, Canada's annual national awards program which then comprised literary awards alone. The awards recognized Canadian writers for new English-language works published in Canada during 1943 and were presented in 1944. There were no cash prizes. As every year from 1942 to 1948, there two awards for non-fiction, and four awards in the three established categories, which recognized English-language works only. Winners * Fiction: Thomas H. Raddall, ''The Pied Piper of Dipper Creek'' * Poetry or drama: A. J. M. Smith, ''News of the Phoenix'' * Non-fiction: John Daniel Robins, ''The Incomplete Anglers'' * Non-fiction: E. K. Brown Edward Killoran Brown (August 15, 1905 – April 24, 1951), who wrote as E. K. Brown, was a Canadian professor and literary critic. He "influenced Canadian literature primarily through his award-winning book ''On Canadian Poetry'' (1943)," wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pauline Johnson
Emily Pauline Johnson (10 March 1861 – 7 March 1913), also known by her Mohawk stage name ''Tekahionwake'' (pronounced ''dageh-eeon-wageh'', ), was a Canadian poet, author, and performer who was popular in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Her father was a hereditary Mohawk chief of mixed ancestry and her mother was an English immigrant. Johnson—whose poetry was published in Canada, the United States, and Great Britain—was among a generation of widely-read writers who began to define Canadian literature. She was a key figure in the construction of the field as an institution and has made an indelible mark on Indigenous women's writing and performance as a whole. Johnson was notable for her poems, short stories, and performances that celebrated her mixed-race heritage, drawing from both Indigenous and English influences. She is most known for her books of poetry ''The White Wampum'' (1895), ''Canadian Born'' (1903), and ''Flint and Feather'' (1912); and her colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick George Scott
Frederick George Scott (7 April 1861 – 19 January 1944) was for the first part of his life an Anglican priest and a Canadian poet to whom the Canadian literary establishment gave the epithet "Poet of the Laurentians." He was associated with Canada's Confederation Poets, and wrote 13 books of Christian and patriotic poetry, often using the natural world to convey deeper spiritual meaning. He is better known for the latter part of his life. In his fifties, Scott became a chaplain in the Canadian Expeditionary Force sent to France during the First World War. Despite his insistence on remaining close to the front line to give assistance to the wounded, he survived many close calls until he was seriously wounded only weeks before the Armistice. He was subsequently decorated for bravery under fire. His memoir, ''The Great War As I Saw It'', was favourably received by both critics and the Canadian public. The book was still in print a century after publication. Scott remained a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Wilfred Campbell
William Wilfred Campbell (1 June ca. 1860 – 1 January 1918) was a Canadian poet. He is often classed as one of the country's Confederation Poets, a group that included fellow Canadians Charles G.D. Roberts, Bliss Carman, Archibald Lampman, and Duncan Campbell Scott; he was a colleague of Lampman and Scott. By the end of the 19th century, he was considered the "unofficial poet laureate of Canada." Although not as well known as the other Confederation poets today, Campbell was a "versatile, interesting writer" who was influenced by Robert Burns, the English Romantics, Edgar Allan Poe, Ralph Waldo Emerson, Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, Thomas Carlyle, and Alfred Tennyson. Inspired by these writers, Campbell expressed his own religious idealism in traditional forms and genres. Life William Wilfred Campbell was born around 1 June circa 1860 in Berlin, Ontario, now Kitchener. His father, Rev. Thomas Swainston Campbell, was an Anglican clergyman who had been assigned the task of se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
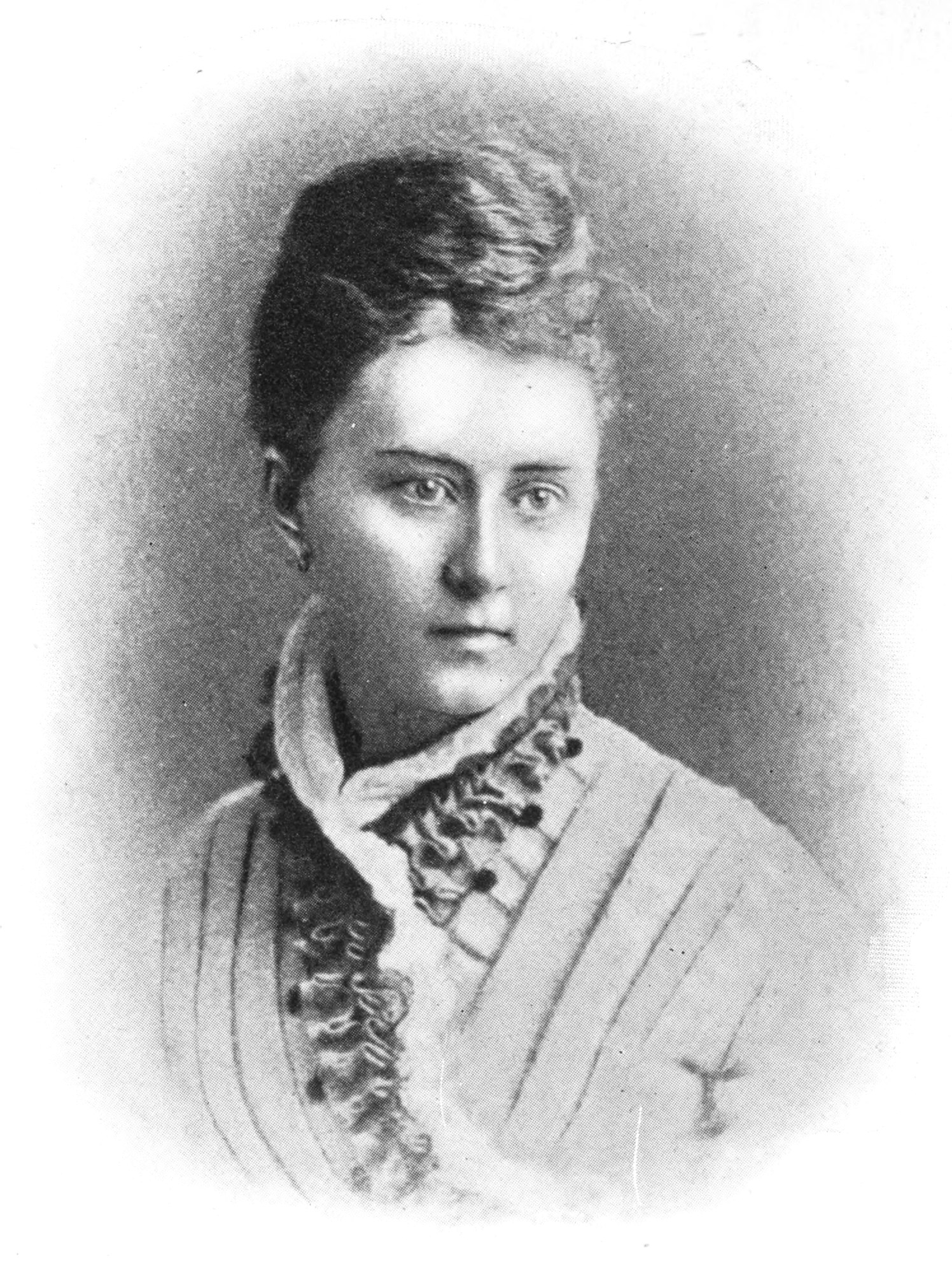
Bliss Carman
William Bliss Carman (April 15, 1861 – June 8, 1929) was a Canadian poet who lived most of his life in the United States, where he achieved international fame. He was acclaimed as Canada's poet laureate during his later years. In Canada, Carman is classed as one of the Confederation Poets, a group which also included Charles G.D. Roberts (his cousin), Archibald Lampman, and Duncan Campbell Scott. "Of the group, Carman had the surest lyric touch and achieved the widest international recognition. But unlike others, he never attempted to secure his income by novel writing, popular journalism, or non-literary employment. He remained a poet, supplementing his art with critical commentaries on literary ideas, philosophy, and aesthetics." Life William Bliss Carman was born on April 15, 1861 in Fredericton, New Brunswick. "Bliss" was his mother's maiden name. He was the great grandson of United Empire Loyalists who fled to Nova Scotia after the American Revolution, settling in New B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
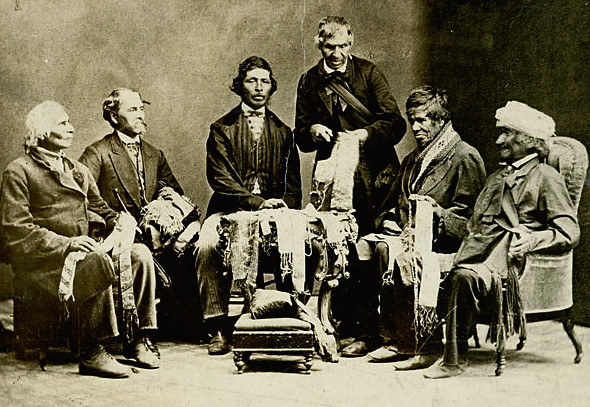
Confederation Poets
''Confederation Poets'' is the name given to a group of Canadian poets born in the decade of Canada's Confederation (the 1860s) who rose to prominence in Canada in the late 1880s and 1890s. The term was coined by Canadian professor and literary critic Malcolm Ross, who applied it to four poets – Charles G.D. Roberts (1860–1943), Bliss Carman (1861–1929), Archibald Lampman (1861–1899), and Duncan Campbell Scott (1862–1947) – in the Introduction to his 1960 anthology, ''Poets of the Confederation''. He wrote, "It is fair enough, I think, to call Roberts, Carman, Lampman, and Scott our 'Confederation poets.'"Malcolm Ross, Introduction, ''Poets of the Confederation'' (Toronto: McClelland and Stewart, 1960), vii-xii. The term has also been used since to include William Wilfred Campbell (?1860-1918) and Frederick George Scott (1861–1944), sometimes Francis Joseph Sherman (1871–1926), sometimes Pauline Johnson (1861–1913) and George Frederick Cameron (1854–1885) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Charles G
''Sir'' is a formal honorific address in English for men, derived from Sire in the High Middle Ages. Both are derived from the old French "Sieur" (Lord), brought to England by the French-speaking Normans, and which now exist in French only as part of "Monsieur", with the equivalent "My Lord" in English. Traditionally, as governed by law and custom, Sir is used for men titled as knights, often as members of orders of chivalry, as well as later applied to baronets and other offices. As the female equivalent for knighthood is damehood, the female equivalent term is typically Dame. The wife of a knight or baronet tends to be addressed as Lady, although a few exceptions and interchanges of these uses exist. Additionally, since the late modern period, Sir has been used as a respectful way to address a man of superior social status or military rank. Equivalent terms of address for women are Madam (shortened to Ma'am), in addition to social honorifics such as Mrs, Ms or Miss. Etymo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Encyclopedia
''The Canadian Encyclopedia'' (TCE; french: L'Encyclopédie canadienne) is the national encyclopedia of Canada, published online by the Toronto-based historical organization Historica Canada, with the support of Canadian Heritage. Available for free online in both English and French, ''The Canadian Encyclopedia'' includes more than 19,500 articles in both languages on numerous subjects including history, popular culture, events, people, places, politics, arts, First Nations, sports and science. The website also provides access to the ''Encyclopedia of Music in Canada'', the ''Canadian Encyclopedia Junior Edition'', ''Maclean's'' magazine articles, and ''Timelines of Canadian History''. , over 700,000 volumes of the print version of ''TCE'' have been sold and over 6 million people visit ''TCE'''s website yearly. History Background While attempts had been made to compile encyclopedic material on aspects of Canada, ''Canada: An Encyclopaedia of the Country'' (1898–19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as '' Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |