|
E.G.S. Paige
Professor Edward George Sydney Paige FRS (18 July 1930 – 20 February 2004), known as Ted Paige, was a British physicist and engineer. His main areas of research were semiconductor devices to improve radar, including work on surface acoustic waves, and optical techniques using programmable phase plates. Early life and education Paige was an only child born and raised in Northiam, Sussex, where he developed a lifelong interest in ornithology. Paige was raised in “a thatched cottage, reputedly of sixteenth-century vintage, in Northiam, a village on the border between Kent and East Sussex.” Paige's father, in keeping with family tradition, worked for the railroad, serving the stationmaster at the town's railway station. The family did not have running water until Paige was five years old, and did not have electricity until some time later. His parents “were encouraging and supportive but…had little contact with the world of learning or with intellectual pursuits.” A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northiam
Northiam is a village and civil parish in the Rother district, in East Sussex, England, 13 miles (21 km) north of Hastings in the valley of the River Rother. The A28 road to Canterbury and Hastings passes through it. Governance Northiam has nine parish councillors elected by the village parishioners. The council usually meet once a month for a general meeting and sometimes twice a month if there are planning applications to be looked at. The Parish Council have an office at the Village Club in the centre of the village. Rother District Council provides the next level of government with services such as refuse collection, planning consent, leisure amenities and council tax collection. Northiam lies within the Rother Levels ward, which provides two councillors. East Sussex county council is the third tier of government, providing education, libraries and highway maintenance. Northiam falls within the Northern Rother ward. The UK Parliament constituency for Northiam is Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classified as gemstones. Since antiquity, varieties of quartz have been the most commonly used minerals in the making of jewelry and hardstone carvings, especially in Eurasia. Quartz is the mineral defini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Filters
Electronic filters are a type of signal processing filter in the form of electrical circuits. This article covers those filters consisting of lumped electronic components, as opposed to distributed-element filters. That is, using components and interconnections that, in analysis, can be considered to exist at a single point. These components can be in discrete packages or part of an integrated circuit. Electronic filters remove unwanted frequency components from the applied signal, enhance wanted ones, or both. They can be: *passive or active *analog or digital *high-pass, low-pass, band-pass, band-stop (band-rejection; notch), or all-pass. *discrete-time (sampled) or continuous-time *linear or non-linear *infinite impulse response (IIR type) or finite impulse response (FIR type) The most common types of electronic filters are linear filters, regardless of other aspects of their design. See the article on linear filters for details on their design and analysis. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graham Marshall (physicist)
Graham Marshall may refer to: * Graham Marshall (rugby union) (born 1960), Scottish international rugby union player * Graham Marshall (footballer), New Zealand footballer {{DEFAULTSORT:Marshall, Graham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanium
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors silicon and tin. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature. Because it seldom appears in high concentration, germanium was discovered comparatively late in the discovery of the elements. Germanium ranks near fiftieth in relative abundance of the elements in the Earth's crust. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted its existence and some of its properties from its position on his periodic table, and called the element ekasilicon. In 1886, Clemens Winkler at Freiberg University found the new element, along with silver and sulfur, in the mineral argyrodite. Winkler named the element after his country, Germany. Germanium is mined primarily from sphalerite (the primary ore of zinc), though germani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Siddeley Nimrod
The Hawker Siddeley Nimrod is a retired maritime patrol aircraft developed and operated by the United Kingdom. It was an extensive modification of the de Havilland Comet, the world's first operational jet airliner. It was originally designed by de Havilland's successor firm, Hawker Siddeley; further development and maintenance work was undertaken by Hawker Siddeley's own successor companies, British Aerospace and, later, BAE Systems. Designed in response to a requirement issued by the Royal Air Force (RAF) to replace its fleet of ageing Avro Shackletons, the ''Nimrod MR1''/''MR2''s were primarily fixed-wing aerial platforms for anti-submarine warfare (ASW) operations; secondary roles included maritime surveillance and anti-surface warfare. It served from the early 1970s until March 2010.Cook, James"Final air miles for 'spy in the sky' crews."''BBC,'' 26 March 2010. Retrieved 20 October 2010. The intended replacement was to be extensively rebuilt Nimrod MR2s, designated Nimrod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS). Following the Allied victory over the Central Powers in 1918, the RAF emerged as the largest air force in the world at the time. Since its formation, the RAF has taken a significant role in British military history. In particular, it played a large part in the Second World War where it fought its most famous campaign, the Battle of Britain. The RAF's mission is to support the objectives of the British Ministry of Defence (MOD), which are to "provide the capabilities needed to ensure the security and defence of the United Kingdom and overseas territories, including against terrorism; to support the Government's foreign policy objectives particularly in promoting international peace and security". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
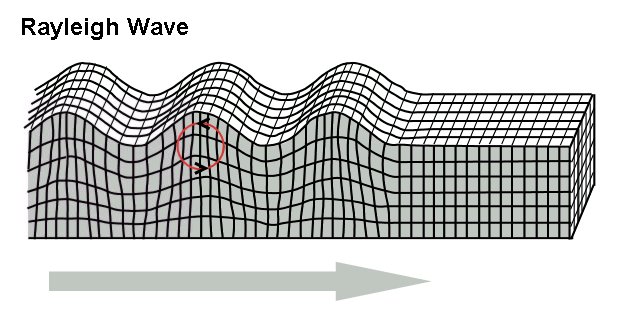
Rayleigh Waves
Rayleigh waves are a type of surface acoustic wave that travel along the surface of solids. They can be produced in materials in many ways, such as by a localized impact or by piezo-electric transduction, and are frequently used in non-destructive testing for detecting defects. Rayleigh waves are part of the seismic waves that are produced on the Earth by earthquakes. When guided in layers they are referred to as Lamb waves, Rayleigh–Lamb waves, or generalized Rayleigh waves. Characteristics Rayleigh waves are a type of surface wave that travel near the surface of solids. Rayleigh waves include both longitudinal and transverse motions that decrease exponentially in amplitude as distance from the surface increases. There is a phase difference between these component motions. The existence of Rayleigh waves was predicted in 1885 by Lord Rayleigh, after whom they were named. In isotropic solids these waves cause the surface particles to move in ellipses in planes normal to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan area has 2,057,142 people. Copenhagen is on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from Malmö, Sweden, by the Øresund strait. The Øresund Bridge connects the two cities by rail and road. Originally a Viking fishing village established in the 10th century in the vicinity of what is now Gammel Strand, Copenhagen became the capital of Denmark in the early 15th century. Beginning in the 17th century, it consolidated its position as a regional centre of power with its institutions, defences, and armed forces. During the Renaissance the city served as the de facto capital of the Kalmar Union, being the seat of monarchy, governing the majority of the present day Nordic region in a personal union with Sweden and Norway ruled by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birmingham University
, mottoeng = Through efforts to heights , established = 1825 – Birmingham School of Medicine and Surgery1836 – Birmingham Royal School of Medicine and Surgery1843 – Queen's College1875 – Mason Science College1898 – Mason University College1900 – gained university status by royal charter , city = Birmingham , province = West Midlands , country = England, UK , coor = , campus = Urban, suburban , academic_staff = 5,495 (2020) , administrative_staff = , head_label = Visitor , head = The Rt Hon Penny Mordaunt MP , chancellor = Lord Bilimoria , vice_chancellor = Adam Tickell , type = Public , endowment = £134.5 million (2021) , budget = £774.1 million (2020–21) , students = () , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , affiliations = Universitas 21 Universities UK EUA ACUSutton 13Russell Group , free_label = , free = , colours = The University , website = , logo = The University of Birmingham (informally Birmingham Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductors
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities (" doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical element for fabric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Signals And Radar Establishment
The Royal Signals and Radar Establishment (RSRE) was a scientific research establishment within the Ministry of Defence (MoD) of the United Kingdom. It was located primarily at Malvern in Worcestershire, England. The RSRE motto was ''Ubique Sentio'' (Latin for "I sense everywhere"). History RSRE was formed in 1976 by an amalgamation of previous research organizations; these included the Royal Radar Establishment (RRE), itself derived from the World War II-era Telecommunications Research Establishment, the Signals Research and Development Establishment (SRDE) in Christchruch, Dorset, and the Services Electronic Research Laboratory (SERL) at Baldock. Beginning in 1979, the SRDE and SERL moved to Malvern to join the RRE's location.EdsRobert Budand Philip Gummett, ''Cold War Hot Science: Applied Research in Britain's Defence Laboratories 1945-1990'', Harwood, 1999 There were several out-stations in Worcestershire, including the ex- RAF airfields at Defford and Persh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



%2C_UK_-_Air_Force_AN1047063.jpg)