|
Diatonic Button Accordion
A melodeon or diatonic button accordion is a member of the free-reed aerophone family of musical instruments. It is a type of button accordion on which the melody-side keyboard contains one or more rows of buttons, with each row producing the notes of a single diatonic scale (music), scale. The buttons on the bass (music), bass-side keyboard are most commonly arranged in pairs, with one button of a pair sounding the fundamental of a chord (music), chord and the other the corresponding major triad (music), triad (or, sometimes, a minor triad). Diatonic button accordions are popular in many countries, and used mainly for playing popular music and traditional folk music, and modern offshoots of these genres. Nomenclature Various terms for the diatonic button accordion are used in different parts of the English-speaking world. * In Britain and Australia, the term ''melodeon'' is commonly used, regardless of whether the instrument has one, two, or three rows of melody buttons. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Reed Aerophone
A free reed aerophone is a musical instrument that produces sound as air flows past a vibrating reed in a frame. Air pressure is typically generated by breath or with a bellows. In the Hornbostel–Sachs system, it is number: 412.13 (a member of interruptive free aerophones). Free reed instruments are contrasted with non-free or enclosed reed instruments, where the timbre is fully or partially dependent on the shape of the instrument body, Hornbostel–Sachs number: 42 (flute, reed, and brass). Operation The following illustrations depict the type of reed typical of harmonicas, pitch pipes, accordions, and reed organs as it goes through a cycle of vibration. One side of the reed frame is omitted from the images for clarity; in reality, the frame completely encloses the reed. Airflow over one side of the reed (labeled “AR”) creates a region of low pressure on that side (see the Bernoulli's principle article for details), causing the reed to flex towards the low-pressure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melodeon (organ)
The pump organ is a type of free-reed organ that generates sound as air flows past a vibrating piece of thin metal in a frame. The piece of metal is called a reed. Specific types of pump organ include the reed organ, harmonium, and melodeon. The idea for the free reed was imported from China through Russia after 1750, and the first Western free-reed instrument was made in 1780 in Denmark. More portable than pipe organs, free-reed organs were widely used in smaller churches and in private homes in the 19th century, but their volume and tonal range were limited. They generally had one or sometimes two manuals, with pedal-boards being rare. The finer pump organs had a wider range of tones, and the cabinets of those intended for churches and affluent homes were often excellent pieces of furniture. Several million free-reed organs and melodeons were made in the US and Canada between the 1850s and the 1920s, some of which were exported. The Cable Company, Estey Organ, and Mason & H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorian Mode
Dorian mode or Doric mode can refer to three very different but interrelated subjects: one of the Ancient Greek ''harmoniai'' (characteristic melodic behaviour, or the scale structure associated with it); one of the medieval musical modes; or—most commonly—one of the modern modal diatonic scales, corresponding to the piano keyboard's white notes from D to D, or any transposition of itself. : Greek Dorian mode The Dorian mode (properly ''harmonia'' or ''tonos'') is named after the Dorian Greeks. Applied to a whole octave, the Dorian octave species was built upon two tetrachords (four-note segments) separated by a whole tone, running from the ''hypate meson'' to the ''nete diezeugmenon''. In the enharmonic genus, the intervals in each tetrachord are quarter tone–quarter tone–major third. : In the chromatic genus, they are semitone–semitone–minor third. : In the diatonic genus, they are semitone–tone–tone. : In the diatonic genus, the sequence over the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixolydian Mode
Mixolydian mode may refer to one of three things: the name applied to one of the ancient Greek ''harmoniai'' or ''tonoi'', based on a particular octave species or scale; one of the medieval church modes; or a modern musical mode or diatonic scale, related to the medieval mode. (The Hypomixolydian mode of medieval music, by contrast, has no modern counterpart.) The modern diatonic mode is the scale forming the basis of both the rising and falling forms of Harikambhoji in Carnatic music, the classical music form of southern India. Greek Mixolydian The idea of a Mixolydian mode comes from the music theory of ancient Greece. The invention of the ancient Greek Mixolydian mode was attributed to Sappho, the poet and musician. However, what the ancient Greeks thought of as Mixolydian is very different from the modern interpretation of the mode. The prefix ''mixo''- (μιξο-) means "half", referring to its resemblance to the Lydian mode. In Greek theory, the Mixolydian ''tonos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Scale
In music theory, the minor scale is three scale patterns – the natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode), the harmonic minor scale, and the melodic minor scale (ascending or descending) – rather than just two as with the major scale, which also has a harmonic form but lacks a melodic form. In each of these scales, the first, third, and fifth scale degrees form a minor triad (rather than a major triad, as in a major scale). In some contexts, ''minor scale'' is used to refer to any heptatonic scale with this property (see Related modes below). Natural minor scale Relationship to relative major A natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode) is a diatonic scale that is built by starting on the sixth degree of its relative major scale. For instance, the A natural minor scale can be built by starting on the 6th degree of the C major scale: : Because of this, the key of A minor is called the ''relative minor'' of C major. Every major key has a relative minor, which st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
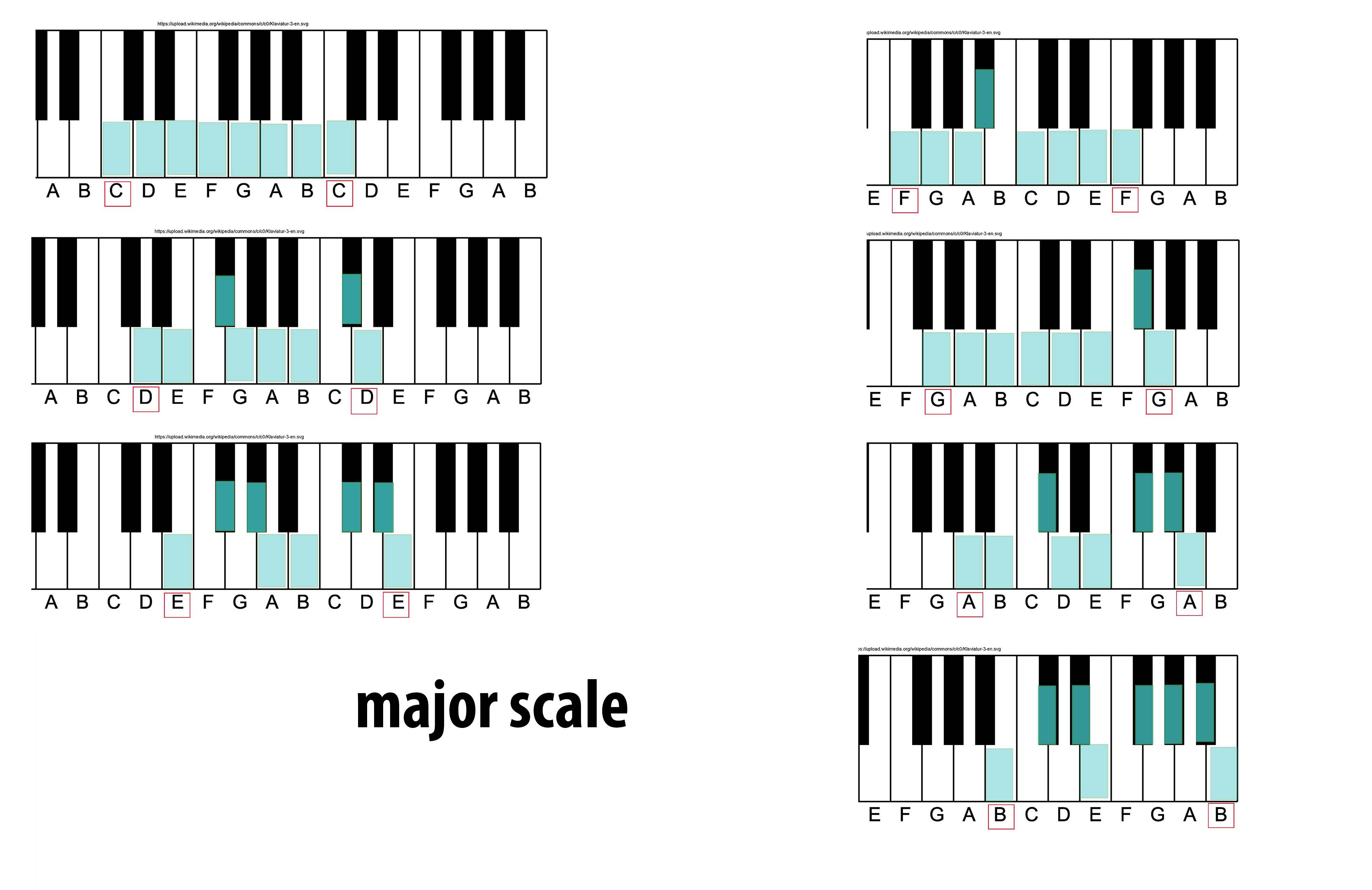
Major Scale
The major scale (or Ionian mode) is one of the most commonly used musical scales, especially in Western music. It is one of the diatonic scales. Like many musical scales, it is made up of seven notes: the eighth duplicates the first at double its frequency so that it is called a higher octave of the same note (from Latin "octavus", the eighth). The simplest major scale to write is C major, the only major scale not requiring sharps or flats: The major scale had a central importance in Western music, particularly in the common practice period and in popular music. In Carnatic music, it is known as '' Sankarabharanam''. In Hindustani classical music, it is known as '' Bilaval''. Structure A major scale is a diatonic scale. The sequence of intervals between the notes of a major scale is: : whole, whole, half, whole, whole, whole, half where "whole" stands for a whole tone (a red u-shaped curve in the figure), and "half" stands for a semitone (a red angled line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Button Accordion
German(s) may refer to: * Germany (of or related to) **Germania (historical use) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman times) * German language **any of the Germanic languages * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (other) * Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonica
The harmonica, also known as a French harp or mouth organ, is a free reed wind instrument used worldwide in many musical genres, notably in blues, American folk music, classical music, jazz, country, and rock. The many types of harmonica include diatonic, chromatic, tremolo, octave, orchestral, and bass versions. A harmonica is played by using the mouth (lips and tongue) to direct air into or out of one (or more) holes along a mouthpiece. Behind each hole is a chamber containing at least one reed. The most common is the diatonic Richter-tuned with ten air passages and twenty reeds, often called the blues harp. A harmonica reed is a flat, elongated spring typically made of brass, stainless steel, or bronze, which is secured at one end over a slot that serves as an airway. When the free end is made to vibrate by the player's air, it alternately blocks and unblocks the airway to produce sound. Reeds are tuned to individual pitches. Tuning may involve changing a reed’s len ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandoneon
The bandoneon (or bandonion, es, bandoneón) is a type of concertina particularly popular in Argentina and Uruguay. It is a typical instrument in most tango ensembles. As with other members of the concertina family, the bandoneon is held between the hands, and by pulling and pushing actions force air through bellows and then routing air through particular reeds as by pressing the instrument's buttons. Bandoneons have a different sound from accordions, because bandoneons do not usually have the register switches that are common on accordions. Nevertheless, the tone of the bandoneon can be changed a great deal using varied bellows pressure and overblowing, thus creating potential for expressive playing and diverse timbres. History The Bandonion, so named by the German instrument dealer Heinrich Band (1821–1860), was originally intended as an instrument for religious and popular music of the day, in contrast to its predecessor, German concertina (), which had predominantly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |