|
Distributed
Distribution may refer to: Mathematics *Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations *Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a variable **Cumulative distribution function In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a real-valued random variable X, or just distribution function of X, evaluated at x, is the probability that X will take a value less than or equal to x. Ev ..., in which the probability of being no greater than a particular value is a function of that value *Frequency distribution, a list of the values recorded in a sample *Inner distribution, and outer distribution, in coding theory *Distribution (differential geometry), a subset of the tangent bundle of a manifold *Distributed parameter system, systems that have an infinite-dimensional state-space *Distribution of terms, a situation in which all members of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Distributed Computing
A distributed system is a system whose components are located on different networked computers, which communicate and coordinate their actions by passing messages to one another from any system. Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems. The components of a distributed system interact with one another in order to achieve a common goal. Three significant challenges of distributed systems are: maintaining concurrency of components, overcoming the lack of a global clock, and managing the independent failure of components. When a component of one system fails, the entire system does not fail. Examples of distributed systems vary from SOA-based systems to massively multiplayer online games to peer-to-peer applications. A computer program that runs within a distributed system is called a distributed program, and ''distributed programming'' is the process of writing such programs. There are many different types of implementations for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
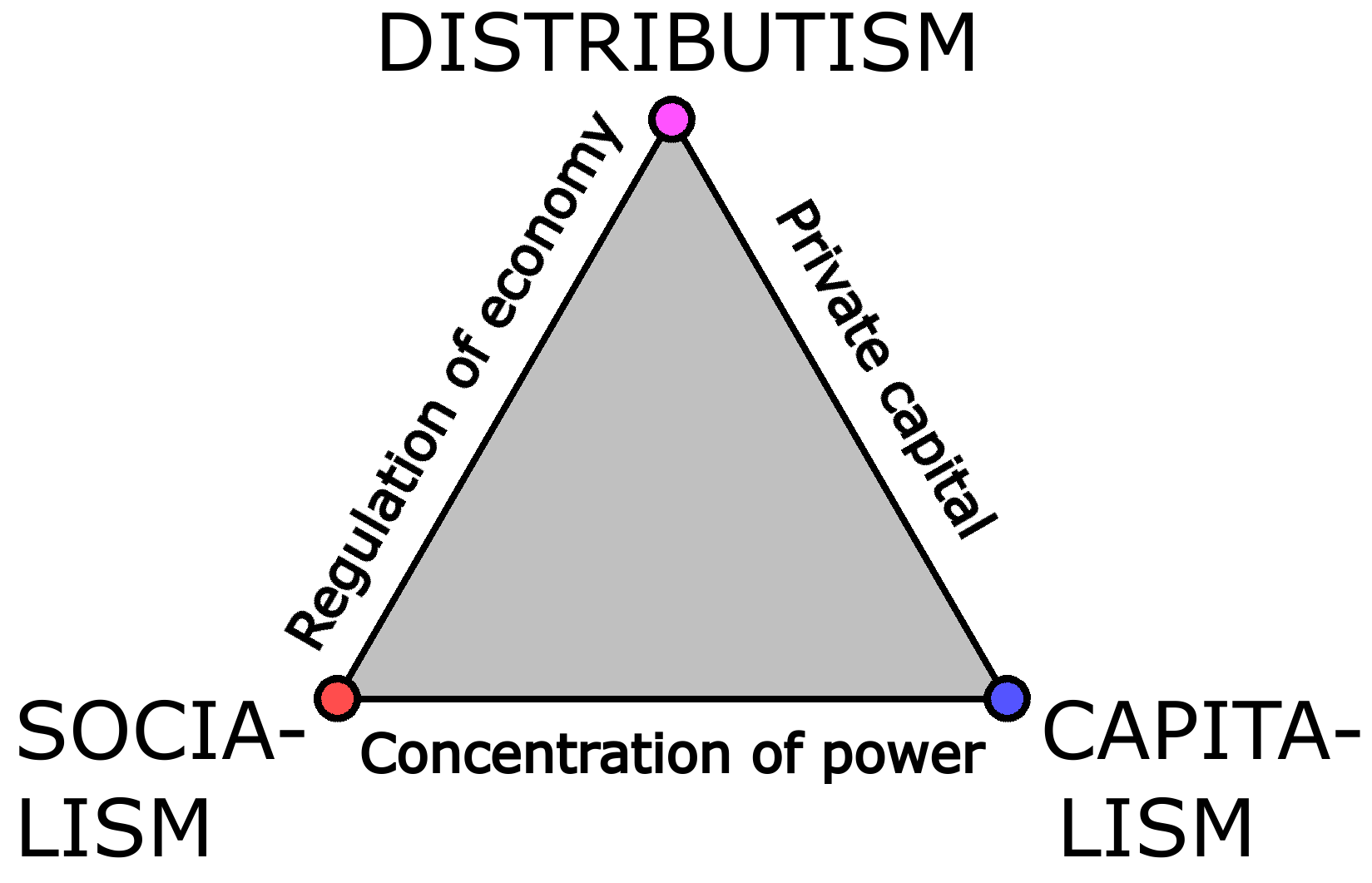 |
Distributism
Distributism is an economic theory asserting that the world's productive assets should be widely owned rather than concentrated. Developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, distributism was based upon Catholic social teaching principles, especially Pope Leo XIII's teachings in his encyclical ''Rerum novarum'' (1891) and Pope Pius XI in '' Quadragesimo anno'' (1931). It has influenced Anglo Christian Democratic movements, and has been recognized as one of many influences on the social market economy. Distributism views ''laissez-faire'' capitalism and state socialism as equally flawed and exploitative, favouring instead small independent craftsmen and producers, or if that is not possible, economic mechanisms such as cooperatives and member-owned mutual organisations as well as small to medium enterprises and large-scale competition law reform such as antitrust regulations. Christian democratic political parties such as the American Solidarity Party have advocated di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Distributed Parameter System
In control theory, a distributed-parameter system (as opposed to a lumped-parameter system) is a system whose state space is infinite-dimensional. Such systems are therefore also known as infinite-dimensional systems. Typical examples are systems described by partial differential equations or by delay differential equations. Linear time-invariant distributed-parameter systems Abstract evolution equations Discrete-time With ''U'', ''X'' and ''Y'' Hilbert spaces and ''A\,'' ∈ ''L''(''X''), ''B\,'' ∈ ''L''(''U'', ''X''), ''C\,'' ∈ ''L''(''X'', ''Y'') and ''D\,'' ∈ ''L''(''U'', ''Y'') the following difference equations determine a discrete-time linear time-invariant system: :x(k+1)=Ax(k)+Bu(k)\, :y(k)=Cx(k)+Du(k)\, with ''x\,'' (the state) a sequence with values in ''X'', ''u\,'' (the input or control) a sequence with values in ''U'' and ''y\,'' (the output) a sequence with values in ''Y''. Continuous-time The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Distribution (mathematics)
Distributions, also known as Schwartz distributions or generalized functions, are objects that generalize the classical notion of functions in mathematical analysis. Distributions make it possible to differentiate functions whose derivatives do not exist in the classical sense. In particular, any locally integrable function has a distributional derivative. Distributions are widely used in the theory of partial differential equations, where it may be easier to establish the existence of distributional solutions than classical solutions, or where appropriate classical solutions may not exist. Distributions are also important in physics and engineering where many problems naturally lead to differential equations whose solutions or initial conditions are singular, such as the Dirac delta function. A function f is normally thought of as on the in the function domain by "sending" a point x in its domain to the point f(x). Instead of acting on points, distribution theory reint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Software Distribution
Software distribution is the process of delivering software to the end user. A distro is a collection of software components built, assembled and configured so that it can essentially be used "as is". It is often the closest thing to turnkey form of free software. A distro may take the form of a ''binary distribution'', with an executable installer which can be downloaded from the Internet. Examples range from whole operating system distributions to server and interpreter distributions (for example WAMP installers). ''Software distribution'' can also refer to careware and donateware. In recent years, the term has come to refer to nearly any "finished" software (i.e. something that is more or less ready for its intended use, whether as a complete system or a component of a larger system) that is assembled primarily from open source components. Examples of distros Examples of software distributions include BSD-based distros (such as FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, and DragonflyBS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Division Of Property
Division of property, also known as equitable distribution, is a judicial division of property rights and obligations between spouses during divorce. It may be done by agreement, through a property settlement, or by judicial decree. Distribution of property is the division, due to a death or the dissolution of a marriage, of property which was owned by the deceased, or acquired during the course of the marriage Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognized union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between t .... United Kingdom law In England & Wales, partners in or out of marriage can agree how the joint and severally hold assets will be divided without the intervention of the courts. Where agreement cannot be reached, the courts may be asked to determine a fair and equitable division. The case of Miller v Miller gave the wife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Distribution Of Wealth
The distribution of wealth is a comparison of the wealth of various members or groups in a society. It shows one aspect of economic inequality or heterogeneity in economics, economic heterogeneity. The distribution of wealth differs from the income distribution in that it looks at the Distribution (economics), economic distribution of ownership of the assets in a society, rather than the current income of members of that society. According to the International Association for Research in Income and Wealth, "the world distribution of wealth is much more unequal than that of income." For rankings regarding wealth, see list of countries by wealth equality or list of countries by wealth per adult. Definition of wealth Wealth of an individual is defined as net worth, expressed as: wealth = assets − liability (financial accounting), liabilities A broader definition of wealth, which is rarely used in the measurement of wealth inequality, also includes human capital. For example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Distribution Resource Planning
{{Business logistics Distribution resource planning (DRP) is a method used in business administration for planning orders within a supply chain. DRP enables the user to set certain inventory control parameters (like a safety stock) and calculate the time-phased inventory requirements. This process is also commonly referred to as ''distribution requirements planning''. DRP uses several variables: *the required quantity of product needed at the beginning of a period *the constrained quantity of product available at the beginning of a period *the recommended order quantity at the beginning of a period *the backordered demand at the end of a period *the on-hand inventory at the end of a period DRP needs the following information: *the demand in a future period *the scheduled receipts at the beginning of a period *the on-hand inventory at the beginning of a period *the safety stock requirement for a period See also * Distribution (business) * Document automation for supply chain a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Distribution (marketing)
Distribution (or place) is one of the four elements of the marketing mix. Distribution is the process of making a product or service available for the consumer or business user who needs it. This can be done directly by the producer or service provider or using indirect channels with distributors or intermediaries. The other three elements of the marketing mix are product, pricing, and promotion. Decisions about distribution need to be taken in line with a company's overall strategic vision and mission. Developing a coherent distribution plan is a central component of strategic planning. At the strategic level, there are three broad approaches to distribution, namely mass, selective and exclusive distribution. The number and type of intermediaries selected largely depend on the strategic approach. The overall distribution channel should add value to the consumer. Definition Distribution is fundamentally concerned with ensuring that products reach target customers in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Companies Act 2006
The Companies Act 2006 (c 46) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which forms the primary source of UK company law. The Act was brought into force in stages, with the final provision being commenced on 1 October 2009. It largely superseded the Companies Act 1985. The Act provides a comprehensive code of company law for the United Kingdom, and made changes to almost every facet of the law in relation to companies. The key provisions are: * the Act codifies certain existing common law principles, such as those relating to directors' duties. * it transposes into UK law the Takeover Directive and the Transparency Directive of the European Union * it introduces various new provisions for private and public companies. * it applies a single company law regime across the United Kingdom, replacing the two separate (if identical) systems for Great Britain and Northern Ireland. * it otherwise amends or restates almost all of the Companies Act 1985 to varying degrees. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Distribution (economics)
In economics, distribution is the way total output, income, or wealth is distributed among individuals or among the factors of production (such as labour, land, and capital). In general theory and in for example the U.S. National Income and Product Accounts, each unit of output corresponds to a unit of income. One use of national accounts is for classifying factor incomes and measuring their respective shares, as in national Income. But, where focus is on income of ''persons'' or ''households'', adjustments to the national accounts or other data sources are frequently used. Here, interest is often on the fraction of income going to the top (or bottom) ''x'' percent of households, the next ''x'' percent, and so forth (defined by equally spaced cut points, say quintiles), and on the factors that might affect them (globalization, tax policy, technology, etc.). Descriptive, theoretical, scientific, and welfare uses Income distribution can describe a prospectively observable elem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Spectral Power Distribution
In radiometry, photometry, and color science, a spectral power distribution (SPD) measurement describes the power per unit area per unit wavelength of an illumination ( radiant exitance). More generally, the term ''spectral power distribution'' can refer to the concentration, as a function of wavelength, of any radiometric or photometric quantity (e.g. radiant energy, radiant flux, radiant intensity, radiance, irradiance, radiant exitance, radiosity, luminance, luminous flux, luminous intensity, illuminance, luminous emittance). Knowledge of the SPD is crucial for optical-sensor system applications. Optical properties such as transmittance, reflectivity, and absorbance as well as the sensor response are typically dependent on the incident wavelength. Physics Mathematically, for the spectral power distribution of a radiant exitance or irradiance one may write: : M(\lambda)=\frac\approx\frac where ''M''(''λ'') is the spectral irradiance (or exitance) of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |