|
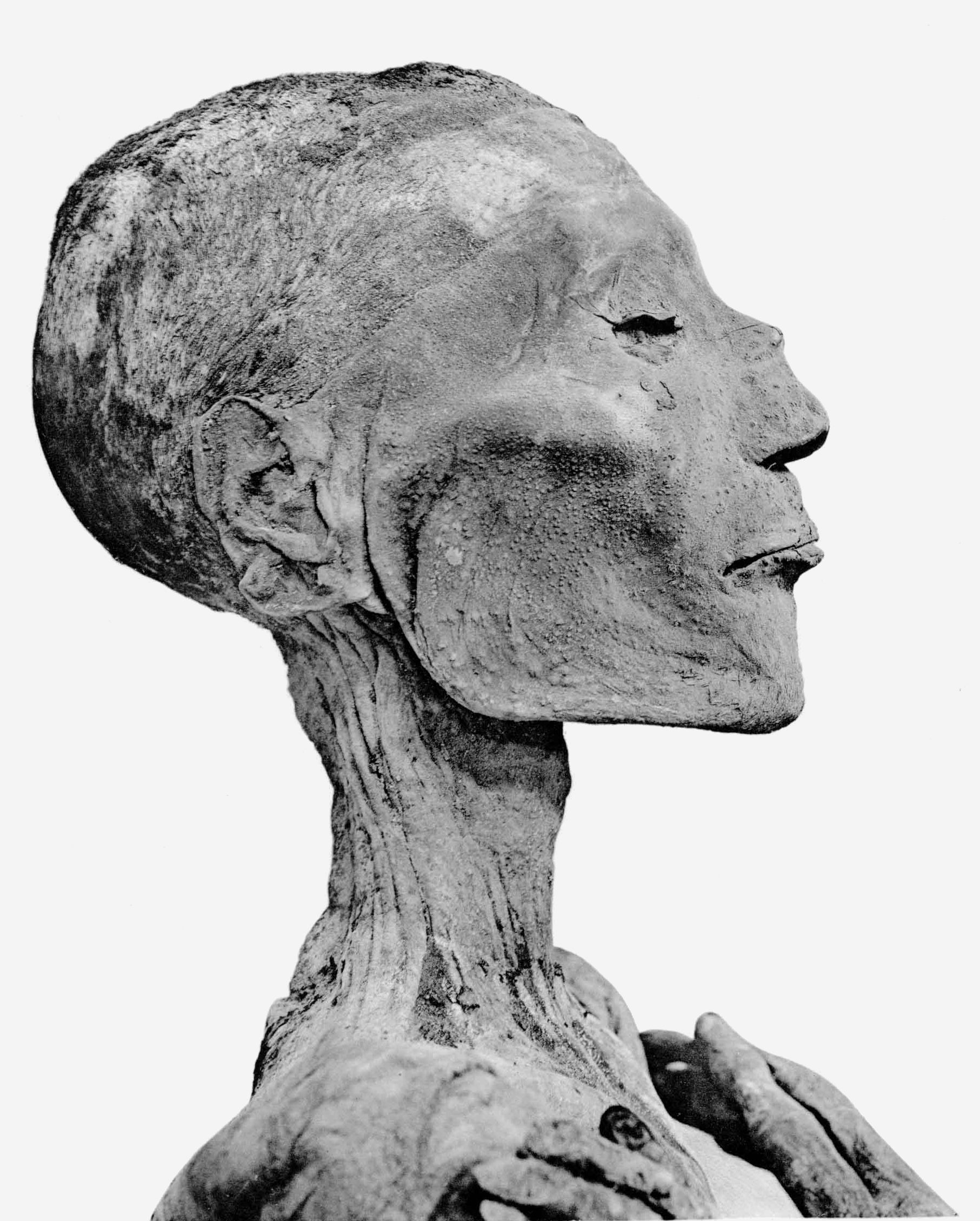
Duatentopet
Duatentopet or Tentopet was an ancient Egyptian queen of the 20th Dynasty, the wife of Pharaoh Ramesses IV Heqamaatre Setepenamun Ramesses IV (also written Ramses or Rameses) was the third pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty of the New Kingdom of Ancient Egypt. He was the second son of Ramesses III and became crown prince when his elder brother Amenhe ..., and mother of Ramesses V. Even though the identity of Ramesses IV's wife has not been clearly stated in history, she is considered the most likely candidate by virtue of the titles she was given and which were found listed in her tomb (QV74). In the Karnak, Karnak Temple Complex, an Adoratrix named Tentopet is shown with Ramesses III in the Temple of Khonsu. It is thought likely that Tentopet and Queen Duatentopet were the same person, and that she was a daughter of Ramesses III. This would make her a sister, or a half-sister, of her husband. Her steward Amenhotep was buried in Theban tomb TT346.Dodson & Hilton, p. 192 Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twentieth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XX, alternatively 20th Dynasty or Dynasty 20) is the third and last dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian New Kingdom period, lasting from 1189 BC to 1077 BC. The 19th and 20th Dynasties furthermore together constitute an era known as the ''Ramesside period''. This dynasty is generally considered to be the start of the decline of Ancient Egypt. History Background Upon the death of the last pharaoh of the 19th Dynasty, Queen Twosret, Egypt descended into a period of civil war, as attested by the Elephantine stela built by Setnakhte. The circumstances of Twosret's demise are uncertain, as she may have died peacefully during her reign or been overthrown by Setnakhte, who was likely already middle aged at the time. 20th Dynasty A consistent theme of this dynasty was the loss of pharaonic power to the High Priests of Amun. Horemheb, a pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty, had restored the traditional Ancient Egyptian religion and the priesth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twentieth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XX, alternatively 20th Dynasty or Dynasty 20) is the third and last dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian New Kingdom period, lasting from 1189 BC to 1077 BC. The 19th and 20th Dynasties furthermore together constitute an era known as the ''Ramesside period''. This dynasty is generally considered to be the start of the decline of Ancient Egypt. History Background Upon the death of the last pharaoh of the 19th Dynasty, Queen Twosret, Egypt descended into a period of civil war, as attested by the Elephantine stela built by Setnakhte. The circumstances of Twosret's demise are uncertain, as she may have died peacefully during her reign or been overthrown by Setnakhte, who was likely already middle aged at the time. 20th Dynasty A consistent theme of this dynasty was the loss of pharaonic power to the High Priests of Amun. Horemheb, a pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty, had restored the traditional Ancient Egyptian religion and the priesth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesses IV
Heqamaatre Setepenamun Ramesses IV (also written Ramses or Rameses) was the third pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty of the New Kingdom of Ancient Egypt. He was the second son of Ramesses III and became crown prince when his elder brother Amenherkhepshef died aged 15A. J. Peden, The Reign of Ramesses IV, Aris & Phillips Ltd, 1994. in 1164 BC, when Ramesses was only 12 years old.A. J. Peden, The Reign of Ramesses IV, Aris & Phillips Ltd, 1994. His promotion to crown prince: is suggested by his appearance (suitably entitled) in a scene of the festival of Min at the Ramesses III temple at Karnak, which may have been completed by Year 22 f his father's reign (the date is mentioned in the poem inscribed there)A. J. Peden, The Reign of Ramesses IV, Aris & Phillips Ltd, 1994. As his father's chosen successor, the prince employed three distinctive titles: "Hereditary Prince", "Royal scribe" and "Generalissimo." The latter two titles are mentioned in a text at the temple of Amenhotep III ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesses V
Usermaatre Sekheperenre Ramesses V (also written Ramses and Rameses) was the fourth pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt and was the son of Ramesses IV and Duatentopet. Reign Ramesses V's reign was characterized by the continued growth of the power of the priesthood of Amun, which controlled much of the temple land in the country and the state finances, at the expense of the ruling pharaohs. The Turin 1887 papyrus records a financial scandal during Ramesses' reign that involved the priests of Elephantine. A period of domestic instability also afflicted his reign, as evidenced by the fact that, according to the Turin Papyrus Cat. 2044, the workmen of Deir el-Medina periodically stopped work on Ramesses V's KV9 tomb in this king's first regnal year, out of fear of "''the enemy''", presumably Libyan raiding parties, who had reached the town of Per-Nebyt and "''burnt its people''." Another incursion by these raiders into Thebes is recorded a few days later.Peden, p.21 This show ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesses III
Usermaatre Meryamun Ramesses III (also written Ramses and Rameses) was the second Pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty in Ancient Egypt. He is thought to have reigned from 26 March 1186 to 15 April 1155 BC and is considered to be the last great monarch of the New Kingdom to wield any substantial authority over Egypt. His long reign saw the decline of Egyptian political and economic power, linked to a series of invasions and internal economic problems that also plagued pharaohs before him. This coincided with a decline in the cultural sphere of Ancient Egypt. However, his successful defense was able to slow down the decline, although it still meant that his successors would have a weaker military. He has also been described as a "warrior Pharaoh" due to his strong military strategies. He led the way by defeating the invaders known as "the Sea Peoples", who had caused destruction in other civilizations and empires. He was able to save Egypt from collapsing at the time when many other e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital and largest city of Egypt, while Alexandria, the second-largest city, is an important industrial and tourist hub at the Mediterranean coast. At approximately 100 million inhabitants, Egypt is the 14th-most populated country in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories of any country, tracing its heritage along the Nile Delta back to the 6th–4th millennia BCE. Considered a cradle of civilisation, Ancient Egypt saw some of the earliest developments of writing, agriculture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Religion
Ancient Egyptian religion was a complex system of polytheistic beliefs and rituals that formed an integral part of ancient Egyptian culture. It centered on the Egyptians' interactions with many deities believed to be present in, and in control of the world. Rituals such as prayer and offerings were provided to the gods to gain their favor. Formal religious practice centered on the pharaohs, the rulers of Egypt, believed to possess divine powers by virtue of their positions. They acted as intermediaries between their people and the gods, and were obligated to sustain the gods through rituals and offerings so that they could maintain Ma'at, the order of the cosmos, and repel Isfet, which was chaos. The state dedicated enormous resources to religious rituals and to the construction of temples. Individuals could interact with the gods for their own purposes, appealing for help through prayer or compelling the gods to act through magic. These practices were distinct from, but cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
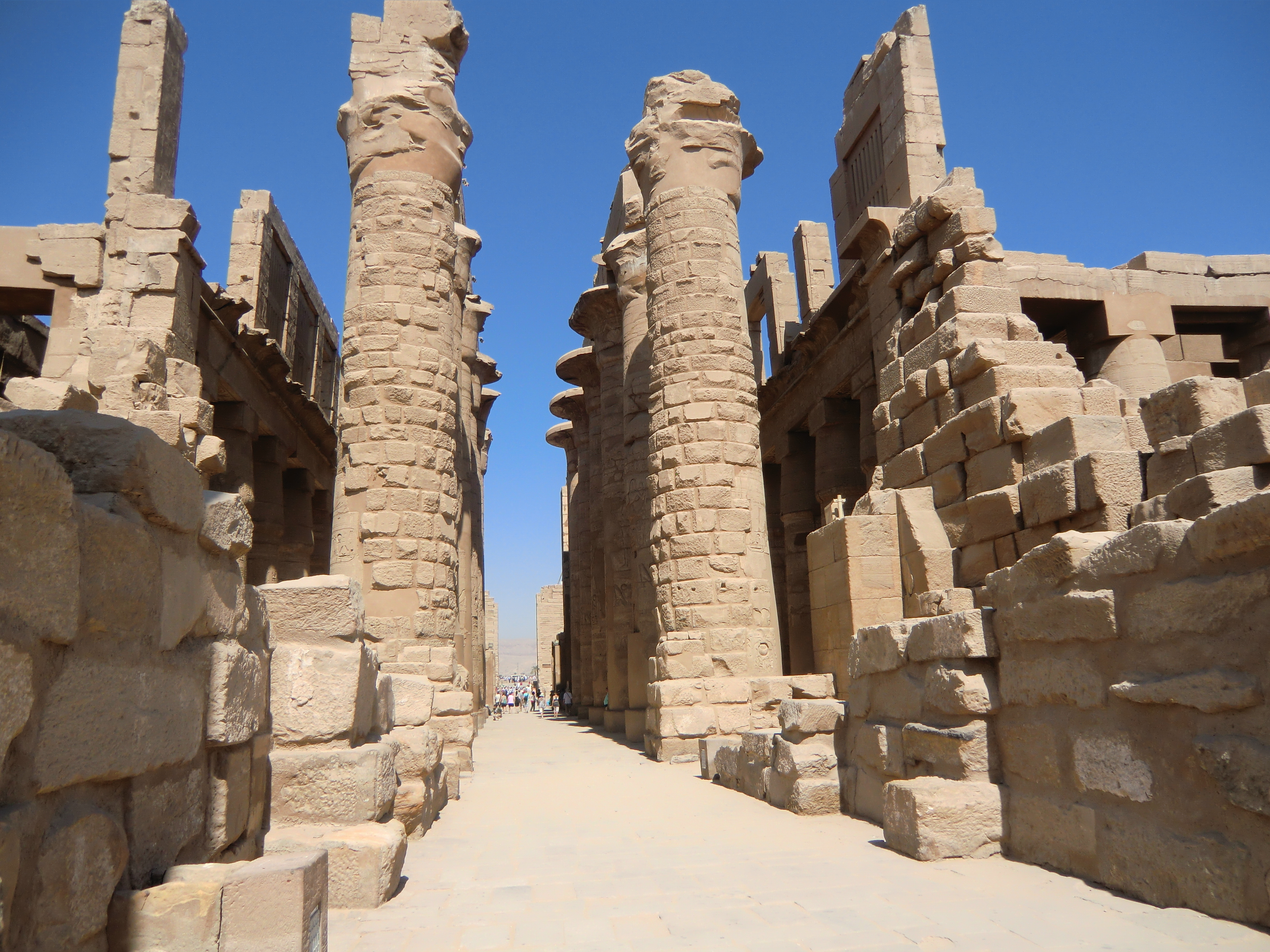
Karnak
The Karnak Temple Complex, commonly known as Karnak (, which was originally derived from ar, خورنق ''Khurnaq'' "fortified village"), comprises a vast mix of decayed temples, pylons, chapels, and other buildings near Luxor, Egypt. Construction at the complex began during the reign of Senusret I (reigned 1971–1926 BCE) in the Middle Kingdom (around 2000–1700 BCE) and continued into the Ptolemaic Kingdom (305–30 BCE), although most of the extant buildings date from the New Kingdom. The area around Karnak was the ancient Egyptian ''Ipet-isut'' ("The Most Selected of Places") and the main place of worship of the 18th Dynastic Theban Triad, with the god Amun as its head. It is part of the monumental city of Thebes, and in 1979 it was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List along with the rest of the city. The Karnak complex gives its name to the nearby, and partly surrounded, modern village of El-Karnak, north of Luxor. Overview The complex is a vast open sit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thames & Hudson
Thames & Hudson (sometimes T&H for brevity) is a publisher of illustrated books in all visually creative categories: art, architecture, design, photography, fashion, film, and the performing arts. It also publishes books on archaeology, history, and popular culture. Headquartered in London, it has a sister company in New York City, and subsidiaries in Melbourne, Singapore, and Hong Kong. In Paris it has a sister company, Éditions Thames & Hudson, and a subsidiary called Interart which distributes English-language books. The Thames & Hudson group currently employs approximately 150 staff in London and approximately 65 more around the world. The publishing company was founded in 1949 by Walter and Eva Neurath, who aimed to make the world of art and the research of top scholars available to a wider public. The company's name reflects its international presence, particularly in London and New York. It remains an independent, family-owned company, and is one of the largest publish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12th-century BC Egyptian Women
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit (measurement), unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest Positive number, positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the sequence (mathematics), infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |