|
Drawing (metalworking)
Drawing is a metalworking process that uses tensile forces to stretch (elongate) metal, glass, or plastic. As the metal is drawn (pulled), it stretches to become thinner, to achieve a desired shape and thickness. Drawing is classified into two types: sheet metal drawing and wire, bar, and tube drawing. Sheet metal drawing is defined as a plastic deformation over a curved axis. For wire, bar, and tube drawing, the starting stock is drawn through a die to reduce its diameter and increase its length. Drawing is usually performed at room temperature, thus classified as a cold working process; however, drawing may also be performed at elevated temperatures to hot work large wires, rods or hollow sections in order to reduce forces.Degarmo, p. 432.Kalpakjian, pp. 415–419. Drawing differs from rolling in that the pressure of drawing is not transmitted through the turning action of the mill but instead depends on force applied locally near the area of compression. This means the am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bar Drawing
Bar or BAR may refer to: Food and drink * Bar (establishment), selling alcoholic beverages * Candy bar * Chocolate bar Science and technology * Bar (river morphology), a deposit of sediment * Bar (tropical cyclone), a layer of cloud * Bar (unit), a unit of pressure * BAR domain, a protein domain * Bar stock, of metal * Sandbar Computing * Bar (computer science), a placeholder * Base Address Register in PCI * Bar, a mobile phone form factor * Bar, a type of graphical control element Law * Bar (law), the legal profession * Bar association * Bar examination Media and entertainment * ''Bar'' (Croatian TV series) * Bar (Czech TV series) * Bar (dance), Turkey * Bar (music), a segment * Bar (Polish TV series) * Bar (Slovenian TV series) * '' Bay Area Reporter'', a newspaper * '' Biblical Archaeology Review'', a magazine Places * Bar (Martian crater) * Bar, Rutog County, Tibet, China * Bar (river), France * Bar, Corrèze, France, a commune * Bar-le-Duc, France, a commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Rolling
In metalworking, rolling is a metal forming process in which metal stock is passed through one or more pairs of rolls to reduce the thickness, to make the thickness uniform, and/or to impart a desired mechanical property. The concept is similar to the rolling of dough. Rolling is classified according to the temperature of the metal rolled. If the temperature of the metal is above its recrystallization temperature, then the process is known as hot rolling. If the temperature of the metal is below its recrystallization temperature, the process is known as cold rolling. In terms of usage, hot rolling processes more tonnage than any other manufacturing process, and cold rolling processes the most tonnage out of all cold working processes... Roll stands holding pairs of rolls are grouped together into rolling mills that can quickly process metal, typically steel, into products such as structural steel (I-beams, angle stock, channel stock), bar stock, and rails. Most steel mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandrel
A mandrel, mandril, or arbor is a gently tapered cylinder against which material can be forged or shaped (e.g., a ring mandrel - also called a triblet - used by jewelers to increase the diameter of a wedding ring), or a flanged or tapered or threaded bar that grips a workpiece to be machined in a lathe. A flanged mandrel is a parallel bar of a specific diameter with an integral flange towards one end, and threaded at the opposite end. Work is gripped between the flange and a nut on the thread. A tapered mandrel (often called a plain mandrel) has a taper of approximately 0.005 inches per foot and is designed to hold work by being driven into an accurate hole on the work, gripping the work by friction. A threaded mandrel may have a male or female thread, and work which has an identical thread is screwed onto the mandrel. On a lathe, mandrels are commonly mounted between centres and driven by a lathe dog (typically the flanged or tapered mandrels), but may also be gripped in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tube Drawing
Tube drawing is a process to size a tube by shrinking a large diameter tube into a smaller one, by drawing the tube through a die. This process produces high-quality tubing with precise dimensions, good surface finish, and the added strength of cold working.Degarmo, p. 433. For this reason this process is established for many materials, mainly metalworking but also glass. Because it is so versatile, tube drawing is suitable for both large- and small-scale production. The large-scale production of glass typically uses a one step process where glass is directly drawn into a tube from a melting tank. There are five types of tube drawing: tube sinking, mandrel drawing, stationary mandrel, moving mandrel, and floating mandrel. A mandrel is used in many of the types to prevent buckling or wrinkling in the workpiece. Processes Tube sinking Tube sinking, also known as ''free tube drawing'', reduces the diameter of the tube without a mandrel inside the tube. The inner diameter is determine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annealing (metallurgy)
In metallurgy and materials science, annealing is a heat treatment that alters the physical and sometimes chemical properties of a material to increase its ductility and reduce its hardness, making it more workable. It involves heating a material above its recrystallization temperature, maintaining a suitable temperature for an appropriate amount of time and then cooling. In annealing, atoms migrate in the crystal lattice and the number of dislocations decreases, leading to a change in ductility and hardness. As the material cools it recrystallizes. For many alloys, including carbon steel, the crystal grain size and phase composition, which ultimately determine the material properties, are dependent on the heating rate and cooling rate. Hot working or cold working after the annealing process alters the metal structure, so further heat treatments may be used to achieve the properties required. With knowledge of the composition and phase diagram, heat treatment can be used t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ductility
Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to drawing (e.g. into wire). In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stress before failure. Ductility is an important consideration in engineering and manufacturing. It defines a material's suitability for certain manufacturing operations (such as cold working) and its capacity to absorb mechanical overload.. Some metals that are generally described as ductile include gold and copper. However, not all metals experience ductile failure as some can be characterized with brittle failure like cast iron. Polymers generally can be viewed as ductile materials as they typically allow for plastic deformation. Malleability, a similar mechanical property, is characterized by a material's ability to deform plastically without failure under compressive stress. Historically, materials were considered malleable if they we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Work Hardening
In materials science, work hardening, also known as strain hardening, is the strengthening of a metal or polymer by plastic deformation. Work hardening may be desirable, undesirable, or inconsequential, depending on the context. This strengthening occurs because of dislocation movements and dislocation generation within the crystal structure of the material. Many non-brittle metals with a reasonably high melting point as well as several polymers can be strengthened in this fashion. Alloys not amenable to heat treatment, including low-carbon steel, are often work-hardened. Some materials cannot be work-hardened at low temperatures, such as indium, however others can be strengthened only via work hardening, such as pure copper and aluminum. Undesirable work hardening An example of undesirable work hardening is during machining when early passes of a cutter inadvertently work-harden the workpiece surface, causing damage to the cutter during the later passes. Certain alloys are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Forming
In metallurgy, cold forming or cold working is any metalworking process in which metal is shaped below its recrystallization temperature, usually at the ambient temperature. Such processes are contrasted with hot working techniques like hot rolling, forging, welding, etc. The same or similar terms are used in glassmaking for the equivalents; for example cut glass is made by "cold work", cutting or grinding a formed object. Cold forming techniques are usually classified into four major groups: squeezing, bending, drawing, and shearing. They generally have the advantage of being simpler to carry out than hot working techniques. Unlike hot working, cold working causes the crystal grains and inclusions to distort following the flow of the metal; which may cause work hardening and anisotropic material properties. Work hardening makes the metal harder, stiffer, and stronger, but less plastic, and may cause cracks of the piece. The possible uses of cold forming are extre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Alloy
An aluminium alloy (or aluminum alloy; see spelling differences) is an alloy in which aluminium (Al) is the predominant metal. The typical alloying elements are copper, magnesium, manganese, silicon, tin, nickel and zinc. There are two principal classifications, namely casting alloys and wrought alloys, both of which are further subdivided into the categories heat-treatable and non-heat-treatable. About 85% of aluminium is used for wrought products, for example rolled plate, foils and extrusions. Cast aluminium alloys yield cost-effective products due to the low melting point, although they generally have lower tensile strengths than wrought alloys. The most important cast aluminium alloy system is Al–Si, where the high levels of silicon (4–13%) contribute to give good casting characteristics. Aluminium alloys are widely used in engineering structures and components where light weight or corrosion resistance is required.I. J. Polmear, ''Light Alloys'', Arnold, 1995 Alloys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draw Bench
A draw bench is a machine used to do cold work on a metal, such as changing the shape of the metal without applying heat and applying only pressure. Machine construction It consists of a chain drive, driven by a motor and a set of gears. The other end of the machine consists of a die mounted on a thick steel plate. The workpiece is inserted through the die and clamped on a trolley which then is hooked onto the chain for pulling across. Die The die is usually made of tungsten carbide Tungsten carbide ( chemical formula: WC) is a chemical compound (specifically, a carbide) containing equal parts of tungsten and carbon atoms. In its most basic form, tungsten carbide is a fine gray powder, but it can be pressed and formed int ... with a steel housing. The die can be made to any desired shape (round, square, rectangular, triangular, half round, L-shaped, oval etc.). Metal forming {{tool-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tube Beading
Tube beading is a metal forming process that forms a bead on the end of a tube. Tube beads can be used to help hold a hose on the end of a tube or to strengthen the end of the tube.Gregory Miller, "Tube Forming Processes: A Comprehensive Guide," 2002 There are two forming processes: ''internal roll forming'' and ''ram forming''. Internal roll forming Internal roll forming is generally slower than ram forming but it holds tight tolerances. Serrated clamp jaws are used to hold the tube while radial pressure is applied by an internal roller to form the bead. Ram forming Ram forming is quicker and usually preferred when speed of production is a concern. The automotive industry usually uses this process over internal roll-forming. A clamp is used to hold the tube, the tube is expanded to desired diameter by an expansion punch Punch commonly refers to: * Punch (combat), a strike made using the hand closed into a fist * Punch (drink), a wide assortment of drinks, non-alcoholic or al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
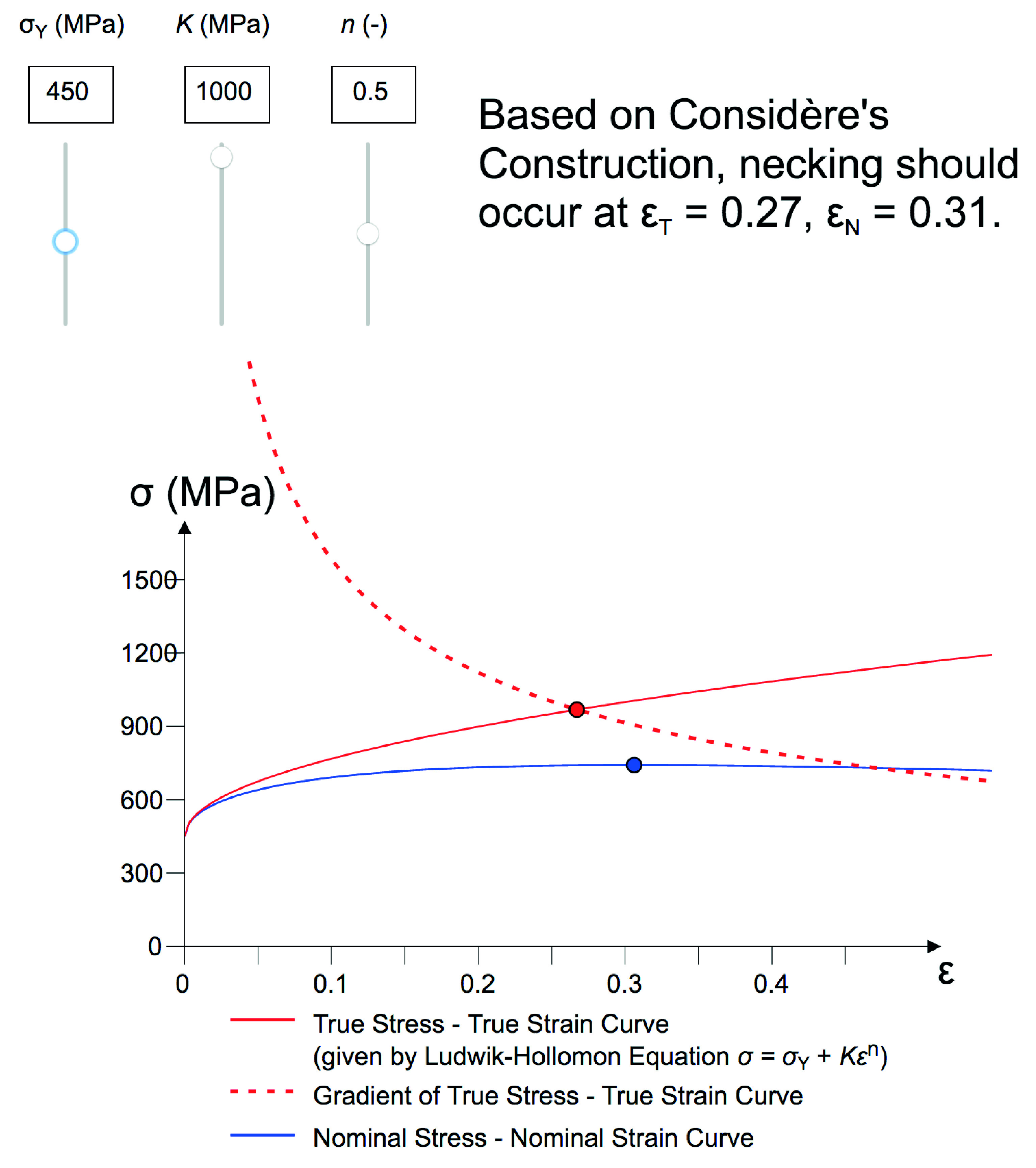
Necking (engineering)
Necking, in engineering or materials science, is a mode of tensile deformation where relatively large amounts of strain localize disproportionately in a small region of the material. The resulting prominent decrease in local cross-sectional area provides the basis for the name "neck". Because the local strains in the neck are large, necking is often closely associated with yielding, a form of plastic deformation associated with ductile materials, often metals or polymers. Once necking has begun, the neck becomes the exclusive location of yielding in the material, as the reduced area gives the neck the largest local stress. Formation Necking results from an instability during tensile deformation when the cross-sectional area of the sample decreases by a greater proportion than the material strain hardens.Armand Considèrepublished the basic criterion for necking in 1885, in the context of the stability of large scale structures such as bridges. Three concepts provide the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |