|
DVD-RW
DVD recordable and DVD rewritable are optical disc recording technologies. Both terms describe DVD optical discs that can be written to by a DVD recorder, whereas only 'rewritable' discs are able to erase and rewrite data. Data is written ('burned') to the disc by a laser, rather than the data being 'pressed' onto the disc during manufacture, like a DVD-ROM. Pressing is used in mass production, primarily for the distribution of home video. Like CD-Rs, DVD recordable uses dye to store the data. During the burning of a single bit, the laser's intensity affects the reflective properties of the burned dye. By varying the laser intensity quickly, high density data is written in precise tracks. Since written tracks are made of darkened dye, the data side of a recordable DVD has a distinct color. Burned DVDs have a higher failure-to-read rate than pressed DVDs, due to differences in the reflective properties of dye compared to the aluminum substrate of pressed discs. Comparing recor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVD-R
DVD recordable and DVD rewritable are optical disc recording technologies. Both terms describe DVD optical discs that can be written to by a DVD recorder, whereas only 'rewritable' discs are able to erase and rewrite data. Data is written ('burned') to the disc by a laser, rather than the data being 'pressed' onto the disc during manufacture, like a DVD-ROM. Pressing is used in mass production, primarily for the distribution of home video. Like CD-Rs, DVD recordable uses dye to store the data. During the burning of a single bit, the laser's intensity affects the reflective properties of the burned dye. By varying the laser intensity quickly, high density data is written in precise tracks. Since written tracks are made of darkened dye, the data side of a recordable DVD has a distinct color. Burned DVDs have a higher failure-to-read rate than pressed DVDs, due to differences in the reflective properties of dye compared to the aluminum substrate of pressed discs. Comparing recor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
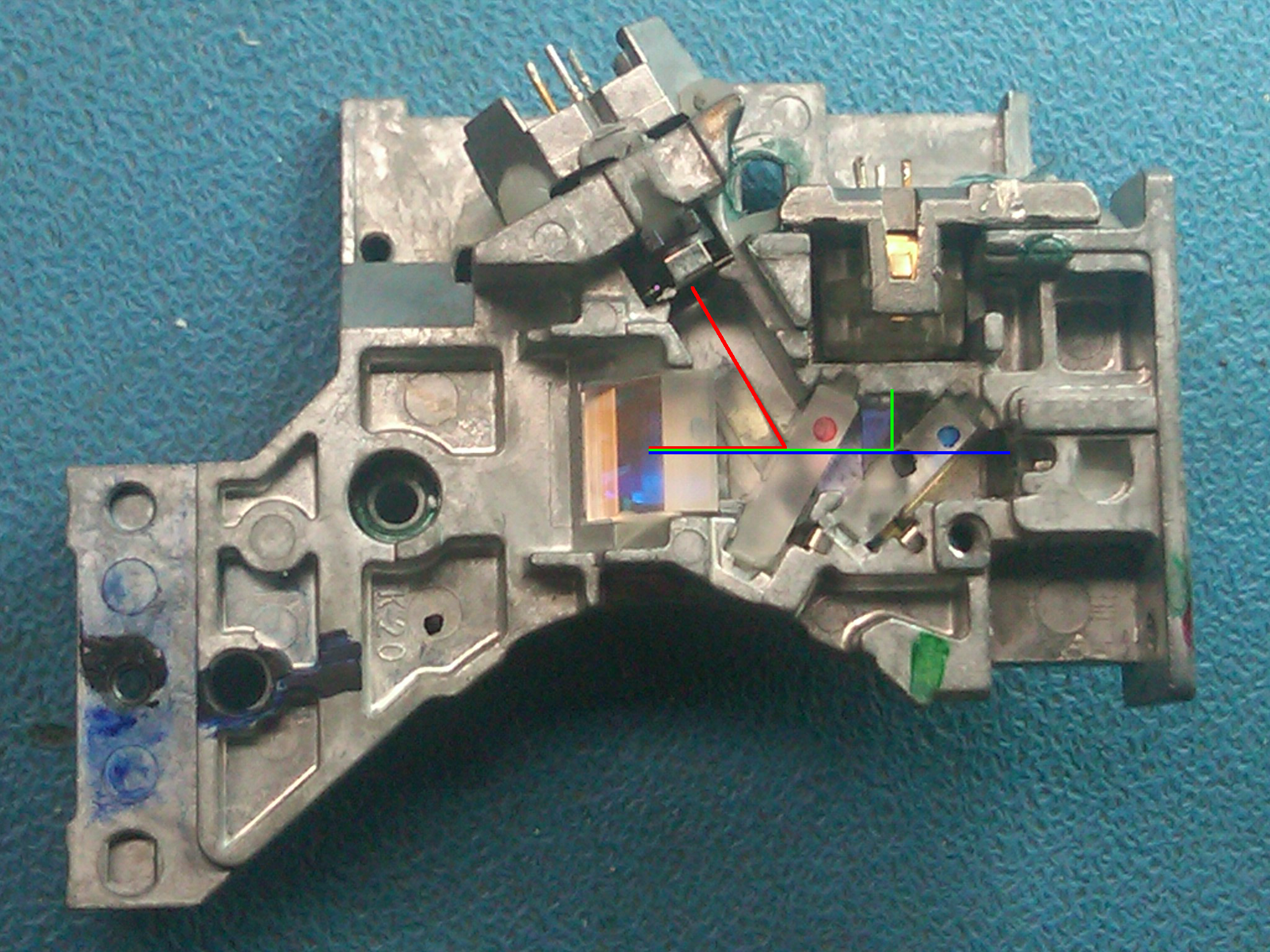
Optical Drive
In computing, an optical disc drive is a disc drive that uses laser light or electromagnetic waves within or near the visible light spectrum as part of the process of reading or writing data to or from optical discs. Some drives can only read from certain discs, but recent drives can both read and record, also called burners or writers (since they physically burn the organic dye on write-once CD-R, DVD-R and BD-R LTH discs). Compact discs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs are common types of optical media which can be read and recorded by such drives. Drive types , most of the optical disc drives on the market are DVD-ROM drives and BD-ROM drives which read and record from those formats, along with having backward compatibility with CD, CD-R and CD-ROM discs; compact disc drives are no longer manufactured outside of audio devices. Read-only DVD and Blu-ray drives are also manufactured, but are less commonly found in the consumer market and mainly limited to media devices such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVD-ROM
The DVD (common abbreviation for Digital Video Disc or Digital Versatile Disc) is a digital optical disc data storage format. It was invented and developed in 1995 and first released on November 1, 1996, in Japan. The medium can store any kind of digital data and has been widely used for video programs (watched using DVD players) or formerly for storing software and other computer files as well. DVDs offer significantly higher storage capacity than compact discs (CD) while having the same dimensions. A standard DVD can store up to 4.7 GB of storage, while variants can store up to a maximum of 17.08 GB. Prerecorded DVDs are mass-produced using molding machines that physically stamp data onto the DVD. Such discs are a form of DVD-ROM because data can only be read and not written or erased. Blank recordable DVD discs (DVD-R and DVD+R) can be recorded once using a DVD recorder and then function as a DVD-ROM. Rewritable DVDs (DVD-RW, DVD+RW, and DVD-RAM) can be recorded and erase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVD-RAM
DVD-RAM (DVD Random Access Memory) is a DVD-based disc specification presented in 1996 by the DVD Forum, which specifies rewritable DVD-RAM media and the appropriate DVD writers. DVD-RAM media have been used in computers as well as camcorders and personal video recorders since 1998. In May 2019, Panasonic, the only remaining manufacturer of DVD-RAM discs, announced that it would end production of DVD-RAM media by the end of that month, citing shrinking demand as the primary motivation. Panasonic made its discs under its own brand name and also under the Verbatim brand. Cartridge types Format DVD-RAM works by means of phase change technology which was chosen instead of magneto-optical technology (an already existing rewritable solution at the time) because it doesn't require a magnetic head and therefore it represented reduced complexity and costs. Phase change technology uses laser light to heat the surface of a phase changing alloy and allows it to go from a crystalline t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVD Recorder
A DVD recorder is an optical disc recorder that uses optical disc recording technologies to digitally record analog or digital signals onto blank writable DVD media. Such devices are available as either installable drives for computers or as standalone components for use in television studios or home theater systems. As of March 1, 2007 all new tuner-equipped television devices manufactured or imported in the United States must include an ATSC tuner. The US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has interpreted this rule broadly, including apparatus such as computers with TV tuner cards with video capture ability, videocassette recorders and standalone DVD recorders. NTSC DVD recorders are undergoing a transformation, either adding a digital ATSC tuner or removing over-the-air broadcast television tuner capability entirely. However, these DVD recorders can still record analog audio and analog video. Standalone DVD recorders, alongside Blu-ray recorders, have been relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wobble Frequency
Optical discs, with the exception of DVD-RAM, have their data encoded on a single spiral, or a ''groove'', which covers the surface of the disc. In the case of recordable media, this spiral contains a slight sinusoidal deviation from a perfect spiral. The period of this sine curve corresponds to the wobble frequency. The wobble frequency is commonly used as a synchronization source to achieve constant linear velocity while writing a disc, but has other uses as well depending on the type of disc. The frequencies quoted all assume that the disc is being written at the '1x' speed. The frequencies are appropriately higher for faster writing speeds. CD-R and CD-RW discs use a frequency modulated wobble of 22.05 kHz to encode information, such as the Absolute Time in Pregroove (ATIP), into the groove. DVD-R and DVD-RW have a constant wobble frequency of 140.6 kHz relying on data 'pits' beside the groove to convey information (Land pre-pit). DVD+R and DVD+RW have a constant wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wobble Frequency
Optical discs, with the exception of DVD-RAM, have their data encoded on a single spiral, or a ''groove'', which covers the surface of the disc. In the case of recordable media, this spiral contains a slight sinusoidal deviation from a perfect spiral. The period of this sine curve corresponds to the wobble frequency. The wobble frequency is commonly used as a synchronization source to achieve constant linear velocity while writing a disc, but has other uses as well depending on the type of disc. The frequencies quoted all assume that the disc is being written at the '1x' speed. The frequencies are appropriately higher for faster writing speeds. CD-R and CD-RW discs use a frequency modulated wobble of 22.05 kHz to encode information, such as the Absolute Time in Pregroove (ATIP), into the groove. DVD-R and DVD-RW have a constant wobble frequency of 140.6 kHz relying on data 'pits' beside the groove to convey information (Land pre-pit). DVD+R and DVD+RW have a constant wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Disc
In computing and optical disc recording technologies, an optical disc (OD) is a flat, usually circular disc that encodes binary data (bits) in the form of pits and lands on a special material, often aluminum, on one of its flat surfaces. Its main uses are physical offline data distribution and long-term archival. Changes from pit to land or from land to pit correspond to a binary value of 1; while no change, regardless of whether in a land or a pit area, corresponds to a binary value of 0. Non-circular optical discs exist for fashion purposes; see shaped compact disc. Design and technology The encoding material sits atop a thicker substrate (usually polycarbonate) that makes up the bulk of the disc and forms a dust defocusing layer. The encoding pattern follows a continuous, spiral path covering the entire disc surface and extending from the innermost track to the outermost track. The data are stored on the disc with a laser or stamping machine, and can be accessed w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Disc Recording Technologies
Optical disc authoring requires a number of different optical disc recorder technologies working in tandem, from the optical disc media to the firmware to the control electronics of the optical disc drive. Types of recordable optical disc There are numerous formats of recordable optical direct to disk on the market, all of which are based on using a laser to change the reflectivity of the digital recording medium in order to duplicate the effects of the pits and lands created when a commercial optical disc is pressed. Emerging technologies such as holographic data storage and 3D optical data storage aim to use entirely different data storage methods, but these products are in development and are not yet widely available. The earliest form is magneto-optical, which uses a magnetic field in combination with a laser to write to the medium. Though not widely used in consumer equipment, the original NeXT cube used MO media as its standard storage device, and consumer MO techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD-RW
CD-RW (Compact Disc-Rewritable) is a digital optical disc storage format introduced in 1997. A CD-RW compact disc (CD-RWs) can be written, read, erased, and re-written. CD-RWs, as opposed to CDs, require specialized readers that have sensitive laser optics. Consequently, CD-RWs cannot be read in many CD readers built prior to the introduction of CD-RW. CD-ROM drives with a "MultiRead" certification are compatible. CD-RWs must be erased or blanked before reuse. Erasure methods include full blanking where the entire surface of the disc is erased and fast blanking where only metadata areas, such as PMA, TOC and pregap, are cleared. Fast blanking is quicker and usually sufficient to allow rewriting the disc. Full blanking removes all traces of the previous data, and is often used for confidentiality purposes. CD-RWs can sustain fewer re-writes compared to other storage media (ca. 1,000 compared up to 100,000). Ideal use is for test discs (e.g. for CD authoring), temporary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVD±R
DVD±R (also DVD+/-R, or "DVD plus/dash R") is not a separate DVD format, but rather is a shorthand term for a DVD drive that can accept both of the common recordable DVD formats (i.e. DVD-R and DVD+R). Likewise, DVD±RW (also written as DVD±R/W, DVD±R/RW, DVD±R/±RW, DVD+/-RW, and other arbitrary ways) handles both common rewritable disc types (i.e. DVD-RW and DVD+RW, but not usually DVD-RAM).. See also * DVD-R * DVD+R * DVD-RW * DVD+RW DVD recordable and DVD rewritable are optical disc recording technologies. Both terms describe DVD optical discs that can be written to by a DVD recorder, whereas only 'rewritable' discs are able to erase and rewrite data. Data is written ('burn ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Dvd R DVD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Disc
In computing and optical disc recording technologies, an optical disc (OD) is a flat, usually circular disc that encodes binary data (bits) in the form of pits and lands on a special material, often aluminum, on one of its flat surfaces. Its main uses are physical offline data distribution and long-term archival. Changes from pit to land or from land to pit correspond to a binary value of 1; while no change, regardless of whether in a land or a pit area, corresponds to a binary value of 0. Non-circular optical discs exist for fashion purposes; see shaped compact disc. Design and technology The encoding material sits atop a thicker substrate (usually polycarbonate) that makes up the bulk of the disc and forms a dust defocusing layer. The encoding pattern follows a continuous, spiral path covering the entire disc surface and extending from the innermost track to the outermost track. The data are stored on the disc with a laser or stamping machine, and can be accessed w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |