|
Days Sales Outstanding
In accountancy, days sales outstanding (also called DSO and days receivables) is a calculation used by a company to estimate the size of their outstanding accounts receivable. It measures this size not in units of currency, but in average sales days. Typically, days sales outstanding is calculated monthly. Generally speaking, higher DSO ratio can indicate a customer base with credit problems and/or a company that is deficient in its collections activity. A low ratio may indicate the firm's credit policy is too rigorous, which may be hampering sales. Days sales outstanding is often misinterpreted as "the average number of days to fully collect payment after making a sale". The formula for this would be Σ. This calculation is sometimes called "True DSO". Instead, days sales outstanding is better interpreted as the "days worth of (average) sales that you currently have outstanding". Accordingly, days sales outstanding can be expressed as the following financial ratio: :DSO ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accountancy
Accounting, also known as accountancy, is the measurement, processing, and communication of financial and non financial information about economic entities such as businesses and corporations. Accounting, which has been called the "language of business", measures the results of an organization's economic activities and conveys this information to a variety of stakeholders, including investors, creditors, management, and regulators. Practitioners of accounting are known as accountants. The terms "accounting" and " financial reporting" are often used as synonyms. Accounting can be divided into several fields including financial accounting, management accounting, tax accounting and cost accounting. Financial accounting focuses on the reporting of an organization's financial information, including the preparation of financial statements, to the external users of the information, such as investors, regulators and suppliers; and management accounting focuses on the measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accounts Receivable
Accounts receivable, abbreviated as AR or A/R, are legally enforceable claims for payment held by a business for goods supplied or services rendered that customers have ordered but not paid for. These are generally in the form of invoices raised by a business and delivered to the customer for payment within an agreed time frame. Accounts receivable is shown in a balance sheet as an asset. It is one of a series of accounting transactions dealing with the billing of a customer for goods and services that the customer has ordered. These may be distinguished from notes receivable, which are debts created through formal legal instruments called promissory notes. Overview Accounts receivable represents money owed by entities to the firm on the sale of products or services on credit. In most business entities, accounts receivable is typically executed by generating an invoice and either mailing or electronically delivering it to the customer, who, in turn, must pay it within an es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Ratio
A financial ratio or accounting ratio is a relative magnitude of two selected numerical values taken from an enterprise's financial statements. Often used in accounting, there are many standard ratios used to try to evaluate the overall financial condition of a corporation or other organization. Financial ratios may be used by managers within a firm, by current and potential shareholders (owners) of a firm, and by a firm's creditors. Financial analysts use financial ratios to compare the strengths and weaknesses in various companies. If shares in a company are traded in a financial market, the market price of the shares is used in certain financial ratios. Ratios can be expressed as a decimal value, such as 0.10, or given as an equivalent percent value, such as 10%. Some ratios are usually quoted as percentages, especially ratios that are usually or always less than 1, such as earnings yield, while others are usually quoted as decimal numbers, especially ratios that are usuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
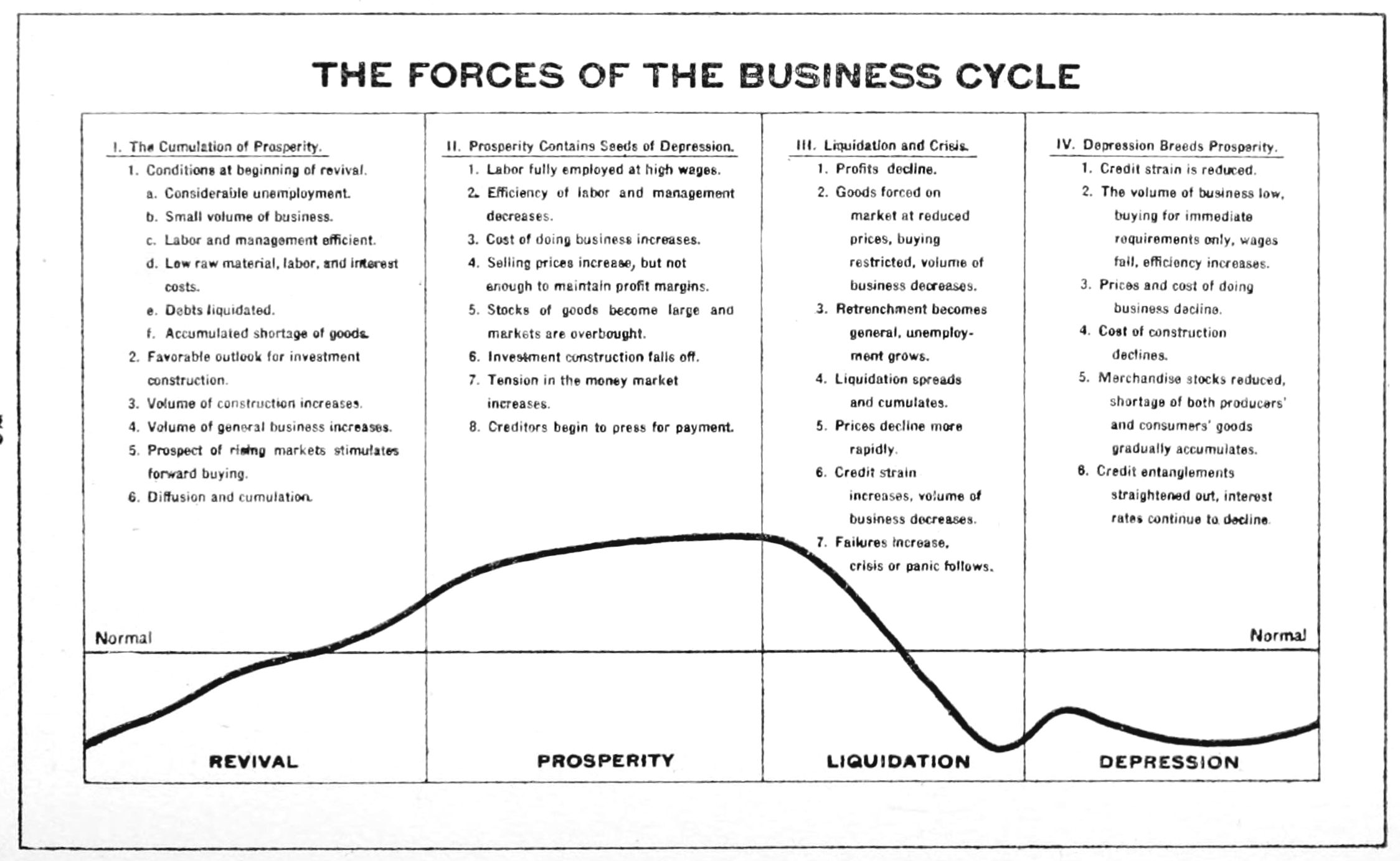
Business Cycle
Business cycles are intervals of expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by examining trends in a broad economic indicator such as Real Gross Domestic Production. Business cycle fluctuations are usually characterized by general upswings and downturns in a span of macroeconomic variables. The individual episodes of expansion/recession occur with changing duration and intensity over time. Typically their periodicity has a wide range from around 2 to 10 years (the technical phrase "stochastic cycle" is often used in statistics to describe this kind of process.) As in arvey, Trimbur, and van Dijk, 2007, ''Journal of Econometrics'' such flexible knowledge about the frequency of business cycles can actually be included in their mathematical study, using a Bayesian statistical paradigm. There are numerous sources of busines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Working Capital
Working capital (WC) is a financial metric which represents operating liquidity available to a business, organisation, or other entity, including governmental entities. Along with fixed assets such as plant and equipment, working capital is considered a part of operating capital. Gross working capital is equal to current assets. Working capital is calculated as current assets minus current liabilities. If current assets are less than current liabilities, an entity has a working capital deficiency, also called a working capital deficit and negative working capital. A company can be endowed with assets and profitability but may fall short of liquidity if its assets cannot be readily converted into cash. Positive working capital is required to ensure that a firm is able to continue its operations and that it has sufficient funds to satisfy both maturing short-term debt and upcoming operational expenses. The management of working capital involves managing inventories, accounts rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Days Payable Outstanding
Days payable outstanding (DPO) is an efficiency ratio that measures the average number of days a company takes to pay its suppliers. The formula for DPO is: DPO = \dfrac{Purchase/day} where ending A/P is the accounts payable balance at the end of the accounting period being considered and Purchase/day is calculated by dividing the total cost of goods sold per year by 365 days.Berman, K., Knight, J., Case, J.: ''Financial Intelligence for Entrepreneurs'', page 151. Harvard Business Press, 2008. DPO provides one measure of how long a business holds onto its cash. DPO can also be used to compare one company's payment policies to another. Having fewer days of payables on the books than your competitors means they are getting better credit terms from their vendors than you are from yours. If a company is selling something to a customer, they can use that customer's DPO to judge when the customer will pay (and thus what payment terms to offer or expect). Having a greater days payabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Days In Inventory
Days in inventory (also known as "Inventory Days of Supply", "Days Inventory Outstanding" or the "Inventory Period") is an efficiency ratio that measures the average number of days the company holds its inventory before selling it. The ratio measures the number of days funds are tied up in inventory. Inventory levels (measured at cost) are divided by sales per day (also measured at cost rather than selling price.) The formula for days in inventory is: DII = \dfrac where DII is days in inventory and COGS is cost of goods sold Cost of goods sold (COGS) is the carrying value of goods sold during a particular period. Costs are associated with particular goods using one of the several formulas, including specific identification, first-in first-out (FIFO), or average cost. .... The average inventory is the average of inventory levels at the beginning and end of an accounting period, and COGS/day is calculated by dividing the total cost of goods sold per year by the number of days in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cash Conversion Cycle
In management accounting, the Cash conversion cycle (CCC) measures how long a firm will be deprived of cash if it increases its investment in inventory in order to expand customer sales. It is thus a measure of the liquidity risk entailed by growth. However, shortening the CCC creates its own risks: while a firm could even achieve a negative CCC by collecting from customers before paying suppliers, a policy of strict collections and lax payments is not always sustainable. Definition ''CCC'' is days between ''disbursing cash'' and ''collecting cash'' in connection with undertaking a discrete unit of operations. : Derivation Cashflows insufficient. The term "Cash Conversion Cycle" refers to the timespan between a firm's disbursing and collecting cash. However, the CCC cannot be directly observed in cashflows, because these are also influenced by investment and financing activities; it must be derived from Statement of Financial Position data associated with the firm's operations. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Ratios
A financial ratio or accounting ratio is a relative magnitude of two selected numerical values taken from an enterprise's financial statements. Often used in accounting, there are many standard ratios used to try to evaluate the overall financial condition of a corporation or other organization. Financial ratios may be used by managers within a firm, by current and potential shareholders (owners) of a firm, and by a firm's creditors. Financial analysts use financial ratios to compare the strengths and weaknesses in various companies. If shares in a company are traded in a financial market, the market price of the shares is used in certain financial ratios. Ratios can be expressed as a decimal value, such as 0.10, or given as an equivalent percent value, such as 10%. Some ratios are usually quoted as percentages, especially ratios that are usually or always less than 1, such as earnings yield, while others are usually quoted as decimal numbers, especially ratios that are usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Working Capital Management
Corporate finance is the area of finance that deals with the sources of funding, the capital structure of corporations, the actions that managers take to increase the value of the firm to the shareholders, and the tools and analysis used to allocate financial resources. The primary goal of corporate finance is to maximize or increase shareholder value. Correspondingly, corporate finance comprises two main sub-disciplines. Capital budgeting is concerned with the setting of criteria about which value-adding projects should receive investment funding, and whether to finance that investment with equity or debt capital. Working capital management is the management of the company's monetary funds that deal with the short-term operating balance of current assets and current liabilities; the focus here is on managing cash, inventories, and short-term borrowing and lending (such as the terms on credit extended to customers). The terms corporate finance and corporate financier are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accounts Receivable
Accounts receivable, abbreviated as AR or A/R, are legally enforceable claims for payment held by a business for goods supplied or services rendered that customers have ordered but not paid for. These are generally in the form of invoices raised by a business and delivered to the customer for payment within an agreed time frame. Accounts receivable is shown in a balance sheet as an asset. It is one of a series of accounting transactions dealing with the billing of a customer for goods and services that the customer has ordered. These may be distinguished from notes receivable, which are debts created through formal legal instruments called promissory notes. Overview Accounts receivable represents money owed by entities to the firm on the sale of products or services on credit. In most business entities, accounts receivable is typically executed by generating an invoice and either mailing or electronically delivering it to the customer, who, in turn, must pay it within an es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |