|
Differential Privacy Composition Theorems
Differential privacy composition theorems are mathematical tools used in differential privacy to analyze and bound the accumulated privacy Privacy (, ) is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves or information about themselves, and thereby express themselves selectively. The domain of privacy partially overlaps with security, which can include the concepts of a ... loss when multiple differentially private mechanisms are applied to the same dataset. They quantify how privacy guarantees degrade as more queries or analyses are performed, and are essential for designing complex differentially private systems and algorithms. For example, if user submits multiple queries to a differentially private database, each query might individually satisfies ε-differential privacy but the repeated interaction can cumulatively leak more information than intended. Composition theorems address this by providing a way to calculate the overall privacy loss after multiple mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Privacy
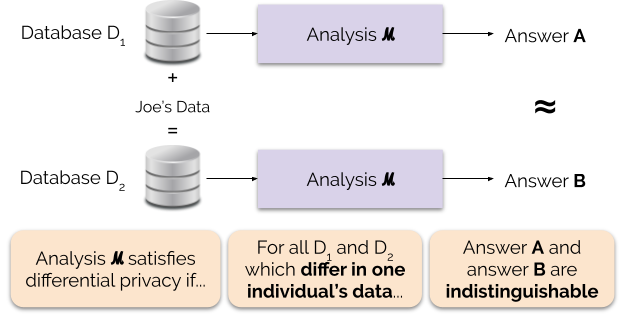
Differential privacy (DP) is a mathematically rigorous framework for releasing statistical information about datasets while protecting the privacy of individual data subjects. It enables a data holder to share aggregate patterns of the group while limiting information that is leaked about specific individuals. This is done by injecting carefully calibrated noise into statistical computations such that the utility of the statistic is preserved while provably limiting what can be inferred about any individual in the dataset. Another way to describe differential privacy is as a constraint on the algorithms used to publish aggregate information about a statistical database which limits the disclosure of private information of records in the database. For example, differentially private algorithms are used by some government agencies to publish demographic information or other statistical aggregates while ensuring confidentiality of survey responses, and by companies to collect informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privacy
Privacy (, ) is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves or information about themselves, and thereby express themselves selectively. The domain of privacy partially overlaps with security, which can include the concepts of appropriate use and Information security, protection of information. Privacy may also take the form of bodily integrity. Throughout history, there have been various conceptions of privacy. Most cultures acknowledge the right of individuals to keep aspects of their personal lives out of the public domain. The right to be free from unauthorized invasions of privacy by governments, corporations, or individuals is enshrined in the privacy laws of many countries and, in some instances, their constitutions. With the rise of technology, the debate regarding privacy has expanded from a bodily sense to include a digital sense. In most countries, the right to digital privacy is considered an extension of the original right to privacy, and many count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Privacy
Differential privacy (DP) is a mathematically rigorous framework for releasing statistical information about datasets while protecting the privacy of individual data subjects. It enables a data holder to share aggregate patterns of the group while limiting information that is leaked about specific individuals. This is done by injecting carefully calibrated noise into statistical computations such that the utility of the statistic is preserved while provably limiting what can be inferred about any individual in the dataset. Another way to describe differential privacy is as a constraint on the algorithms used to publish aggregate information about a statistical database which limits the disclosure of private information of records in the database. For example, differentially private algorithms are used by some government agencies to publish demographic information or other statistical aggregates while ensuring confidentiality of survey responses, and by companies to collect informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |