|
Diplica
Diplica or diplice is a single-reed instrument from the Balkans, which has been playing in different forms through many parts of Croatia Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ..., but now survives mainly in the Baranya region. Diplicas are double-clarinets. The widespread practice of playing wind instruments in pairs led to the development of the double, or even triple or quadruple, clarinets. Most were double clarinets, with two tubes of reed firmly tied or glued together in a parallel position where one of the tubes functions as a drone. Instruments of this kind can be traced back to approximately 2700 BCE in Egypt, where they were originally called ‘memet’. During the Old Kingdom in Egypt (2778-2723 BCE), memets were depicted on the reliefs of seven tombs at Saqqar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-reed Instrument
A single-reed instrument is a woodwind instrument that uses only one reed to produce sound. The very earliest single-reed instruments were documented in ancient Egypt, ancient Greece as well as the Middle East, and the Roman Empire. The earliest types of single-reed instruments used idioglottal reeds, where the vibrating reed is a tongue cut and shaped on the tube of cane. Much later, single-reed instruments started using heteroglottal reeds, where a reed is cut and separated from the tube of cane and attached to a mouthpiece of some sort. By contrast, in a double reed instrument (such as the oboe and bassoon), there is no mouthpiece; the two parts of the reed vibrate against one another. Reeds are traditionally made of cane and produce sound when air is blown across or through them. The type of instruments that use a single reed are clarinets and saxophone. The timbre of a single and double reed instrument is related to the harmonic series caused by the shape of the corpus. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sipsi
The sipsi () is a clarinet-like, single-reed instrument used mainly in Turkish folk music, folk music and native to the Aegean region of Turkey. The word ''sipsi'' is possibly Onomatopoeia, onomatopoeic. The sipsi can be made of bone, wood, or Reed (plant), reed, though the reed variant is most common. Its size varies from region to region, but it generally contains five Tone hole, finger holes in the front, and one finger hole in the back. The sipsi is one of many reed instruments in Turkey used to play lead melodies in instrumental folk music. It is generally played in the Western part in the Aegean Region of Turkey. Most folk tunes played in this area with the sipsi are in 9/8 Time signature, time. Playing The timbre of the sipsi is similar to that of the Uilleann pipes, Irish bagpipe. Players of the sipsi employ the circular breathing method, in which air is breathed through the nose while it is being pumped out of stored air in the cheeks. This breathing method is used to f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key (music)
In music theory, the key of a piece is the group of pitches, or scale, that forms the basis of a musical composition in Western classical music, jazz music, art music, and pop music. A particular key features a '' tonic (main) note'' and its corresponding '' chords'', also called a ''tonic'' or ''tonic chord'', which provides a subjective sense of arrival and rest. The tonic also has a unique relationship to the other pitches of the same key, their corresponding chords, and pitches and chords outside the key. Notes and chords other than the tonic in a piece create varying degrees of tension, resolved when the tonic note or chord returns. The key may be in the major mode, minor mode, or one of several other modes. Musicians assume major when this is not specified; for example, "this piece is in C" implies that the key of the piece is C major. Popular songs and classical music from the common practice period are usually in a single key; longer pieces in the classical repe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tone Hole
A tone hole is an opening in the body of a wind instrument which, when alternately closed and opened, changes the pitch (music), pitch of the sound produced. Tone holes may serve specific purposes, such as a trill hole or register hole. A tone hole is, "in wind instruments[,] a hole that may be stopped by the Fingering (music), finger, or a key (instrument), key, to change the pitch of the tone produced."William Lines Hubbard, ed. (1908). ''The American history and encyclopedia of music, Volume 10'', p.532. Squire. The Acoustic resonance, resonant frequencies of the air column in a pipe are inversely proportional to the pipe's ''effective length''. In other words, a shorter pipe produces higher notes. For a pipe with no tone holes but open at both ends, the effective length is the physical length of the pipe plus a little more for the small volumes of air just beyond the ends of the pipe that are also involved in the resonance. An open hole anywhere along the middle of the pipe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
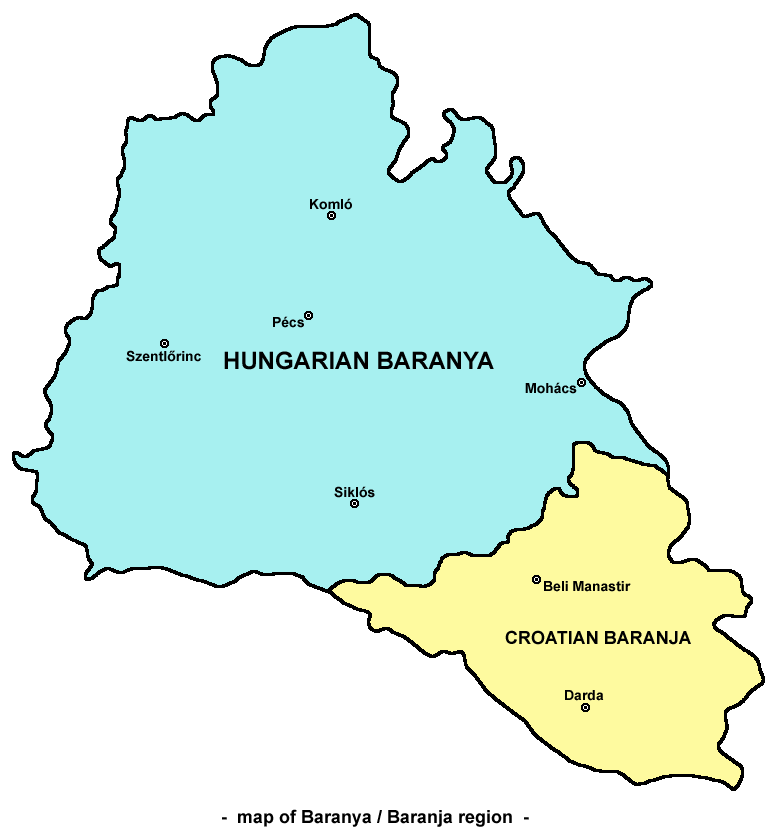
Baranya (region)
Baranya or Baranja (, ; , ) is a geographical and list of historical regions of Central Europe, historical region between the Danube and the Drava rivers located in the Pannonian Plain. Its territory is divided between Hungary and Croatia. In Hungary, the region is included in Baranya (county), Baranya county, while in Croatia, it is part of Osijek-Baranja county. Name The name of the region come from the Slavic languages, Slavic word 'bara', which means 'marsh', 'bog', thus the name of Baranya means 'marshland'. Even today large parts of the region are swamps, such as the natural reservation Kopački Rit in its southeast. Another theory states that the name of the region comes from the , an adaptation of Proto-Slavic language, Proto-Slavic 'ram'. History Historically, the region of Baranya was part of the Roman Empire, the Huns, Hunnic Empire, the Kingdom of the Ostrogoths, the Kingdom of the Lombards, the Avars (Carpathians), Avar Kingdom, the Frankish Empire, the Balaton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Montenegro to the southeast, and shares a maritime border with Italy to the west. Its capital and largest city, Zagreb, forms one of the country's Administrative divisions of Croatia, primary subdivisions, with Counties of Croatia, twenty counties. Other major urban centers include Split, Croatia, Split, Rijeka and Osijek. The country spans , and has a population of nearly 3.9 million. The Croats arrived in modern-day Croatia, then part of Illyria, Roman Illyria, in the late 6th century. By the 7th century, they had organized the territory into Duchy of Croatia, two duchies. Croatia was first internationally recognized as independent on 7 June 879 during the reign of Duke Branimir of Croatia, Branimir. Tomislav of Croatia, Tomis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whole of Bulgaria. The Balkan Peninsula is bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the northwest, the Ionian Sea in the southwest, the Aegean Sea in the south, the Turkish straits in the east, and the Black Sea in the northeast. The northern border of the peninsula is variously defined. The highest point of the Balkans is Musala, , in the Rila mountain range, Bulgaria. The concept of the Balkan Peninsula was created by the German geographer August Zeune in 1808, who mistakenly considered the Balkan Mountains the dominant mountain system of southeastern Europe spanning from the Adriatic Sea to the Black Sea. In the 19th century the term ''Balkan Peninsula'' was a synonym for Rumelia, the parts of Europe that were provinces of the Ottoman E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zummara
The term double clarinet refers to any of several woodwind instruments consisting of two parallel pipes made of cane, bird bone, or metal, played simultaneously, with a single reed for each. Commonly, there are five or six tone holes in each pipe, or holes in only one pipe while the other acts as a drone, and the reeds are either cut from the body of the instrument or created by inserting smaller, slit tubes into the ends of the pipes. The player typically uses circular breathing. The double clarinet is not a clarinet in the modern western sense of the term, since it lacks a register key; in this regard it is more closely related to the chalumeau. Varieties Double clarinets are found primarily in Middle Eastern music, but also in India; there are different versions and names in different countries. In Yemen, the double clarinet is called a '' mizmār.'' This word is used for other types of instruments in other countries. More common terms are ''zamr'', ''zammāra'', '' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilili
Pilili is a reed wind instrument in Adjara, west Georgia. It is a pipe of 25-30cm in length with 5-7 keys. File:Musical Instruments and Musicians. Various Musical Instruments, Including a Koshnai WDL10771.png, Instruments from Russian Turkestan, 1869-1872...from left: nagaras, sorna, bülban, ghoshmeh, tas. The unknown reed-tipped pipe bears close resemblance to the Pilili. File:Troupe of Musicians. Group of Musicians and a Batcha, or Dancing Boy WDL11112.png, Troop of Tajik or Uzbek musicians from Russian Turkestan. Musician on far left has pilili-like instrument. Description The main parts of the pilili are the trunk and the mouthpiece. The stem or trunk is a tube about 25-30 cm long, on which 5-7 holes are made. The mouthpiece is a small tube, the length of which depends on the desired sound. It has a split it its sidewall, creating a reed that makes sound when a musician blows through the top tip. The stem of the pilili is made from Tkemli (Prunus cerasifera plum tree) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arghul
The ''arghul'' (), also spelled ''argul'', ''arghoul'', ''arghool'', ''argol'', or ''yarghul'', is a Instrument (music), musical instrument in the reed instrument, reed family. It has been used since ancient Egyptian times and is still used as a traditional instrument in Egypt, Palestine, Syria and Jordan. Basic characteristics ''Modern Egyptians''.) Modern Arghul, 3 ft. 2½ in. long. The arghul is a double-pipe, Single-reed instrument, Single-reed Wind instrument, woodwind instrument that consists of two tubes: a melody pipe with between five and seven holes and a longer Drone (music), drone (Arabic ''ardiyya'', "ground") pipe. Its tone is similar to that of a clarinet, although a bit more reed-like. Unlike the similar mijwiz, the arghul has fingering holes on only one of the instrument's pipes (the melody pipe), and the drone pipe has a detachable length that allows the player to alter the pitch of the drone. In the illustration above all three lengths are shown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mijwiz
The ''mijwiz'' (, DIN: ''miǧwiz'') is a traditional Middle East musical instrument popular in Palestine, Egypt, Syria, Lebanon and Jordan. Its name in Arabic means "dual", because of its consisting of two, short, bamboo pipes with reed tips put together, making the mijwiz a double-pipe, single-reed woodwind instrument. Background The mijwiz consists of two pipes of equal length; each pipe has around five or six small holes for fingering. It requires a special playing technique known as "circular breathing," which is tricky but produces a continuous tone, without pausing to take a breath. The mijwiz is played in the Levant as an accompaniment to either belly dancing or dabke, the folkloric line dance of the Levant. The mijwiz is most popular today in the Levant (Palestine, Lebanon, Syria and Jordan). Many popular folk songs either include the mijwiz on recordings, or include the instrument's name in the song's lyrics. One example is the famous Lebanese dabke song "Jee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Launeddas
The launeddas (also called Sardinian triple clarinet) are a traditional Sardinian woodwind instrument made of three pipes, each of which has an idioglot single reed. They are a polyphonic instrument, with one of the pipes functioning as a drone and the other two playing the melody in thirds and sixths. Predecessors of the launeddas are found throughout Northern Africa and the Middle East. In 2700 BCE, the Egyptian reed pipes were originally called " memet"; during the Old Kingdom of Egypt (2778–2723 BCE), memets were depicted on the reliefs of seven tombs at Saqqara, six tombs at Giza, and the pyramids of Queen Khentkaus. The Sardinian launeddas themselves are an ancient instrument, being traced back to at least the eighth century BCE,Surian, Alesso. "Tenores and Tarantellas". 2000. In Broughton, Simon and Ellingham, Mark with McConnachie, James and Duane, Orla (Ed.), ''World Music, Vol. 1: Africa, Europe and the Middle East'', pg. 189–201. Rough Guides Ltd, Penguin Boo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |