|
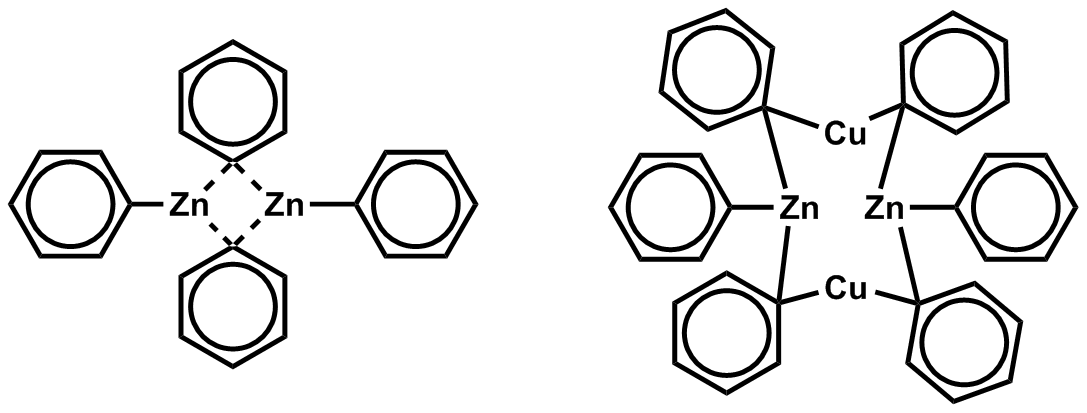
Diphenylzinc
Diphenylzinc is an organozinc compound. It is commonly used as the synthetic equivalent of a Ph− synthon. Solvent-free diphenylzinc exists as dimeric molecules in the solid state. Diphenylzinc is commercially available. It may be prepared by reaction of phenyllithium with zinc bromide: :2 PhLi + ZnBr2 → Ph2Zn + 2 LiBr It may also be prepared by the reaction of phenylmagnesium bromide with zinc chloride or diphenylmercury Diphenylmercury is the organomercury compound with the formula Hg(C6H5)2. It is a white solid. The compound is of historic interest as a particularly stable organometallic compound but it finds few uses because of its high toxicity. Preparation ... with zinc metal. References {{Zinc compounds Organozinc compounds Phenyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organozinc Compound
Organozinc compounds in organic chemistry contain carbon (C) to zinc (Zn) chemical bonds. Organozinc chemistry is the science of organozinc compounds describing their physical properties, synthesis and reactions.The Chemistry of Organozinc Compounds' (Patai Series, (Eds. Z. Rappoport and I. Marek), John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2006, .''Organozinc reagents – A Practical Approach'', (Eds. P. Knochel and P. Jones), Oxford Medical Publications, Oxford, 1999, . Organozinc compounds were among the first organometallic compounds made. They are less reactive than many other analogous organometallic reagents, such as Grignard and organolithium reagents. In 1848 Edward Frankland prepared the first organozinc compound, diethylzinc, by heating ethyl iodide in the presence of zinc metal.E. Frankland, Liebigs Ann. Chem.,1849, 71, 171 This reaction produced a volatile colorless liquid that spontaneous combusted upon contact with air. Due to their pyrophoric nature, organozinc compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organozinc Compounds
Organozinc compounds in organic chemistry contain carbon (C) to zinc (Zn) chemical bonds. Organozinc chemistry is the science of organozinc compounds describing their physical properties, synthesis and reactions.The Chemistry of Organozinc Compounds' (Patai Series, (Eds. Z. Rappoport and I. Marek), John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2006, .''Organozinc reagents – A Practical Approach'', (Eds. P. Knochel and P. Jones), Oxford Medical Publications, Oxford, 1999, . Organozinc compounds were among the first organometallic compounds made. They are less reactive than many other analogous organometallic reagents, such as Grignard and organolithium reagents. In 1848 Edward Frankland prepared the first organozinc compound, diethylzinc, by heating ethyl iodide in the presence of zinc metal.E. Frankland, Liebigs Ann. Chem.,1849, 71, 171 This reaction produced a volatile colorless liquid that spontaneous combusted upon contact with air. Due to their pyrophoric nature, organozinc compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthon
In retrosynthetic analysis, a synthon is a hypothetical unit within a target molecule that represents a potential starting reagent in the retroactive synthesis of that target molecule. The term was coined in 1967 by E. J. Corey. He noted in 1988 that the "word ''synthon'' has now come to be used to mean synthetic ''building block'' rather than retrosynthetic fragmentation structures". It was noted in 1998 that the phrase did not feature very prominently in Corey's 1981 book ''The Logic of Chemical Synthesis'', as it was not included in the index. Because synthons are charged, when placed into a synthesis a neutral form is found commercially instead of forming and using the potentially very unstable charged synthons. Example : In planning the synthesis of phenylacetic acid, two synthons are identified: a nucleophilic "COOH−" group, and an electrophilic "PhCH2+" group. Of course, both synthons do not exist per se; synthetic equivalents corresponding to the synthons are reacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallics
''Organometallics'' is a biweekly journal published by the American Chemical Society. Its area of focus is organometallic and organometalloid chemistry. This peer-reviewed journal has an impact factor of 3.837 as reported by the 2021 Journal Citation Reports by Thomson Reuters. Since 2015 Paul Chirik is the editor-in-chief of ''Organometallics''. He is an American chemist and the Edwards S. Sanford Professor of Chemistry at Princeton University, and associate director for external partnerships of the Andlinger Center for Energy and the Environment. He writes about the catalysis of hydrocarbons. Past editors-in-chief are Dietmar Seyferth and John Gladysz. Retrieved on 2014-07-30. This journal is indexed in |
Phenyllithium
Phenyllithium or lithobenzene is an organometallic agent with the empirical formula C6H5Li. It is most commonly used as a metalating agent in organic syntheses and a substitute for Grignard reagents for introducing phenyl groups in organic syntheses. Crystalline phenyllithium is colorless; however, solutions of phenyllithium are various shades of brown or red depending on the solvent used and the impurities present in the solute. Preparation Phenyllithium was first produced by the reaction of lithium metal with diphenylmercury: :(C6Η5)2Ηg + 2Li → 2C6Η5Li + Ηg Reaction of a phenyl halide with lithium metal produces phenyllithium: :X-Ph + 2Li → Ph-Li + LiX Phenyllithium can also be synthesized with a metal-halogen exchange reaction: :n-BuLi + X-Ph → n-BuX + Ph-Li The predominant method of producing phenyllithium today are the latter two syntheses. Reactions The primary use of PhLi is to facilitate formation of carbon-carbon bonds by nucleophilic addition and substitut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Bromide
Zinc bromide ( Zn Br2) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Zn Br2. It is a colourless salt that shares many properties with zinc chloride (ZnCl2), namely a high solubility in water forming acidic solutions, and good solubility in organic solvents. It is hygroscopic and forms a dihydrate ZnBr2·2H2O. Production ZnBr2 · 2H2O is prepared by treating zinc oxide or zinc metal with hydrobromic acid. : ZnO + 2HBr + H2O → ZnBr2·2H2O : Zn + 2HBr → ZnBr2 + H2 The anhydrous material can be produced by dehydration of the dihydrate with hot CO2 or by reaction of zinc metal and bromine. Sublimation in a stream of hydrogen bromide also gives the anhydrous derivative. Structure ZnBr2 crystallizes in the same structure as ZnI2: four tetrahedral Zn centers share three vertices to form “super-tetrahedra” of nominal composition 2−, which are linked by their vertices to form a three-dimensional structure. The dihydrate ZnBr2 · 2H2O can be described as ( n(H2O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylmagnesium Bromide
Phenylmagnesium bromide, with the simplified formula , is a magnesium-containing organometallic compound. It is commercially available as a solution in diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran (THF). Phenylmagnesium bromide is a Grignard reagent. It is often used as a synthetic equivalent for the phenyl "Ph−" synthon. Preparation Phenylmagnesium bromide is commercially available as solutions of diethyl ether or THF. Laboratory preparation involves treating bromobenzene with magnesium metal, usually in the form of turnings. A small amount of iodine may be used to activate the magnesium to initiate the reaction. Coordinating solvents such as ether or THF, are required to solvate (complex) the magnesium(II) center. The solvent must be aprotic since alcohols and water contain an acidic proton and thus react with phenylmagnesium bromide to give benzene. Carbonyl-containing solvents, such as acetone and ethyl acetate, are also incompatible with the reagent. Structure Although phen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Chloride
Zinc chloride is the name of inorganic chemical compounds with the formula ZnCl2 and its hydrates. Zinc chlorides, of which nine crystalline forms are known, are colorless or white, and are highly soluble in water. This salt is hygroscopic and even deliquescent. Zinc chloride finds wide application in textile processing, metallurgical fluxes, and chemical synthesis. No mineral with this chemical composition is known aside from the very rare mineral simonkolleite, Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O. Structure and properties Four crystalline forms ( polymorphs) of ZnCl2 are known: α, β, γ, and δ. Each case features tetrahedral Zn2+ centers. Here ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' are lattice constants, ''Z'' is the number of structure units per unit cell, and ρ is the density calculated from the structure parameters. The orthorhombic form (δ) rapidly changes to one of the other forms on exposure to the atmosphere. A possible explanation is that the OH− ions originating from the absorbed water f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphenylmercury
Diphenylmercury is the organomercury compound with the formula Hg(C6H5)2. It is a white solid. The compound is of historic interest as a particularly stable organometallic compound but it finds few uses because of its high toxicity. Preparation Commercially available, this compound can be prepared by several routes. It results from treating phenylmercury acetate with sodium stannite, by the reaction of mercuric halides with phenylmagnesium bromide, and the reaction of bromobenzene with sodium amalgam Sodium amalgam, commonly denoted Na(Hg), is an alloy of mercury and sodium. The term amalgam is used for alloys, intermetallic compounds, and solutions (both solid solutions and liquid solutions) involving mercury as a major component. Sodium am .... Safety Diphenylmercury is highly toxic. References {{Mercury compounds Organomercury compounds Phenyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Of Reagents For Organic Synthesis
The ''Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis'' is published in print and online by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. The online version is also known as e-EROS. The encyclopedia contains a description of the use of reagents used in organic chemistry. The eight-volume print version includes 3500 alphabetically arranged articles and the online version is regularly updated to include new reagents and catalyst Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...s. References External links *Print version Encyclopedias of science Chemistry books {{encyclopedia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |