|
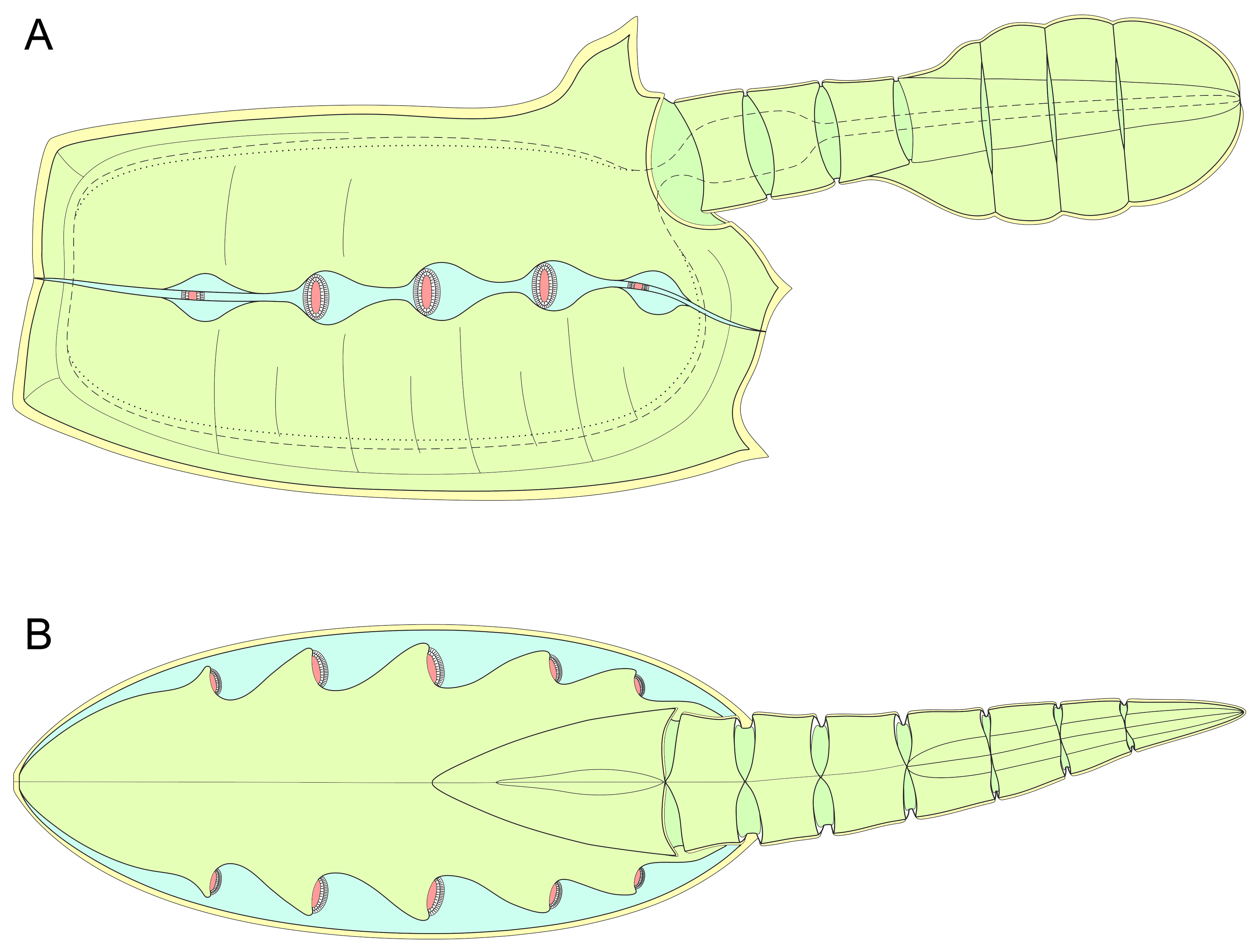
Didazoon Haoae
''Didazoon haoae'' is an extinct species of vetulicolid vetulicolian described by Shu, et al. based on fossils found in the Qiongzhusi (Chiungchussu) Formation, Yu'anshan Member (Eoredlichia zone), Early Cambrian, Lower Cambrian, in the Dabanqiao area (Kunming), about 60 km northwest of Chengjiang, China. Etymology "Dida" abbreviates (in Chinese) the China University of Geosciences (other), China University of Geosciences. Description The fossils show that the body of the animal was covered in a thin, flexible cuticle. The anterior part of the body was divided into six Segment (biology), segments, with fairly broad membranes separating the segments, and the Posterior (anatomy), posterior part of the body was divided into seven segments. The constriction between the anterior and posterior parts of the animal shows creasing, and the authors hypothesize that it was quite flexible. The fossils are interpreted as showing a large anterior opening, presumably a mouth, a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vetulicolia
Vetulicolia is a group of bilaterian marine animals encompassing several extinct species from the Cambrian, and possibly Ediacaran, periods. As of 2023, the majority of workers favor placing Vetulicolians in the stem group of the Chordata, but some continue to favor a more crownward placement as a sister group to the Tunicata. It was initially erected as a monophyletic clade with the rank of phylum in 2001, with subsequent work supporting its monophyly. However, more recent research suggests that vetulicolians may be paraphyletic and form a basal evolutionary grade of stem chordates. Etymology The taxon name, Vetulicolia, is derived from the type genus, '' Vetulicola'', which is a compound Latin word composed of ''vetuli'' "old" and ''cola'' "inhabitant". It was named after '' Vetulicola cuneata'', the first species of the group described in 1987. Description The vetulicolian body plan comprises two parts: a voluminous rostral (anterior) forebody, tipped with an anteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endostyle
The endostyle is an organ found in invertebrate chordate species of tunicates, lancelets, and in the larval stage of vertebrate lampreys. It assists in filter-feeding. It has evolved into the thyroid in vertebrate chordates. Since the endostyle is found in all three chordate lineages, it is presumed to have arisen in the common ancestor of these taxa, along with a shift to internal feeding for extracting suspended food particles from the water. When feeding, food particles suspended in the water adhere to the mucus the endostyle produces. The filtered water is then expelled through the gill slits, while the food and mucus are swept into the esophagus by movements of the cilia that coat the endostyle. The endostyle of larval lampreys ( ammocoetes) metamorphoses into the thyroid gland in adults, and is regarded as being homologous to the thyroid in other vertebrates due to its iodine-concentrating activity. One early hypothesis for the function of the endostyle, developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuyuanozoon
''Yuyuanozoon magnificissimi'', from the Cambrian Stage 3 Chengjiang lagerstatte, is the largest known vetulicolian, an extinct species of marine animal, with specimens up to 20 cm in length compared to 5–14 cm for other vetulicolian species. Etymology The generic name translates as "Animal of Yu Yuan," Yu Yuan being an ancient name for Chengjiang County. The specific name, ''magnificissimi'', translates as "of the most magnificent one," in reference to the great size of the holotype. Description Its body is non-biomineralized and consists of an elongate ovoid anterior section, with a segmented posterior section roughly one-third of the width and half the length of the anterior. The anterior opening is wide, with a narrow, raised circumventing rim 5 mm posterior to the opening. The anterior section is divided into six subdivisions by five circumventing lines, with gill openings placed symmetrically on each side, coinciding with the lines. In the holotype, gill filaments a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomatrum
''Pomatrum'' is an extinct vetulicolian, the senior synonym of ''Xidazoon''; the latter taxon was described by Shu, et al. (1999) based on fossils found in the Qiongzhusi (Chiungchussu) Formation, Yu'anshan Member (Eoredlichia zone), Lower Cambrian, Haikou, (Kunming), about 50 km west of Chengjiang, China. The fossils show that the body of the animal was divided into two parts. The anterior part of the body is moderately inflated, with a prominent mouth circlet. It has faint transverse divisions towards the front, but is otherwise smooth. The mouth circlet consists of about 30 plates divided into inner and outer regions. The anterior section has five structures on each side, which are interpreted as gills. A dark region running close to the ventral and posterior margins is interpreted as an endostyle. The condition of the anterior portion of the fossils suggests that it was thin-walled, i.e., that the anterior portion was largely hollow. The posterior part of the body tape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vetulicolidae
Vetulicolidae is a vetulicolian family from the Cambrian Stage 3 Maotianshan Shale and Sirius Passet Lagerstätte that consists of ''Vetulicola'', ''Beidazoon'', and ''Ooedigera''. It is distinguished from the Didazoonidae by a harder body wall and the lack of an oral disc. Description Members of the Vetulicolidae have relatively robust body coverings, with a subquadrate to elongate (in lateral view) anterior part and an elongate, segmented posterior part. The marginal zone of the anterior part may have short projections dorsally and postereodorsally. As diagnosed by Aldridge ''et al.'' in 2007, the anterior part is said to bear five annulations, and a lateral groove is not mentioned for the family. However, with and the addition of ''Ooedigera'' not all genera possess annulations in the anterior section, and with the re-classification of ''Yuyuannozoon'' each genus currently assigned to this family bears a lateral groove. Vetulicolids range in size from ''Beidazoon'' (around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nesonektris
''Nesonektris aldridgei'' is an extinct vetulicolian from the Late Botomian-aged Emu Bay Shale Lagerstätte in Kangaroo Island, Australia. So far, it is the fourth described vetulicolian that is not restricted to the Maotianshan Shales (the other three being '' Ooedigera'' of Sirius Passet, '' Banffia'' of the Burgess Shale, and '' Skeemella'' of the Pierson Cove Formation above the Wheeler Shale). Description ''N. aldridgei'' is known from several incomplete fossils which suggest that, in life, it was a fairly large animal (when compared to other vetulicolians). The largest fossil is about 150 millimetres ( 5.9 inches) long, leading researchers to estimate that that individual was about 170 millimetres (6.7 inches) long. The exquisitely preserved fossils show that running the length inside the tail was a notochord, thereby demonstrating the animal's chordate affinities as being related to tunicates. The forebody, and overall form are similar to vetulicolids of Vetulicol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeemella
''Skeemella'' is a genus of elongate animal from the Middle Cambrian Wheeler Shale and Marjum lagerstätte of Utah. It has been classified with the banffozoan vetulicolians. Description ''Skeemella'', which was first described in 2005, is diagnosed as having a body in two sections, covered in cuticle. The anterior section is short and wide, has a straight dorsal margin and a curving ventral margin, and is divided longitudinally in a way that makes it resemble a head shield. The anterior region is interpreted as being made of nine segments separated by thinner membranes (rather than as a single unit with multiple openings). ''Skeemella'' has a narrow, worm-shaped rear section with 43 segments in holotype specimen, identified as tergites separated by flexible membranes. The rear section terminates in what appears to be an arthropod telson, an elongate, unsegmented flattened structure that ends in two backward-pointing spines. In 2020, two more specimens of ''S. clavula'' were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heteromorphus
''Heteromorphus'' is an extinct genus of banffiid from the lower Cambrian Chengjiang lagerstatte. It contains one broadly accepted species, ''Heteromorphus confusus'', as well as a proposed junior synonym, ''Heteromorphus longicaudatus'' that may prove to be a separate species as additional specimens are examined. A much smaller species labeled "Form A" is allied with ''Heteromorphus'' at the class level but has not been formally described or assigned to ''Heteromorphus'' itself. Description Like ''Banffia'', ''Heteromorphus'' has a two-part body with a notable constriction between the parts, and a crossover that effectively reverses the dorsal and ventral sides between the anterior and posterior sections. The posterior portion is segmented, although the common presence of wrinkling makes counting the segments difficult. The anterior body shape ranges from torpedo-like to more rectangular, with a near-vertical anterior edge. ''Heteromorphus'' is separated from ''Banffia'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banffia
''Banffia'' is a genus of animals described from Middle Cambrian fossils. The genus commemorates Banff, Alberta, near where the first fossil specimens were discovered. Its placement in higher taxa is controversial, with it mostly being considered to be a member of the enigmatic phylum Vetulicolia. Anatomy ''Banffia constricta'' is known from hundreds of fossils found in the Burgess Shales. It is up to 10 cm in length, and divided equally into anterior and posterior parts. The entire body is twisted in a clockwise spiral, as seen from the front. This is believed to be a secondary adaptation from an initial bilateral condition for a burrowing lifestyle. The anterior section is covered by two carapace-like un-mineralized shells that are fused together. A crown-like structure formed of three concentric circular features surrounds the mouth. An antenna-form structure just posterior to the mouth may be a sensory organ. The posterior section is composed of 40 to 50 segments. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Group
In phylogenetics, the crown group or crown assemblage is a collection of species composed of the living representatives of the collection, the most recent common ancestor of the collection, and all descendants of the most recent common ancestor. It is thus a way of defining a clade, a group consisting of a species and all its extant or extinct descendants. For example, Neornithes (birds) can be defined as a crown group, which includes the most recent common ancestor of all modern birds, and all of its extant or extinct descendants. The concept was developed by Willi Hennig, the formulator of phylogenetic systematics, as a way of classifying living organisms relative to their extinct relatives in his "Die Stammesgeschichte der Insekten", and the "crown" and "stem" group terminology was coined by R. P. S. Jefferies in 1979. Though formulated in the 1970s, the term was not commonly used until its reintroduction in 2000 by Graham Budd and Sören Jensen. Contents of the crown gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordata
A chordate ( ) is a bilaterian animal belonging to the phylum Chordata ( ). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five distinctive physical characteristics (Apomorphy and synapomorphy, synapomorphies) that distinguish them from other Taxon, taxa. These five synapomorphies are a notochord, a neural tube, hollow dorsal nerve cord, an endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anus, anal tail. In addition to the morphological characteristics used to define chordates, analysis of genome sequences has identified two conserved signature indels (CSIs) in their proteins: cyclophilin-like protein and inner mitochondrial membrane protease ATP23, which are exclusively shared by all vertebrates, tunicates and cephalochordates. These CSIs provide molecular means to reliably distinguish chordates from all other animals. Chordates are divided into three phylum, subphyla: Vertebrata (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals), whose notochor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleobiology Database
The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Paleofaunal Database initiative, which operated from August 1998 through August 2000. From 2000 to 2015, PBDB received funding from the National Science Foundation. PBDB also received support form the Australian Research Council. From 2000 to 2010 it was housed at the National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis, a cross-disciplinary research center within the University of California, Santa Barbara. It is currently housed at University of Wisconsin-Madison and overseen by an international committee of major data contributors. The Paleobiology Database works closely with the Neotoma Paleoecology Database, which has a similar intellectual history, but has focused on the Quaternary (with an emphasis on the late Pleistocene and Holoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |