|
Dutch Conjugation
This article explains the conjugation of verbs in Dutch by their classification, which is based on conjugational class and derivation. These classifications describe different aspects of verb structure and usage. Classification of verbs By conjugational class Dutch verbs can be grouped by their conjugational class, as follows: * Weak verbs: past tense and past participle formed with a dental suffix ** Weak verbs with past in ''-de'' ** Weak verbs with past in ''-te'' * Strong verbs: past tense formed by changing the vowel of the stem, past participle in ''-en'' ** Class 1: pattern ''ij-ee-ee'' ** Class 2: pattern ''ie-oo-oo'' or ''ui-oo-oo'' ** Class 3: pattern ''i-o-o'' or ''e-o-o'' ** Class 4: pattern ''ee-a/aa-oo'' ** Class 5: pattern ''ee-a/aa-ee'' or ''i-a/aa-ee'' ** Class 6: pattern ''aa-oe-aa'' ** Class 7: pattern ''X-ie-X'' (specifically, ''oo-ie-oo'', ''a-ie-a'', ''a-i-a'', ''ou-iel-ou'', ''aa-ie-aa'' or ''oe-ie-oe'') ** Other strong verbs, which do not follow any of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Conjugation
In linguistics, conjugation ( ) is the creation of derived forms of a verb from its principal parts by inflection (alteration of form according to rules of grammar). For instance, the verb ''break'' can be conjugated to form the words ''break'', ''breaks'', and ''broke''. While English has a relatively simple conjugation, other languages such as French and Arabic or Spanish are more complex, with each verb having dozens of conjugated forms. Some languages such as Georgian and Basque (some verbs only) have highly complex conjugation systems with hundreds of possible conjugations for every verb. Verbs may inflect for grammatical categories such as person, number, gender, case, tense, aspect, mood, voice, possession, definiteness, politeness, causativity, clusivity, interrogatives, transitivity, valency, polarity, telicity, volition, mirativity, evidentiality, animacy, associativity, pluractionality, and reciprocity. Verbs may also be affected by agreement, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiceless
In linguistics, voicelessness is the property of sounds being pronounced without the larynx vibrating. Phonologically, it is a type of phonation, which contrasts with other states of the larynx, but some object that the word phonation implies voicing and that voicelessness is the lack of phonation. The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) has distinct letters for many voiceless and modally voiced pairs of consonants (the obstruents), such as . Also, there are diacritics for voicelessness, and , which is used for letters with a descender. Diacritics are typically used with letters for prototypically voiced sounds, such as vowels and sonorant consonants: . In Russian use of the IPA, the voicing diacritic may be turned for voicelessness, e.g. . Voiceless vowels and other sonorants Sonorants are sounds such as vowels and nasals that are voiced in most of the world's languages. However, in some languages sonorants may be voiceless, usually allophonically. For example, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
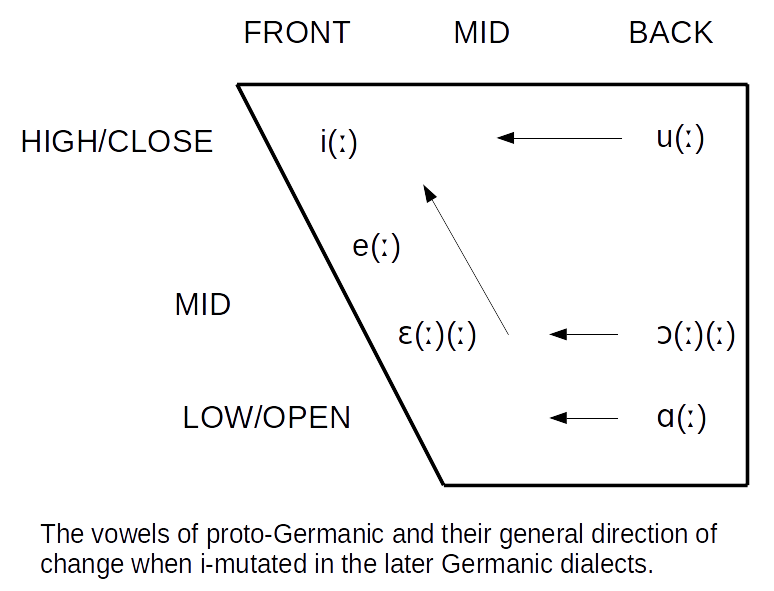
Rückumlaut
The Germanic umlaut (sometimes called i-umlaut or i-mutation) is a type of linguistic umlaut in which a back vowel changes to the associated front vowel ( fronting) or a front vowel becomes closer to ( raising) when the following syllable contains , , or . It took place separately in various Germanic languages starting around 450 or 500 CE and affected all of the early languages except Gothic. An example of the resulting vowel alternation is the English plural ''foot ~ feet'' (from Proto-Germanic , pl. ). Germanic umlaut, as covered in this article, does not include other historical vowel phenomena that operated in the history of the Germanic languages such as Germanic a-mutation and the various language-specific processes of u-mutation, nor the earlier Indo-European ablaut (''vowel gradation''), which is observable in the conjugation of Germanic strong verbs such as ''sing/sang/sung''. While Germanic umlaut has had important consequences for all modern Germanic language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ablaut
In linguistics, the Indo-European ablaut ( , from German ) is a system of apophony (regular vowel variations) in the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). An example of ablaut in English is the strong verb ''sing, sang, sung'' and its related noun ''song'', a paradigm inherited directly from the Proto-Indo-European stage of the language. Traces of ablaut are found in all modern Indo-European languages, though its prevalence varies greatly. History of the concept The phenomenon of Indo-European ablaut was first recorded by Sanskrit grammarians in the later Vedic period (roughly 8th century BCE), and was codified by Pāṇini in his ''Aṣṭādhyāyī'' (4th century BCE), where the terms ' and '' '' were used to describe the phenomena now known respectively as the ''full grade'' and ''lengthened grade''.Burrow, §2.1. In the context of European languages, the phenomenon was first described in the early 18th century by the Dutch linguist Lambert ten Kate, in his book ''G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reduplication
In linguistics, reduplication is a Morphology (linguistics), morphological process in which the Root (linguistics), root or Stem (linguistics), stem of a word, part of that, or the whole word is repeated exactly or with a slight change. The classic observation on the semantics of reduplication is Edward Sapir, Edward Sapir's: "Generally employed, with self-evident symbolism, to indicate such concepts as distribution, plurality, repetition, customary activity, increase of size, added intensity, continuance." It is used in inflections to convey a grammatical function, such as plurality or intensification, and in Lexicon, lexical Derivation (linguistics), derivation to create new words. It is often used when a speaker adopts a tone more expressive or figurative than ordinary speech and is also often, but not exclusively, Iconicity, iconic in meaning. It is found in a wide range of languages and language groups, though its level of Productivity (linguistics), linguistic productivit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatischer Wechsel
In historical linguistics, the German term ' ("grammatical alternation") refers to the effects of Verner's law when they are viewed synchronically within the paradigm of a Germanic verb. Overview According to Grimm's law, the Proto-Indo-European (PIE) voiceless stops ''*p'', ''*t'', ''*k'' and ''*kʷ'' usually became Proto-Germanic ''*f'', ''*θ'' (dental fricative), ''*x'' and ''*xʷ'' (velar fricative). Karl Verner identified the principle that they instead become the voiced consonants ''*b'', ''*d'', ''*g'', ''*gʷ'' if they were word-internal and immediately preceded by an unaccented vowel in PIE. Furthermore, PIE ''*s'', which usually came into Germanic unchanged, became ''*z'' in this position; this ''*z'' later became North and West Germanic ''*r''. Consequently, five pairs of consonants emerged, each pair representing a single PIE phoneme. The following table shows the precise developments from Proto-Indo-European through Proto-Germanic to Old Norse, West Germanic, Ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suppletion
In linguistics and etymology, suppletion is traditionally understood as the use of one word as the inflected form of another word when the two words are not cognate. For those learning a language, suppletive forms will be seen as "irregular" or even "highly irregular". For example, ''go:went'' is a suppletive paradigm, because ''go'' and ''went'' are not etymologically related, whereas ''mouse:mice'' is irregular but not suppletive, since the two words come from the same Old English ancestor. The term "suppletion" implies that a gap in the paradigm was filled by a form "supplied" by a different paradigm. Instances of suppletion are overwhelmingly restricted to the most commonly used lexical items in a language. Irregularity and suppletion An irregular paradigm is one in which the derived forms of a word cannot be deduced by simple rules from the base form. For example, someone who knows only a little English can deduce that the plural of ''girl'' is ''girls'' but cannot deduce t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxiliary Verb
An auxiliary verb ( abbreviated ) is a verb that adds functional or grammatical meaning to the clause in which it occurs, so as to express tense, aspect, modality, voice, emphasis, etc. Auxiliary verbs usually accompany an infinitive verb or a participle, which respectively provide the main semantic content of the clause. An example is the verb ''have'' in the sentence ''I have finished my lunch.'' Here, the auxiliary ''have'' helps to express the perfect aspect along with the participle, ''finished''. Some sentences contain a chain of two or more auxiliary verbs. Auxiliary verbs are also called helping verbs, helper verbs, or (verbal) auxiliaries. Research has been conducted into split inflection in auxiliary verbs. Basic examples Below are some sentences that contain representative auxiliary verbs from English, Spanish, German and French, with the auxiliary verb marked in bold: ::a. Do you want tea? – ''do'' is an auxiliary accompanying the infinitive, ''want'', used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Verbs
The Germanic language family is one of the language groups that resulted from the breakup of Proto-Indo-European (PIE). It in turn divided into North, West and East Germanic groups, and ultimately produced a large group of mediaeval and modern languages, most importantly: Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish (North); English, Dutch and German (West); and Gothic (East, extinct). The Germanic verb system lends itself to both descriptive (synchronic) and historical (diachronic) comparative analysis. This overview article is intended to lead into a series of specialist articles discussing historical aspects of these verbs, showing how they developed out of PIE, and how they came to have their present diversity. Verb types The Germanic verb system carried two innovations over the previous Proto-Indo-European verb system: # Simplification to two tenses: present (also conveying future meaning) and past (sometimes called "preterite" and conveying the meaning of all of the following Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-vocalization
''L''-vocalization, in linguistics, is a process by which a lateral approximant sound such as , or, perhaps more often, velarized , is replaced by a vowel or a semivowel. Types There are two types of ''l''-vocalization: * A labiovelar approximant, velar approximant, or back vowel: > or > or * A front vowel or palatal approximant: > > West Germanic languages Examples of L-vocalization can be found in many West Germanic languages, including English, Scots, Dutch, and some German dialects. Early Modern English L-vocalization has occurred, since Early Modern English, in certain ''-al-'' and ''-ol-'' sequences before coronal consonant, coronal or velar consonant, velar consonants, or at the end of a word or morpheme. In those sequences, became and diphthonged to , while became and diphthonged to . At the end of a word or morpheme, it produced ''all'', ''ball'', ''call'', ''control'', ''droll'', ''extol'', ''fall'', ''gall'', ''hall'', ''knoll'', ''mall'', ''pall'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Germanic Gemination
West Germanic gemination was a sound change that took place in all West Germanic languages around the 3rd or 4th century AD. It affected consonants directly followed by , which were generally lengthened or geminated in that position. Because of Sievers' law, only consonants immediately after a short vowel were affected by the process. Overview When followed by , consonants were lengthened (doubled). The consonant , whether original or from earlier through rhotacization, was generally not affected; it occasionally shows gemination in Old High German, but inconsistently and this may be an analogical change. In contrast, the second element of the diphthongs ''iu'' and ''au'' was still underlyingly the consonant at this time, and therefore was lengthened as well. In Proto-Germanic, only appeared at the beginning of a syllable, primarily as the onset of a variety of suffixes and endings. It alternated with its syllabic counterpart in accordance with a phonological rule known as S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstruent Consonant
An obstruent ( ) is a speech sound such as , , or that is formed by ''obstructing'' airflow. Obstruents contrast with sonorants, which have no such obstruction and so resonate. All obstruents are consonants, but sonorants include vowels as well as consonants. Subclasses Obstruents are subdivided into: * plosives (oral stops), such as , with complete occlusion of the vocal tract, often followed by a release burst; * fricatives, such as , with limited closure, not stopping airflow but making it turbulent; * affricates, which begin with complete occlusion but then release into a fricative-like release, such as . Voicing Obstruents are often prototypically voiceless, but voiced obstruents are common. This contrasts with sonorants, which are prototypically voiced and only rarely phonemically voiceless. See also *List of phonetics topics A * Acoustic phonetics * Active articulator * Affricate * Airstream mechanism * Alexander John Ellis * Alexander Melville Bell * Alfre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |