|
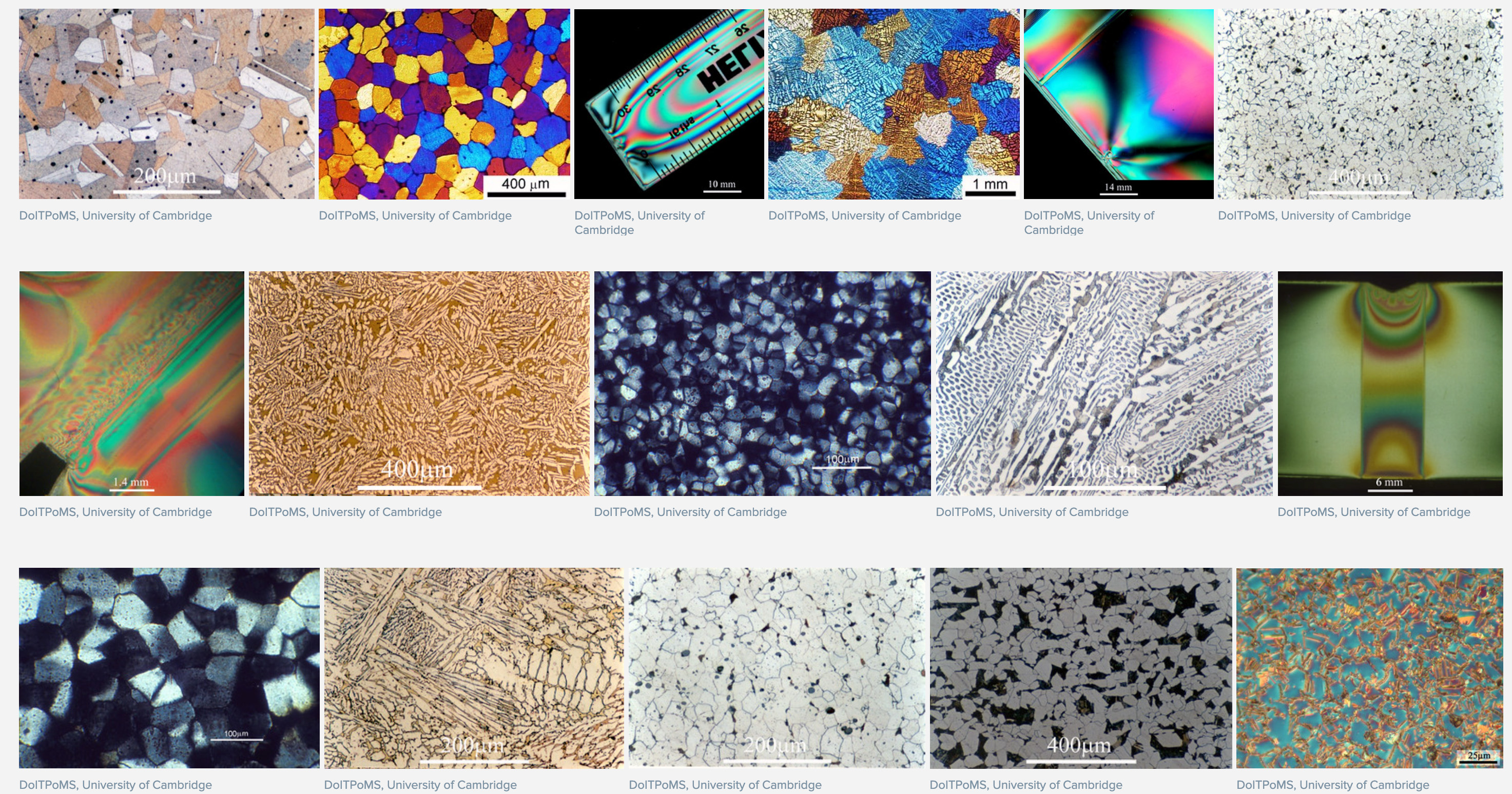
DoITPoMS
Dissemination of IT for the Promotion of Materials Science (DoITPoMS) is a web-based educational software resource designed to facilitate the teaching and learning of Materials science, at the tertiary level for free. History The DoITPoMS project originated in the early 1990s, incorporating customized online sources into the curriculum of the Materials Science courses in the Natural Sciences Tripos of the University Cambridge. The initiative became formalized in 2000, with the start of a project supported by the UK national Fund for the Development of Teaching and Learning (FDTL). This was led by the Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy at the University of Cambridge with five partner institutions, including the University of Leeds, London Metropolitan University, the University of Manchester, Oxford Brookes University, and the University of Sheffield. This period of cooperation lasted for about 10 years. The FDTL project was aimed at building on expertise concerning th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instructional Materials
Instructional materials, also known as teaching materials, learning materials, or teaching/learning materials (TLM), are any collection of materials including animate and inanimate objects and human and non-human resources that a teacher may use in teaching and learning situations to help achieve desired learning objectives. Instructional materials may aid a student in concretizing a learning experience so as to make learning more exciting, interesting and interactive. They are tools used in instructional activities, which include active learning and assessment. The term encompasses all the materials and physical means an instructor might use to implement instruction and facilitate students achievement of instructional objectives. Background The value of instructional materials as a pedagogical aid can be seen in Vachel Lindsay's poem "Euclid": Types of instructional materials Instructional materials can be classified by type, including print, visual, and audiovisual, amon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most battery (electricity), batteries in requiring a continuous source of fuel and oxygen (usually from air) to sustain the chemical reaction, whereas in a battery the chemical energy usually comes from substances that are already present in the battery. Fuel cells can produce electricity continuously for as long as fuel and oxygen are supplied. The first fuel cells were invented by Sir William Robert Grove, William Grove in 1838. The first commercial use of fuel cells came almost a century later following the invention of the hydrogen–oxygen fuel cell by Francis Thomas Bacon in 1932. The alkaline fuel cell, also known as the Bacon fuel cell after its inventor, has been used in NASA space programs since the mid-1960s to generate power for sate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Battery
An electric battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices. When a battery is supplying power, its positive Terminal (electronics), terminal is the cathode and its negative terminal is the anode. The terminal marked negative is the source of electrons. When a battery is connected to an external electric load, those negatively charged electrons flow through the circuit and reach the positive terminal, thus causing a redox reaction by attracting positively charged ions, or cations. Thus, higher energy reactants are converted to lower energy products, and the Gibbs free energy, free-energy difference is delivered to the external circuit as electrical energy. Historically the term "battery" specifically referred to a device composed of multiple cells; however, the usage has evolved to include devices composed of a single cell. Primary battery, Primary (single-use or "disposable") batter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Materials Science And Metallurgy, University Of Cambridge
The Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy (DMSM) is a large research and teaching division of the University of Cambridge. Since 2013 it has been located in West Cambridge, having previously occupied several buildings on the New Museums Site in the centre of Cambridge. Following the changes to academic titles in 2021/2022 at the University of Cambridge, the academic staff of the Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy no longer use the academic titles of Reader and Lecturer. The list below reflects the new academic titles. Academic staff Professorial staff include:People in the Department of Materials Science & Metallurgy University of Cambridge # Serena Best, CBE, FREng, Professor of Materials Science # Ruth Cameron (scientist), Ruth Cameron, Professor of Materials Sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The UK includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and most of List of islands of the United Kingdom, the smaller islands within the British Isles, covering . Northern Ireland shares Republic of Ireland–United Kingdom border, a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the UK is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. It maintains sovereignty over the British Overseas Territories, which are located across various oceans and seas globally. The UK had an estimated population of over 68.2 million people in 2023. The capital and largest city of both England and the UK is London. The cities o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volunteering
Volunteering is an elective and freely chosen act of an individual or group giving their time and labor, often for community service. Many volunteers are specifically trained in the areas they work, such as medicine, education, or emergency rescue. Others serve on an as-needed basis, such as in response to a natural disaster. Etymology and history The verb was first recorded in 1755. It was derived from the noun ''volunteer'', in 1600, "one who offers himself for military service," from the Middle French ''voluntaire''. In the non-military sense, the word was first recorded during the 1630s. The word ''volunteering'' has more recent usage—still predominantly military—coinciding with the phrase ''community service''. In a military context, a volunteer army is a military body whose soldiers have chosen to enlist, as opposed to having been conscripted. Such volunteers do not work "for free" and are given regular pay. 19th century During this time, America experienced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
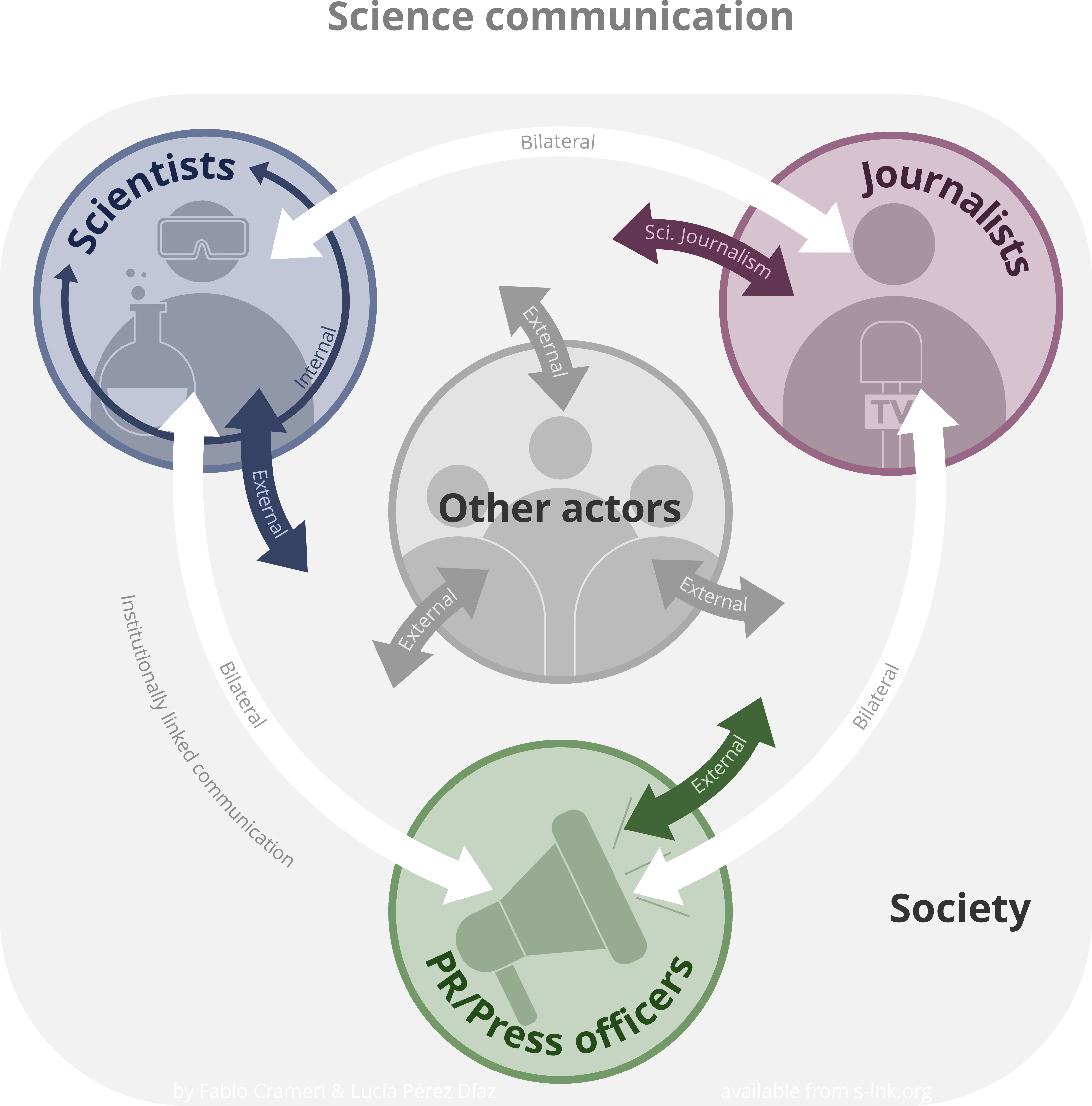
Science Communication
Science communication encompasses a wide range of activities that connect science and society. Common goals of science communication include informing non-experts about scientific findings, raising the Public awareness of science, public awareness of and interest in science, influencing people's attitudes and behaviors, informing public policy, and Public engagement, engaging with diverse communities to address societal problems. The term "science communication" generally refers to settings in which audiences are not experts on the scientific topic being discussed (Science outreach, outreach), though some authors categorize expert-to-expert communication ("inreach" such as publication in scientific journals) as a type of science communication. Examples of outreach include science journalism and health communication. Since science has political, moral, and legal implications, science communication can help bridge gaps between different stakeholders in public policy, industry, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Learning Environments
Virtual may refer to: * Virtual image, an apparent image of an object (as opposed to a real object), in the study of optics * Virtual (horse), a thoroughbred racehorse * Virtual channel, a channel designation which differs from that of the actual radio channel (or range of frequencies) on which the signal travels * Virtual function, a programming function or method whose behaviour can be overridden within an inheriting class by a function with the same signature * Virtual machine, the virtualization of a computer system * Virtual meeting, or web conferencing * Virtual memory, a memory management technique that abstracts the memory address space in a computer * Virtual particle, a type of short-lived particle of indeterminate mass * Virtual reality (virtuality), computer programs with an interface that gives the user the impression that they are physically inside a simulated space * Virtual world, a computer-based simulated environment populated by many users who can create a person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Materials
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education also follows a structured approach but occurs outside the formal schooling system, while informal education involves unstructured learning through daily experiences. Formal and non-formal education are categorized into levels, including early childhood education, primary education, secondary education, and tertiary education. Other classifications focus on teaching methods, such as teacher-centered and Student-centered learning, student-centered education, and on subjects, such as science education, language education, and physical education. Additionally, the term "education" can denote the mental states and qualities of educated individuals and the academic field studying educational phenomena. The precise definition of education is disputed, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Educational Websites
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. * British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** British Isles, an island group ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** British Empire, a historical global colonial empire ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) * British Raj, colonial India under the British Empire * British Hong Kong, colonial H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite Element Method
Finite element method (FEM) is a popular method for numerically solving differential equations arising in engineering and mathematical modeling. Typical problem areas of interest include the traditional fields of structural analysis, heat transfer, fluid flow, mass transport, and electromagnetic potential. Computers are usually used to perform the calculations required. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved and are often required to solve the largest and most complex problems. FEM is a general numerical method for solving partial differential equations in two- or three-space variables (i.e., some boundary value problems). There are also studies about using FEM to solve high-dimensional problems. To solve a problem, FEM subdivides a large system into smaller, simpler parts called finite elements. This is achieved by a particular space discretization in the space dimensions, which is implemented by the construction of a mesh of the object: the numer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |