|
Duction
A duction is an eye movement involving only one eye. There are generally six possible movements depending upon the eye's axis of rotation: # Abduction refers to the outward movement of an eye. #Adduction refers to the inward movement of an eye #Supraduction / sursumduction / elevation #Infraduction / deorsumduction / depression #Incycloduction / intorsion #Excycloduction / extorsion Forced duction test The forced duction test is performed in order to determine whether the absence of movement of the eye is due to a neurological disorder or a mechanical restriction. The anesthetized conjunctiva is grasped with forceps and an attempt is made to move the eyeball in the direction where the movement is restricted. If a mechanical restriction is present, it will not be possible to induce a passive movement of the eyeball.Kunimoto D, Kanitkar K & Makar M. ''The Wills Eye Manual. Office and Emergency Room Diagnosis and Treatment of Eye Disease.'' Fourth Edition. Lippincott Williams & W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vergence
A vergence is the simultaneous movement of both eyes in opposite directions to obtain or maintain single binocular vision. When a creature with binocular vision looks at an object, the eyes must rotate around a vertical axis so that the projection of the image is in the centre of the retina in both eyes. To look at an object closer, the eyes rotate towards each other (convergence), while for an object farther away, they rotate away from each other (divergence). Exaggerated convergence is called ''cross eyed viewing'' (focusing on the nose, for example). When looking into the distance, the eyes diverge until parallel, effectively fixating on the same point at infinity (or very far away). Vergence movements are closely connected to accommodation of the eye. Under normal visual conditions, looking at an object at a different distance will automatically cause changes in both vergence and accommodation, sometimes known as the '' accommodation-convergence reflex''. When under non- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Movement (sensory)
Eye movement includes the voluntary or involuntary movement of the eyes. Eye movements are used by a number of organisms (e.g. primates, rodents, flies, birds, fish, cats, crabs, octopus) to fixate, inspect and track visual objects of interests. A special type of eye movement, rapid eye movement, occurs during REM sleep. The eyes are the visual organs of the human body, and move using a system of six muscles. The retina, a specialised type of tissue containing photoreceptors, senses light. These specialised cells convert light into electrochemical signals. These signals travel along the optic nerve fibers to the brain, where they are interpreted as vision in the visual cortex. Primates and many other vertebrates use three types of voluntary eye movement to track objects of interest: smooth pursuit, vergence shifts and saccades. These types of movements appear to be initiated by a small cortical region in the brain's frontal lobe. This is corroborated by removal of the fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Eye
The human eye is a sensory organ in the visual system that reacts to light, visible light allowing eyesight. Other functions include maintaining the circadian rhythm, and Balance (ability), keeping balance. The eye can be considered as a living optics, optical device. It is approximately spherical in shape, with its outer layers, such as the outermost, white part of the eye (the sclera) and one of its inner layers (the pigmented choroid) keeping the eye essentially stray light, light tight except on the eye's optic axis. In order, along the optic axis, the optical components consist of a first lens (the cornea, cornea—the clear part of the eye) that accounts for most of the optical power of the eye and accomplishes most of the Focus (optics), focusing of light from the outside world; then an aperture (the pupil) in a Diaphragm (optics), diaphragm (the Iris (anatomy), iris—the coloured part of the eye) that controls the amount of light entering the interior of the eye; then an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axis Of Rotation
Rotation or rotational/rotary motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an ''axis of rotation''. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersecting anywhere inside or outside the figure at a ''center of rotation''. A solid figure has an infinite number of possible axes and angles of rotation, including chaotic rotation (between arbitrary orientation (geometry), orientations), in contrast to rotation around a fixed axis, rotation around a axis. The special case of a rotation with an internal axis passing through the body's own center of mass is known as a spin (or ''autorotation''). In that case, the surface intersection of the internal ''spin axis'' can be called a ''pole''; for example, Earth's rotation defines the geographical poles. A rotation around an axis completely external to the moving body is called a revolution (or ''orbit''), e.g. Earth's orbit around the Sun. The en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abduction (physiology)
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adduction
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
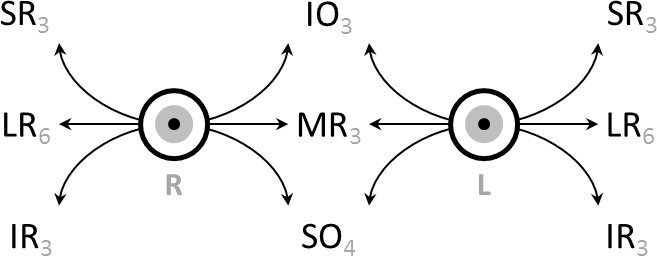
Extraocular Muscles
The extraocular muscles, or extrinsic ocular muscles, are the seven extrinsic muscles of the eye in human eye, humans and other animals. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior oblique muscle, superior and inferior oblique muscles, control Eye movement, movement of the eye. The other muscle, the Levator palpebrae superioris muscle, levator palpebrae superioris, controls eyelid elevation and depression, elevation. The actions of the six muscles responsible for eye movement depend on the position of the eye at the time of muscle contraction. The ciliary muscle, pupillary sphincter muscle and pupillary dilator muscle sometimes are called intrinsic ocular muscles or intraocular muscles. Structure Since only a small part of the eye called the Fovea centralis, fovea provides sharp vision, the eye must move to follow a target. Eye movements must be precise and fast. This is seen in scenarios like reading, where the reader must shift gaze constantly. Alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Examination
An eye examination, commonly known as an eye test, is a series of tests performed to assess Visual acuity, vision and ability to Focus (optics), focus on and discern objects. It also includes other tests and examinations of the human eye, eyes. Eye examinations are primarily performed by an optometrist, ophthalmologist, or an orthoptist. Health care professionals often recommend that all people should have periodic and thorough eye examinations as part of routine primary care, especially since many eye diseases are asymptomatic. Typically, a healthy individual who otherwise has no concerns with their eyes receives an eye exam once in their 20s and twice in their 30s. Eye examinations may detect potentially treatable blindness, blinding eye diseases, ocular manifestation of systemic disease, ocular manifestations of systemic disease, or signs of tumour, tumors or other anomalies of the Human brain, brain. A full eye examination consists of a comprehensive evaluation of medical h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Version (eye)
Eye movement includes the voluntary or involuntary movement of the eyes. Eye movements are used by a number of organisms (e.g. primates, rodents, flies, birds, fish, cats, crabs, octopus) to fixate, inspect and track visual objects of interests. A special type of eye movement, rapid eye movement, occurs during REM sleep. The eyes are the visual organs of the human body, and move using a system of six muscles. The retina, a specialised type of tissue containing photoreceptors, senses light. These specialised cells convert light into electrochemical signals. These signals travel along the optic nerve fibers to the brain, where they are interpreted as vision in the visual cortex. Primates and many other vertebrates use three types of voluntary eye movement to track objects of interest: smooth pursuit, vergence shifts and saccades. These types of movements appear to be initiated by a small cortical region in the brain's frontal lobe. This is corroborated by removal of the front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |