|
Dunwich Heath
Dunwich Heath is an area of coastal lowland heath just south of the village of Dunwich, in the Suffolk Coast and Heaths AONB, England. It is adjacent to the RSPB reserve at Minsmere. It lies within the area of the Minsmere-Walberswick Heaths and Marshes Site of Special Scientific Interest, Special Area of Conservation and Special Protection Area. It has been owned by the National Trust since 1968, when it was bought with the help of a donation from the Heinz company as part of Enterprise Neptune. Dunwich Heath is a rare survival of coastal lowland heath; the Suffolk Sandlings used to form a lot of the Suffolk coast, but have mostly been developed for agriculture or built upon. The heath is mostly covered with heather, both Common Heather and Bell Heather, and European and Western Gorse but there is also some woodland and grassland included in the reserve. The heather and gorse flower from June until September; the heather is purple and pink while the gorse is yellow. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunwich Heath
Dunwich Heath is an area of coastal lowland heath just south of the village of Dunwich, in the Suffolk Coast and Heaths AONB, England. It is adjacent to the RSPB reserve at Minsmere. It lies within the area of the Minsmere-Walberswick Heaths and Marshes Site of Special Scientific Interest, Special Area of Conservation and Special Protection Area. It has been owned by the National Trust since 1968, when it was bought with the help of a donation from the Heinz company as part of Enterprise Neptune. Dunwich Heath is a rare survival of coastal lowland heath; the Suffolk Sandlings used to form a lot of the Suffolk coast, but have mostly been developed for agriculture or built upon. The heath is mostly covered with heather, both Common Heather and Bell Heather, and European and Western Gorse but there is also some woodland and grassland included in the reserve. The heather and gorse flower from June until September; the heather is purple and pink while the gorse is yellow. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Gorse
''Ulex gallii'', the western gorse or dwarf furzeA R Clapham, T G Tutin, E F Warburg, ''Flora of the British Isles'', Cambridge, 1962, p. 332 is an evergreen shrub in the pea family (Fabaceae), native to the Atlantic coasts of western Europe: southern Scotland, England, Wales, Ireland, the Isle of Man, western France and the northern coast of Spain. It favours acidic heathy soils and is frequently found in exposed maritime and montane environments. It is more common in the west of its distribution; in eastern England it is replaced in similar habitats by the closely related Dwarf Furze ('' Ulex minor''), with very little overlap in the distribution of the two species. ''Ulex gallii'' is usually tall although it may grow up to . The stems are modified into spines, mostly about long, but with some regularly spaced recurved spines of about . Like other members of the genus '' Ulex'' it has trifoliate leaves as a seedling, but later the leaves are reduced to small scales or spine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
True Lover's Knot (moth)
The true lover's knot (''Lycophotia porphyrea'') is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Michael Denis and Ignaz Schiffermüller in 1775. It is found in the west Palearctic in a wide band through northern, central and eastern Europe and Russia (up to the Ural Mountains). In the south it is spread through northern Spain and northern Portugal, northern Italy, Macedonia, Bulgaria, and northern Greece. In Europe it is found wherever its food plants grow. It is traditionally thought of as a species typical of heathland and moorland but it can often be found in places where heather and its relatives are in garden cultivation. In the mountains it is found up to an elevation of over 2000 metres above sea level. This is a small but attractive species, with a wingspan of 26–34 mm (individuals hatched in higher altitudes tend to be smaller than those from the lowlands). The forewings are brown, often tinged with purple and marked with a complex p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mining Bee
''Andrena'' is a genus of bees in the family Andrenidae. With over 1,500 species, it is one of the largest genera of animals. It is a strongly monophyletic group that is difficult to split into more manageable divisions; currently, ''Andrena'' is organized into 104 subgenera. It is nearly worldwide in distribution, with the notable exceptions of Oceania and South America. Bees in this genus are commonly known as mining bees due to their ground-nesting lifestyle. Morphology ''Andrena'' are generally medium-sized bees; body length ranges between 8 and 17 mm with males being smaller and more slender than females. Most are black with white to tan hair, and their wings have either two or three submarginal cells. They carry pollen mainly on femoral scopal hairs, but many ''Andrena'' have an additional propodeal corbicula for carrying some pollen on their thorax. C. D. Michener (2007) ''The Bees of the World'', 2nd Edition, Johns Hopkins University Press. They can be dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphex
Wasps of the genus ''Sphex'' (commonly known as digger wasps) are cosmopolitan predators that sting and paralyze prey insects. ''Sphex'' is one of many genera in the old digger wasp family Sphecidae ('' sensu lato''), though most apart from the Sphecinae have now been moved to the family Crabronidae. There are over 130 known ''Sphex'' species. Behaviour In preparation for egg laying, they construct a protected "nest" (some species dig nests in the ground, while others use pre-existing holes) and then stock it with captured insects. Typically, the prey are left alive, but paralyzed by wasp toxins. The wasps lay their eggs in the provisioned nest and the wasp larvae feed on the paralyzed insects as they develop. The great golden digger wasp ('' Sphex ichneumoneus'') is found in North America. The developing wasps spend the winter in their nest. When the new generation of adults emerge, they contain the genetically programmed behaviors required to carry out another season of nes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ant Lion
The antlions are a group of about 2,000 species of insect in the neuropteran family Myrmeleontidae. They are known for the predatory habits of their larvae, which mostly dig pits to trap passing ants or other prey. In North America, the larvae are sometimes referred to as doodlebugs because of the marks they leave in the sand. The adult insects are less well known due to their relatively short lifespans compared to the larvae. Adults, sometimes known as antlion lacewings, mostly fly at dusk or after dark and may be mistakenly identified as dragonflies or damselflies. Antlions have a worldwide distribution. The greatest diversity occurs in the tropics, but a few species are found in cold-temperate locations, one such being the European ''Euroleon nostras''. They most commonly occur in dry and sandy habitats where the larvae can easily excavate their pits, but some larvae hide under debris or ambush their prey among leaf litter. Antlions are poorly represented in the fossil rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Lizard
The viviparous lizard, or common lizard, (''Zootoca vivipara'', formerly ''Lacerta vivipara''), is a Eurasian lizard. It lives farther north than any other species of non-marine reptile, and is named for the fact that it is viviparous, meaning it not only lays eggs, but also gives birth to live young. Both "''Zootoca''" and "''vivipara''" mean "live birth," in Greek and Latin respectively. It was called ''Lacerta vivipara'' until the genus ''Lacerta'' was split into nine genera in 2007 by Arnold, Arribas & Carranza. Male and female ''Zootoca vivipara'' are equally likely to contract blood parasites. Additionally, larger males have been shown to reproduce more times in a given reproductive season than smaller ones. The lizard is also unique as it is exclusively carnivorous, eating only flies, spiders, and insects. Studies show that the more carnivorous an individual is (the more insects they eat), the less diverse the population of parasitic helminths that infest the lizards. ''Z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
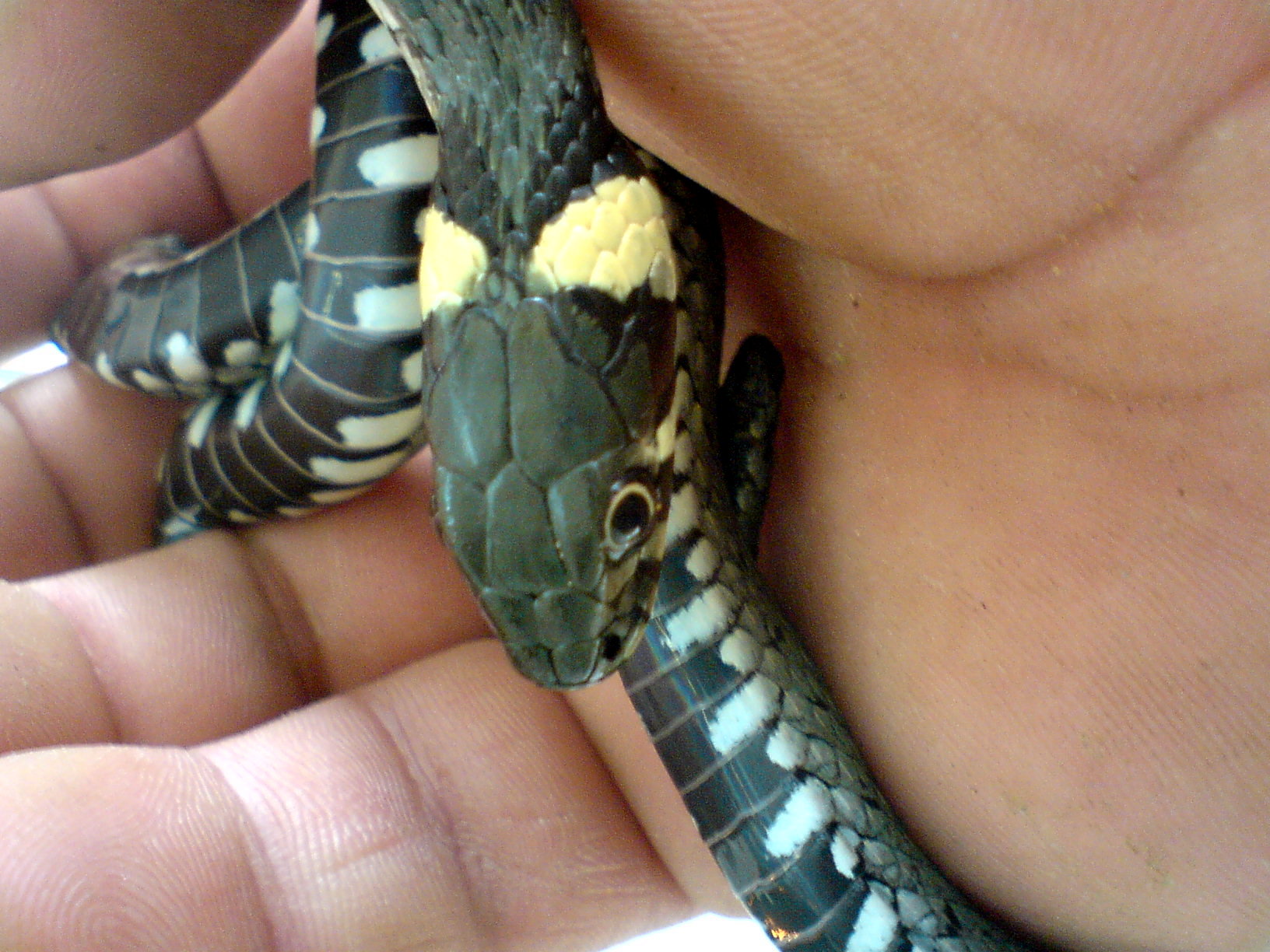
Grass Snake
The grass snake (''Natrix natrix''), sometimes called the ringed snake or water snake, is a Eurasian non-venomous colubrid snake. It is often found near water and feeds almost exclusively on amphibians. Subspecies Many subspecies are recognized, including: ''Natrix natrix helvetica'' ( Lacépède, 1789) was formerly treated as a subspecies, but following genetic analysis it was recognised in August 2017 as a separate species, ''Natrix helvetica'', the barred grass snake. Four other subspecies were transferred from ''N. natrix'' to ''N. helvetica'', becoming ''N. helvetica cettii'', ''N. helvetica corsa'', ''N. helvetica lanzai'' and ''N. helvetica sicula''. Description The grass snake is typically dark green or brown in colour with a characteristic yellow or whitish collar behind the head, which explains the alternative name ringed snake. The colour may also range from grey to black, with darker colours being more prevalent in colder regions, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
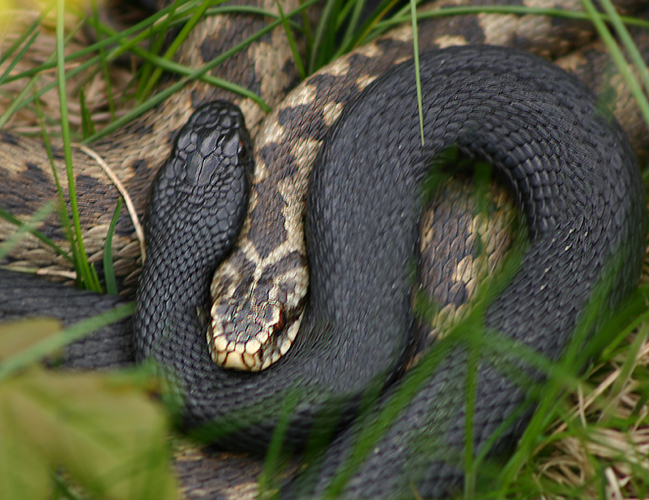
Slowworm
The slow worm (''Anguis fragilis'') is a reptile native to western Eurasia. It is also called a deaf adder, a slowworm, a blindworm, or regionally, a long-cripple and hazelworm. These legless lizards are also sometimes called common slowworms. The "blind" in blindworm refers to the lizard's small eyes, similar to a blindsnake (although the slowworm's eyes are functional). Slow worms are semifossorial (burrowing) lizards, spending much of their time hiding underneath objects. The skin of slow worms is smooth with scales that do not overlap one another. Like many other lizards, they autotomize, meaning that they have the ability to shed their tails to escape predators. While the tail regrows, it does not reach its original length. In the UK, they are common in gardens and allotments, and can be encouraged to enter and help remove pest insects by placing black plastic or providing places to shelter such as piles of logs, corrugated iron sheets or under tiles. On warm days, one o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vipera Berus
''Vipera berus'', the common European adderMallow D, Ludwig D, Nilson G. (2003). ''True Vipers: Natural History and Toxinology of Old World Vipers''. Malabar, Florida: Krieger Publishing Company. . or common European viper,Stidworthy J. (1974). ''Snakes of the World''. New York: Grosset & Dunlap Inc. 160 pp. . is a venomous snake that is extremely widespread and can be found throughout most of central and eastern Europe and as far as East Asia. Known by a host of common names including common adder and common viper, adders have been the subject of much folklore in Britain and other European countries. They are not regarded as especially dangerous; the snake is not aggressive and usually bites only when really provoked, stepped on, or picked up. Bites can be very painful, but are seldom fatal. The specific name, ''berus'', is New Latin and was at one time used to refer to a snake, possibly the grass snake, ''Natrix natrix''.Gotch AF. (1986). ''Reptiles: Their Latin Names Explaine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Nightjar
The European nightjar (''Caprimulgus europaeus''), common goatsucker, Eurasian nightjar or just nightjar, is a crepuscular and nocturnal bird in the nightjar family that breeds across most of Europe and the Palearctic to Mongolia and Northwestern China. The Latin generic name refers to the old myth that the nocturnal nightjar suckled from goats, causing them to cease to give milk. The six subspecies differ clinally, the birds becoming smaller and paler towards the east of the range. All populations are migratory, wintering in sub-Saharan Africa. Their densely patterned grey and brown plumage makes individuals difficult to see in the daytime when they rest on the ground or perch motionless along a branch, although the male shows white patches in the wings and tail as he flies at night. The preferred habitat is dry, open country with some trees and small bushes, such as heaths, forest clearings or newly planted woodland. The male European nightjar occupies a territory in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Stonechat
The European stonechat (''Saxicola rubicola'') is a small passerine bird that was formerly classed as a subspecies of the common stonechat. Long considered a member of the thrush family, Turdidae, genetic evidence has placed it and its relatives in the Old World flycatcher family, Muscicapidae. Taxonomy and systematics The European stonechat was formally described by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1766 in the twelfth edition of his '' Systema Naturae'' under the binomial name ''Motacilla rubicola''. This species is now placed in the genus ''Saxicola'' that was introduced by the German naturalist Johann Matthäus Bechstein in 1802. The English name derives from its call, sounding like two stones knocked together. The scientific name ''Saxicola'' means "rock-dweller", from Latin ''saxum'' meaning "a rock" and ''incola'' meaning "dwelling in". The specific epithet combines the Latin ''rubus'' meaning "brambles" with ''incola''. The subspecies name ''hibernans'' ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_in_the_Aamsveen%2C_The_Netherlands.jpg)