|
Drepanopteridae
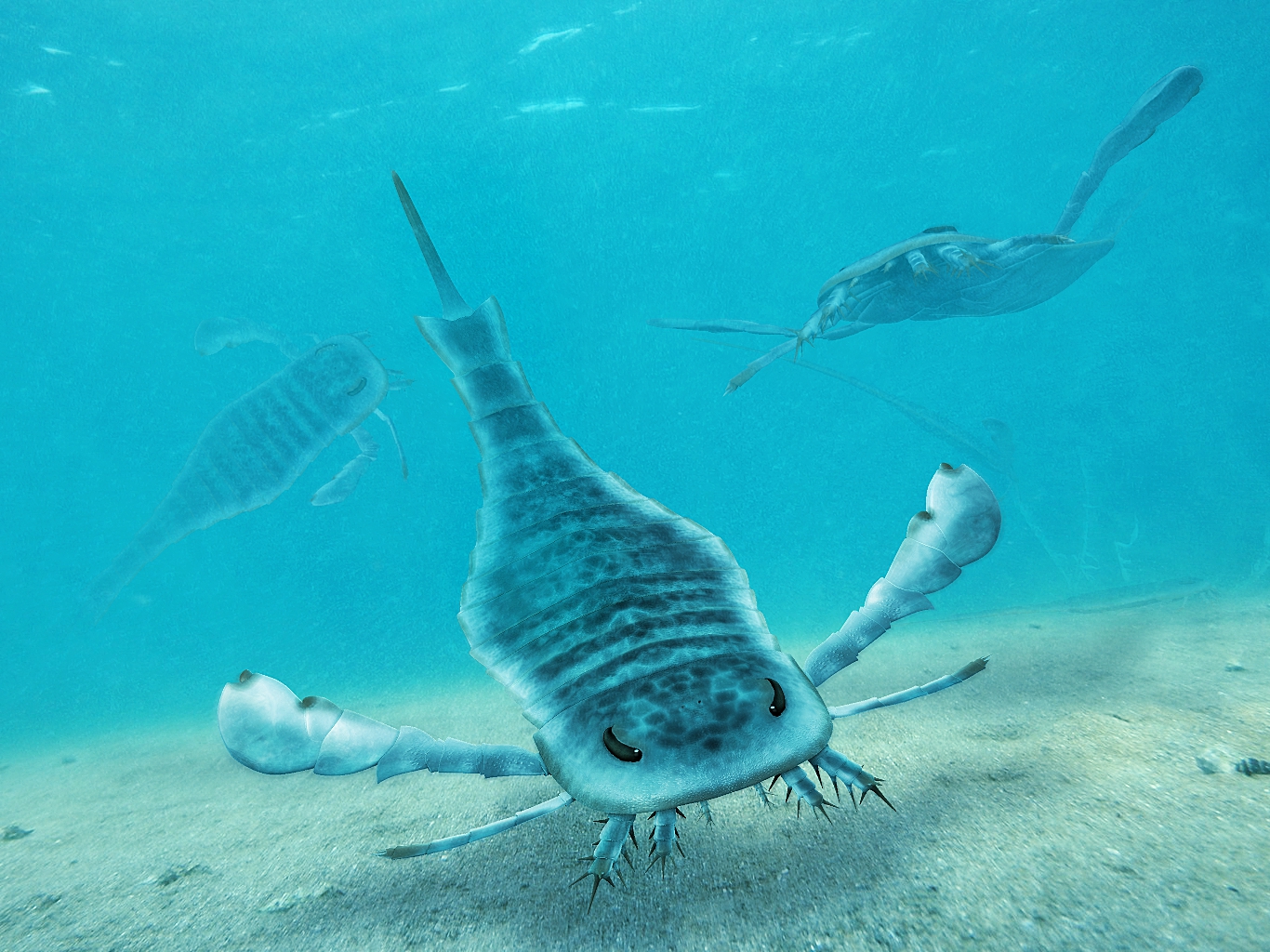
''Drepanopterus'' is an extinct genus of eurypterid and the only member of the family Drepanopteridae within the Mycteropoidea superfamily. There are currently three species assigned to the genus. The genus has historically included more species, with nine species having been associated with the genus ''Drepanopterus''. Five of these have since been proven to be synonyms of pre-existing species, assigned to their own genera, or found to be based on insubstantial fossil data. The holotype of one species proved to be a lithic clast. ''Drepanopterus pentlandicus'' was first described from the Silurian strata of the Pentland Hills in Scotland. The only other fully described valid species is ''Drepanopterus abonensis'', from the Upper Devonian of Portishead, Somerset. The exact relationship of ''Drepanopterus'' to other eurypterids has long been unclear; however, it is now apparent that it is a primitive mycteropoid, and an early relative of the Carboniferous ''Hibbertopterus''. Desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycteropoidea
Mycteropoidea is an extinct superfamily of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". It is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina. Mycteropoids have been recovered from Europe, Russia, South America and South Africa. Mycteropoid specimens are often fragmentary, making it difficult to establish relationships between the included taxa. Only two mycteropoid taxa are known from reasonable complete remains, ''Hibbertopterus scouleri'' and ''H. wittebergensis''. Mycteropoids were large bizarre Eurypterids found from the Early Silurian to the end of the Permian period. They were sweep feeders, inhabiting freshwater swamps and rivers, feeding by raking through the soft sediment with blades on their anterior appendages to capture small invertebrates. Their morphology was so unusual that they have been thought to be an order separate to Eurypterida. Recent work however confirms them to be derived members of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drepanopterus Size
''Drepanopterus'' is an extinct genus of eurypterid and the only member of the family Drepanopteridae within the Mycteropoidea superfamily. There are currently three species assigned to the genus. The genus has historically included more species, with nine species having been associated with the genus ''Drepanopterus''. Five of these have since been proven to be synonyms of pre-existing species, assigned to their own genera, or found to be based on insubstantial fossil data. The holotype of one species proved to be a lithic clast. ''Drepanopterus pentlandicus'' was first described from the Silurian strata of the Pentland Hills in Scotland. The only other fully described valid species is ''Drepanopterus abonensis'', from the Upper Devonian of Portishead, Somerset. The exact relationship of ''Drepanopterus'' to other eurypterids has long been unclear; however, it is now apparent that it is a primitive mycteropoid, and an early relative of the Carboniferous ''Hibbertopterus''. Desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurypterids Of Europe
Eurypterids, often informally called sea scorpions, are a group of extinct marine arthropods that form the order Eurypterida. The earliest known eurypterids date to the Darriwilian stage of the Ordovician period, 467.3 million years ago. The group is likely to have appeared first either during the Early Ordovician or Late Cambrian period. With approximately 250 species, the Eurypterida is the most diverse Paleozoic chelicerate order. Following their appearance during the Ordovician, eurypterids became major components of marine faunas during the Silurian, from which the majority of eurypterid species have been described. The Silurian genus ''Eurypterus'' accounts for more than 90% of all known eurypterid specimens. Though the group continued to diversify during the subsequent Devonian period, the eurypterids were heavily affected by the Late Devonian extinction event. They declined in numbers and diversity until becoming extinct during the Permian–Triassic extinction event (or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
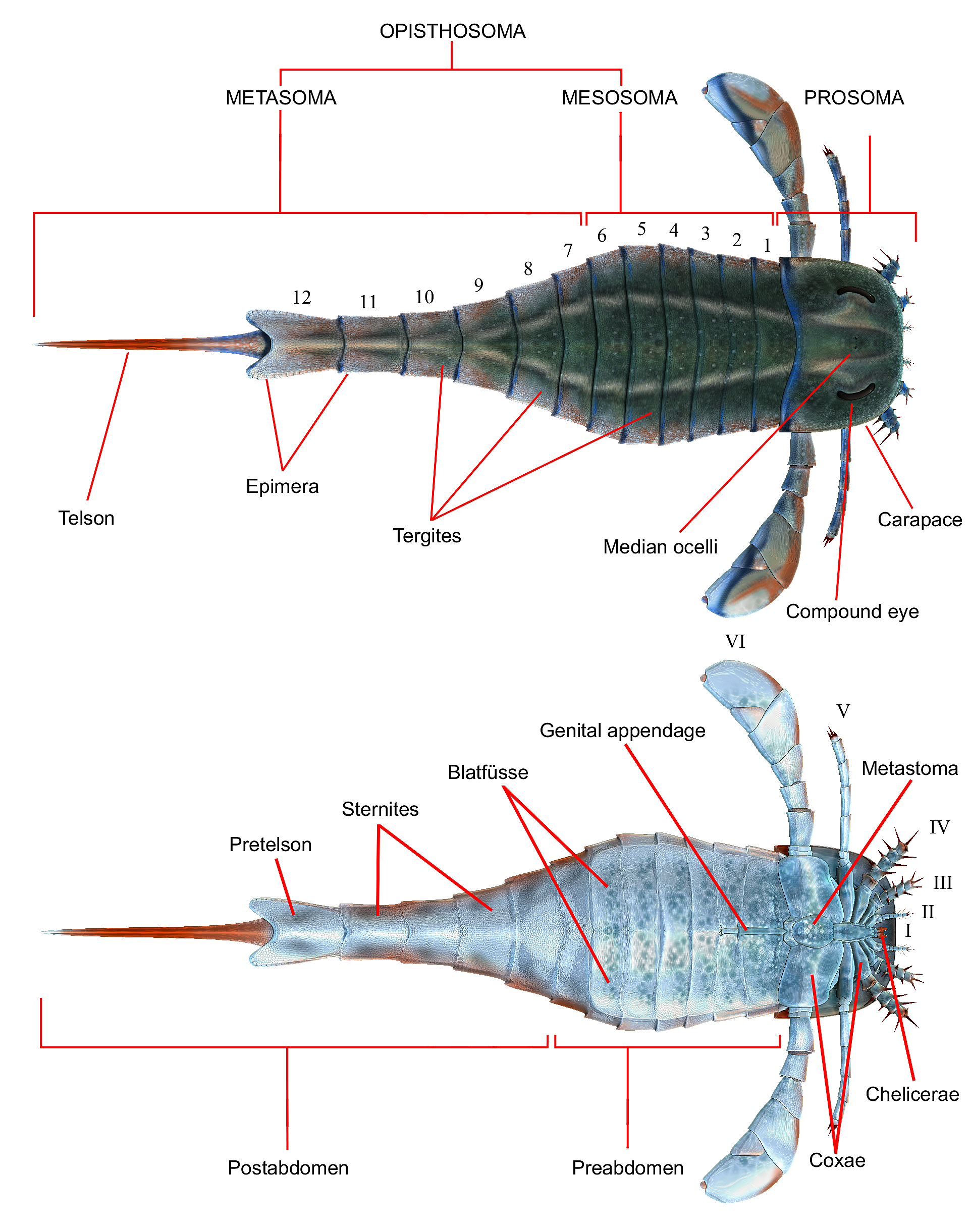
Eurypterid
Eurypterids, often informally called sea scorpions, are a group of extinct marine arthropods that form the Order (biology), order Eurypterida. The earliest known eurypterids date to the Darriwilian stage of the Ordovician period, 467.3 Myr, million years ago. The group is likely to have appeared first either during the Early Ordovician or Late Cambrian period. With approximately 250 species, the Eurypterida is the most diverse Paleozoic Chelicerata, chelicerate order. Following their appearance during the Ordovician, eurypterids became major components of marine faunas during the Silurian, from which the majority of eurypterid species have been described. The Silurian genus ''Eurypterus'' accounts for more than 90% of all known eurypterid specimens. Though the group continued to diversify during the subsequent Devonian period, the eurypterids were heavily affected by the Late Devonian extinction event. They declined in numbers and diversity until becoming extinct during the Permi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hibbertopterus
''Hibbertopterus'' is a genus of eurypterid, a group of extinct marine arthropods. Fossils of ''Hibbertopterus'' have been discovered in deposits ranging from the Devonian period in Belgium, Scotland and the United States to the Carboniferous period in Scotland, Ireland, the Czech Republic and South Africa. The type species, ''H. scouleri'', was first named as a species of the significantly different ''Eurypterus'' by Samuel Hibbert in 1836. The generic name ''Hibbertopterus'', coined more than a century later, combines his name and the Greek word πτερόν (''pteron'') meaning "wing". ''Hibbertopterus'' was the largest eurypterid within the stylonurine suborder, with the largest fossil specimens suggesting that ''H. scouleri'' could reach lengths around 180–200 centimetres (5.9–6.6 ft). Though this is significantly smaller than the largest eurypterid overall, '' Jaekelopterus'', which could reach lengths of around , ''Hibbertopterus'' is likely to have been the hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylonurina
Stylonurina is one of two suborders of eurypterids, a group of extinct arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". Members of the suborder are collectively and informally known as "stylonurine eurypterids" or "stylonurines". They are known from deposits primarily in Europe and North America, but also in Siberia. Compared to the other suborder, Eurypterina, the stylonurines were comparatively rare and retained their posterior prosomal appendages for walking. Despite their rarity, the stylonurines have the longest temporal range of the two suborders. The suborder contains some of the oldest known eurypterids, such as ''Brachyopterus'', from the Middle Ordovician as well as the youngest known eurypterids, from the Late Permian. They remained rare throughout the Ordovician and Silurian, though the radiation of the mycteropoids (a group of large sweep-feeding forms) in the Late Devonian and Carboniferous is the last major radiation of the eurypterids before their extinction in the Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kokomopterus
''Kokomopterus'' is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid. The genus contains a single species, ''Kokomopterus longicaudatus'', known from the Silurian of Kokomo, Indiana.Dunlop, J. A., Penney, D. & Jekel, D. 2015. A summary list of fossil spiders and their relatives. In World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern, online at http://wsc.nmbe.ch, version 16.0 http://www.wsc.nmbe.ch/resources/fossils/Fossils16.0.pdf (PDF). See also * List of eurypterids This list of eurypterid genera is a comprehensive listing of all Genus, genera that have ever been included in the order Eurypterida, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now c ... References Stylonurina Silurian eurypterids Silurian arthropods of North America Eurypterids of North America {{eurypterid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanahughmilleria
''Nanahughmilleria'' ("dwarf ''Hughmilleria''") is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of ''Nanahughmilleria'' have been discovered in deposits of Devonian and Silurian age in the United States, Norway, Russia, England and Scotland, and have been referred to several different species. ''Nanahughmilleria'' is classified in the family Adelophthalmidae, the only clade in the superfamily Adelophthalmoidea. This clade was characterised by their small size, their parabolic (approximately U-shaped) carapaces and the presence of epimera (lateral "extensions" of the segment) on the seventh segment, among others. ''Nanahughmilleria'' was different from its relatives by the presence of more spines in its appendages (limbs) and by its genital morphology. The largest species confidently assigned to the genus was ''N. norvegica'' at 10 cm (3.9 in), making it a comparatively small eurypterid. Description Like the other adelophthalmid eurypterids, ''Nanahug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where sexes of the same species exhibit different Morphology (biology), morphological characteristics, including characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most dioecy, dioecious species, which consist of most animals and some plants. Differences may include secondary sex characteristics, size, weight, color, markings, or behavioral or cognitive traits. Male-male reproductive competition has evolved a diverse array of sexually dimorphic traits. Aggressive utility traits such as "battle" teeth and blunt heads reinforced as battering rams are used as weapons in aggressive interactions between rivals. Passive displays such as ornamental feathering or song-calling have also evolved mainly through sexual selection. These differences may be subtle or exaggerated and may be subjected to sexual selection and natural selection. The opposite of dimorphism is ''monomorphism'', when both biological sexes are phenotype, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Eurypterids
This list of eurypterid genera is a comprehensive listing of all Genus, genera that have ever been included in the order Eurypterida, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful (''nomen dubium''), or were not formally published (''nomen nudum''), as well as Synonym (zoology), junior synonyms of more established names and genera that are no longer considered eurypterids. The list currently includes 115 names out of which 74 are considered valid eurypterid genera. There are approximately 250 species of eurypterids recognized as valid. Naming conventions and terminology There is no "official" or "canonical" list of eurypterid genera. The closest thing is found contained in the regularly updated ''Summary list'' ''of fossil spiders and their relatives'' in the World Spider Catalog. The vast majority of the content of the list below, including the valid genera, preoccupied names, junior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithic Fragment (geology)
Lithic fragments, or lithics, are pieces of other rocks that have been eroded down to sand size and now are sand grains in a sedimentary rock. They were first described and named (in their modern definitions) by Bill Dickinson in 1970. Lithic fragments can be derived from sedimentary, igneous or metamorphic rocks. A lithic fragment is defined using the Gazzi-Dickinson point-counting method and being in the sand-size fraction. Sand grains in sedimentary rocks that are fragments of larger rocks that are not identified using the Gazzi-Dickinson method are usually called rock fragments instead of lithic fragments. Sandstones rich in lithic fragments are called lithic sandstones. Types Igneous (Lv) These can include granular (~ rhyolitic), microlitic (~ andesitic), lathwork (~basaltic), and vitric ( glassy). These correlations between composition and volcanic lithic fragment type are approximate, at best.Mathew D. Affolter, Raymond V. Ingersoll; Quantitative Analysis of Volcanic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinetopterus
''Vinetopterus'' is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid from the Devonian period in Europe classified as part of the Moselopteridae family. The genus contains two species, both from Germany: ''V. struvei'' and ''V. martini''.Dunlop, J. A., Penney, D. & Jekel, D. 2015. A summary list of fossil spiders and their relatives. In World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern, online at http://wsc.nmbe.ch , version 16.0 http://www.wsc.nmbe.ch/resources/fossils/Fossils16.0.pdf (PDF). See also * List of eurypterids This list of eurypterid genera is a comprehensive listing of all Genus, genera that have ever been included in the order Eurypterida, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now c ... References Eurypterina Devonian eurypterids Devonian arthropods of Europe Eurypterids of Europe {{Eurypterid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |