|
Diasoma
Diasoma is a proposed clade of mollusks uniting the classes Scaphopoda and Bivalvia. Whether scaphopods and bivalves are each other's closest living relatives among mollusks is disputed, leaving the monophyly of Diasoma in doubt. Diasoma was originally proposed on morphological grounds by Bruce Runnegar and John Pojeta Jr., in 1974. The name means "through-body", referring to the relatively straight gut with a mouth at the anterior end and anus at the posterior end, contrasting with gastropods and cephalopods, in which the gut is more curved and the mouth and anus are usually much closer together. The grouping was accepted by many studies in the 1980s and 1990s, but a phylogenetic analysis of 18s rDNA conducted by Gerhard Steiner and Hermann Dreyer in 2003 found scaphopods to be more closely related to cephalopods than bivalves. A 2020 phylogenetic analysis by Kevin Kocot and colleagues found scaphopods to be more closely related to gastropods than bivalves. However, a molecular phyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scaphopoda
Scaphopoda (plural scaphopods , from Ancient Greek σκᾰ́φης ''skáphē'' "boat" and πούς ''poús'' "foot"), whose members are also known as tusk shells or tooth shells, are a class of shelled marine invertebrates belonging to the phylum Mollusca with worldwide distribution and are the only class of exclusively infaunal marine molluscs. Shells of species within this class range in length (with ''Fissidentalium metivieri'' as the longest). Members of the order Dentaliida tend to be larger than those of the order Gadilida. These molluscs live in soft substrates offshore (usually not intertidally). Because of this subtidal habitat and the small size of most species, many beachcombers are unfamiliar with them; their shells are not as common or as easily visible in the beach drift as the shells of sea snails and clams. Molecular data suggest that the scaphopods are a sister group to the cephalopods, although higher-level molluscan phylogeny remains unresolved. Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watsonella
''Watsonella'' is an extinct genus of mollusc known from early (Terreneuvian) Cambrian strata. It has been hypothesized to be close to the origin of bivalves. It contains a single species, ''Watsonella crosbyi''. The genus is closely related to '' Anabarella'', with which it bears many morphological similarities, including a laminar internal shell microstructure said to connect it with the early bivalves '' Fordilla'' and ''Pojetaia''. Taxonomy ''Watsonella'' was described by Amadeus William Grabau in 1900, with the type species ''Watsonella crosbyi''. The type specimen was found in a fossil-filled boulder collected by Thomas Augustus Watson, the assistant of Alexander Graham Bell who received the first-ever telephone call. The genus name honors Watson and the species name honors Professor William Otis Crosby. Grabau initially interpreted ''Watsonella'' as a heteropod gastropod similar to the modern genus '' Carinaria''. In 1935, E. S. Cobbold named the genus ''Heraultia'' base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusks
Mollusca is a phylum of protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum after Arthropoda. The number of additional fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000, and the proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat, as numerous groups are freshwater and even terrestrial species. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known extant invertebrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bivalvia
Bivalvia () or bivalves, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class (biology), class of aquatic animal, aquatic molluscs (marine and freshwater) that have laterally compressed soft bodies enclosed by a calcified exoskeleton consisting of a hinged pair of half-bivalve shell, shells known as valve (mollusc), valves. As a group, bivalves have no head and lack some typical molluscan organs such as the radula and the odontophore. Their gills have evolved into ctenidium (mollusc), ctenidia, specialised organs for feeding and breathing. Common bivalves include clams, oysters, Cockle (bivalve), cockles, mussels, scallops, and numerous other family (biology), families that live in saltwater, as well as a number of families that live in freshwater. Majority of the class are benthic filter feeders that bury themselves in sediment, where they are relatively safe from predation. Others lie on the sea floor or attach themselves to rocks or other h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropods
Gastropods (), commonly known as slugs and snails, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, freshwater, and from the land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, land snails and slugs. The class Gastropoda is a diverse and highly successful class of mollusks within the phylum Mollusca. It contains a vast total of named species, second only to the insects in overall number. The fossil history of this class goes back to the Late Cambrian. , 721 families of gastropods are known, of which 245 are extinct and appear only in the fossil record, while 476 are currently extant with or without a fossil record. Gastropoda (previously known as univalves and sometimes spelled "Gasteropoda") are a major part of the phylum Mollusca, and are the most highly diversified class in the phylum, with 65,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopods
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symmetry, bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of cephalopod arm, arms or tentacles (muscular hydrostats) modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt Cephalopod ink, ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology. Cephalopods became dominant during the Ordovician period, represented by primitive nautiloids. The class now contains two, only distantly related, Extant taxon, extant subclasses: Coleoidea, which includes octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish; and Nautiloidea, represented by ''Nautilus (genus), Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. In the Coleoidea, the molluscan shell has been internalized or is absent, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
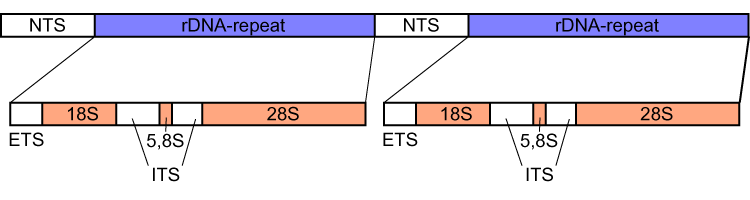
18S Ribosomal RNA
18S ribosomal RNA (abbreviated 18S rRNA) is a part of the ribosomal RNA in eukaryotes. It is a component of the Eukaryotic small ribosomal subunit (40S) and the cytosolic homologue of both the 12S ribosomal RNA, 12S rRNA in mitochondria and the 16S ribosomal RNA, 16S rRNA in plastids and prokaryotes. Similar to the prokaryotic 16S rRNA, the genes of the 18S ribosomal RNA have been widely used for Phylogenetics, phylogenetic studies and biodiversity screening of eukaryotes. Research history Along with the 28S ribosomal RNA, 28S and 5.8S ribosomal RNA, 5.8S rRNA in eukaryotes, the 18S rRNA was early identified as integral structural element of ribosomes which were first characterized by their sedimentation properties and named according to measured Svedberg, Svedberg units. Given its ubiquitous presence in eukaryotic life, the evolution of the 18S rRNA was soon proposed as marker for phylogenetics, phylogenetic studies to resolve the evolution of eukaryotes. Structure and function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rostroconchs
The Rostroconchia is a class of extinct molluscs dating from the early Cambrian to the Late Permian. They were initially thought to be bivalves, but were later given their own class. They have a single shell in their larval stage, and the adult typically has a single, pseudo-bivalved shell enclosing the mantle and muscular foot. The anterior part of the shell probably pointed downward and had a gap from which the foot could probably emerge. Rostroconchs probably lived a sedentary semi-infaunal lifestyle. There were probably more than 1,000 species of members of this class. Approximately 3 dozen genera and an even greater number of species have been described. Generally, rostroconchs are small, less than two centimeters in length, but larger forms, found in United States Devonian limestones, can grow to a length of 15 cm. Morphology and lifestyle Externally, rostroconchs look much like bivalves and rostroconchs probably had an extendable muscular foot, indicated by a pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian Period
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period 486.85 Ma. Most of the continents lay in the southern hemisphere surrounded by the vast Panthalassa, Panthalassa Ocean. The assembly of Gondwana during the Ediacaran and early Cambrian led to the development of new Convergent boundary, convergent plate boundaries and Volcanic arc, continental-margin arc magmatism along its margins that helped drive up global temperatures. Laurentia lay across the equator, separated from Gondwana by the opening Iapetus Ocean. The Cambrian marked a profound change in Life, life on Earth; prior to the Period, the majority of living organisms were small, Unicellular organism, unicellular and poorly preserved. Complex, multicellular organisms gradually became more common during the Ediacaran, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anabarella
''Anabarella'' is a species of bilaterally-flattened monoplacophoran mollusc, with a morphological similarity to the rostroconchs. Its shell preserves evidence of three mineralogical textures on its outer surface: it is polygonal near the crest of the shell, subsequently changing to both spiny and stepwise. Its internal microstructure is calcitic and semi-nacreous. Its name reflects its provenance from Anabar, Siberia. It has been interpreted as ancestral to the rostroconchs, and has been aligned to the Helcionellidae. The genus is closely related to ''Watsonella'', with which it bears many morphological similarities, including a laminar internal shell microstructure said to connect it with the early bivalves '' Fordilla'' and ''Pojetaia ''Pojetaia'' is an extinct genus of early bivalves, one of two genera in the extinct family Fordillidae. The genus is known solely from Early to Middle Cambrian fossils found in North America, Greenland, Europe, North Africa, Asia, and Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Group
In phylogenetics, the crown group or crown assemblage is a collection of species composed of the living representatives of the collection, the most recent common ancestor of the collection, and all descendants of the most recent common ancestor. It is thus a way of defining a clade, a group consisting of a species and all its extant or extinct descendants. For example, Neornithes (birds) can be defined as a crown group, which includes the most recent common ancestor of all modern birds, and all of its extant or extinct descendants. The concept was developed by Willi Hennig, the formulator of phylogenetic systematics, as a way of classifying living organisms relative to their extinct relatives in his "Die Stammesgeschichte der Insekten", and the "crown" and "stem" group terminology was coined by R. P. S. Jefferies in 1979. Though formulated in the 1970s, the term was not commonly used until its reintroduction in 2000 by Graham Budd and Sören Jensen. Contents of the crown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |