|
Demodex Brevis
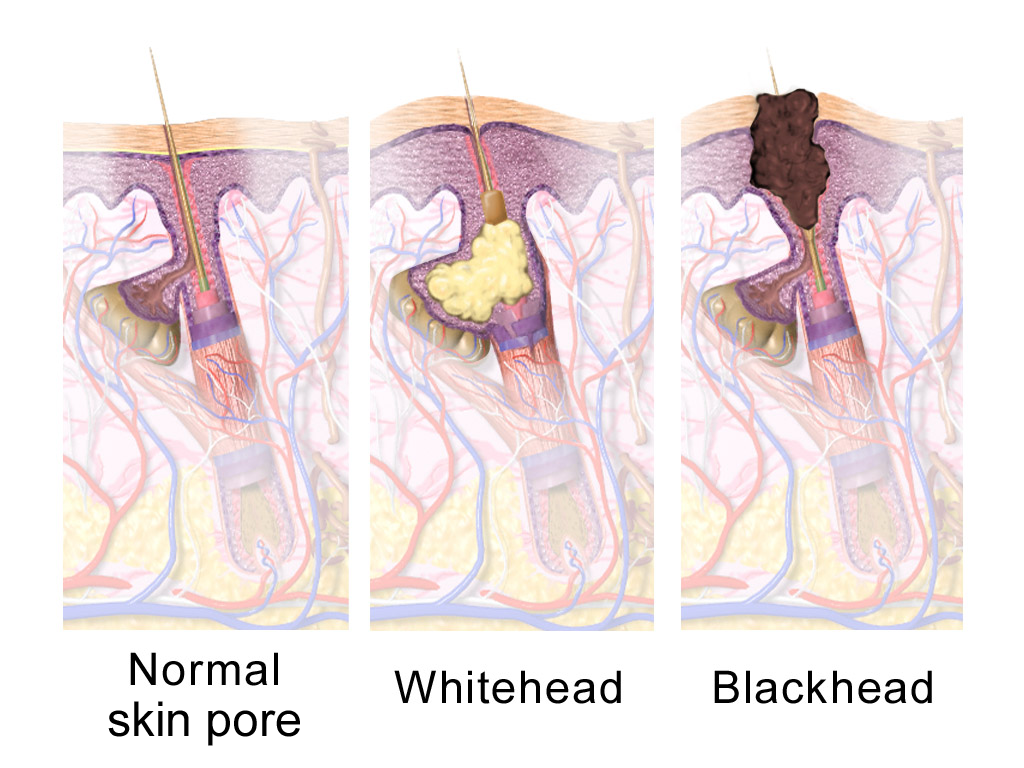
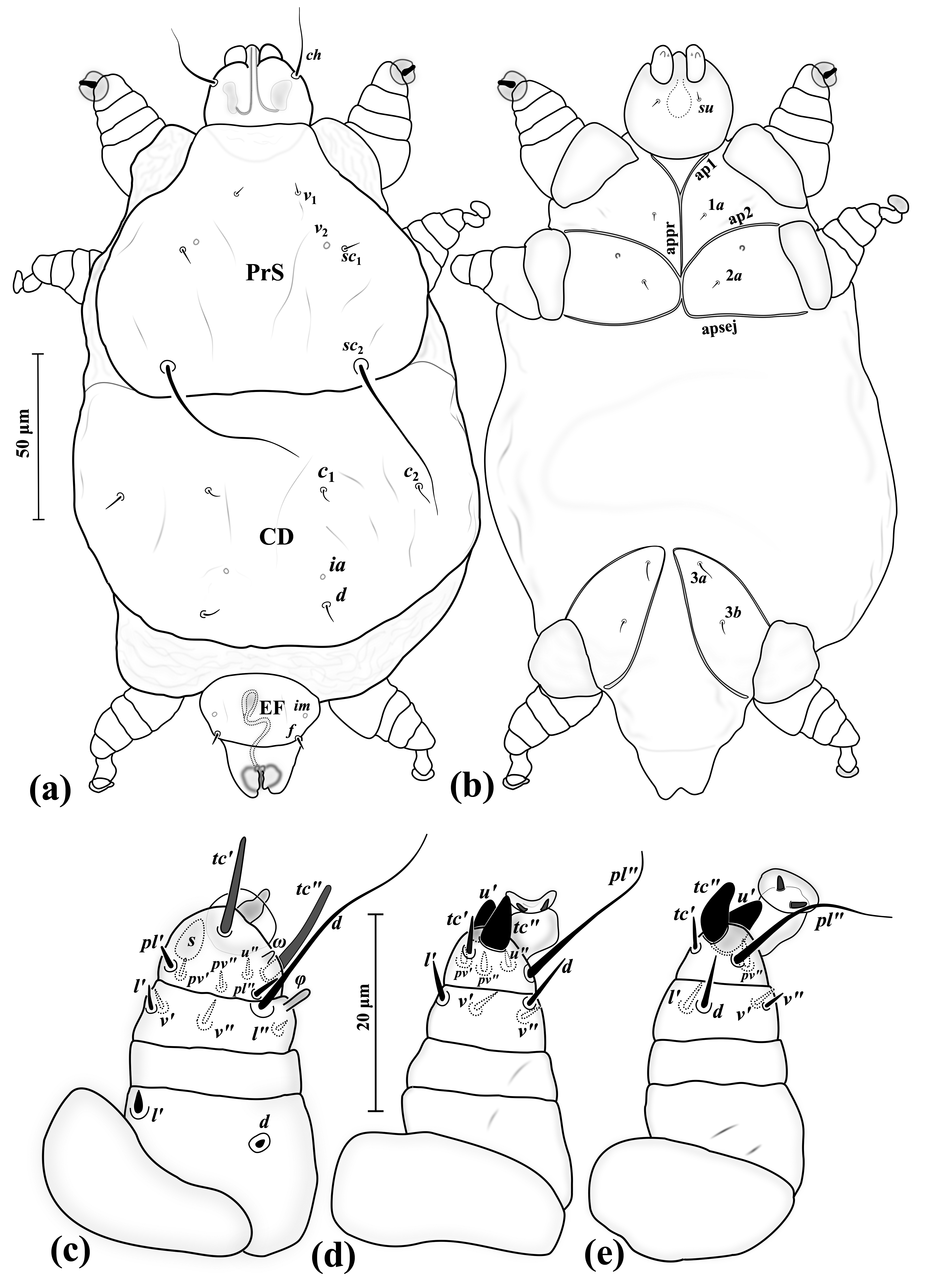
''Demodex brevis'' is one of the two species of face mite that inhabit humans (the other being ''Demodex folliculorum''). They are about half as long, at 0.15 to 0.2 mm (6 to 8 thousandths of an inch), as ''D. folliculorum'', but otherwise have few differences. Most of the article on ''Demodex folliculorum'' applies equally to ''D. brevis''. They are usually found in the sebaceous glands of the human body. ''D. brevis'' reproduces in the sebaceous glands in the same way that ''D. folliculorum'' reproduces in the follicles. Under normal conditions, they are not harmful, and are considered commensals, whereby the mite benefits but there is no harm or benefit to the host, rather than parasites where the host is harmed, or mutualistic organisms where the host benefits. During a severe infestation, though, there may be adverse effects on the host, such as demodicosis Demodicosis , also called Demodex folliculitis in humans and demodectic mange () or red mange in animals, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demodex
''Demodex'' is a genus of tiny mites that live in or near hair follicles of mammals. Around 65 species of ''Demodex'' are known. Two species live on humans: ''Demodex folliculorum'' and ''Demodex brevis'', both frequently referred to as eyelash mites, alternatively face mites or skin mites. Different species of animals host different species of ''Demodex''. ''Demodex#D. canis, Demodex canis'' lives on the domestic dog. The presence of ''Demodex'' species on mammals is common and usually does not cause any symptoms. ''Demodex'' is derived from Greek language, Greek () and , δηκός (, ''dēkós'') . Notable species ''D. folliculorum'' and ''D. brevis'' ''Demodex folliculorum'' and ''D. brevis'' are typically found on humans. The former was first described in 1842 by German physician and dermatologist Gustav Simon (physician), Gustav Simon, with English biologist Richard Owen naming the genus ''Demodex'' the following year. ''Demodex brevis'' was identified as separate in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demodex Folliculorum
''Demodex folliculorum'' is a microscopic mite that can survive only on the skin of humans. Most people host ''D.folliculorum'' on their skin particularly on the face, where sebaceous glands are most concentrated. Usually, the mites do not cause any harm, so are considered an example of commensalism rather than parasitism; but they can cause disease, known as demodicosis. Anatomy Due to being adapted to live inside hair follicles, ''D. folliculorum'' is thin and worm-like, with short legs. As an adult, ''D.folliculorum'' measures long. Adults have four pairs of legs; larvae and nymphs have only three pairs. ''D.folliculorum'' has a rudimentary gut but lacks an anus, so waste accumulates within the body until it dies. Reproduction and life cycle The entire life cycle of ''D.folliculorum'' takes 14–16 days. Adult mites copulate at the top of the hair follicle, near the skin surface. Eggs are deposited in the sebaceous gland inside the hair follicle. The heart-shaped egg is l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebaceous Gland
A sebaceous gland or oil gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the eyelids, meibomian glands, also called tarsal glands, are a type of sebaceous gland that secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Surrounding the female nipples, areolar glands are specialized sebaceous glands for lubricating the nipples. Fordyce spots are benign, visible, sebaceous glands found usually on the lips, gums and inner cheeks, and genitals. Structure Location In humans, sebaceous glands are found throughout all areas of the skin, except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There are two types of sebaceous glands: those connected to hair follicles and those that ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commensalism
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit from each other; amensalism, where one is harmed while the other is unaffected; and parasitism, where one is harmed and the other benefits. The commensal (the species that benefits from the association) may obtain nutrients, shelter, support, or locomotion from the host species, which is substantially unaffected. The commensal relation is often between a larger host and a smaller commensal; the host organism is unmodified, whereas the commensal species may show great structural adaptation consistent with its habits, as in the remoras that ride attached to sharks and other fishes. Remoras feed on their hosts' fecal matter, while pilot fish feed on the leftovers of their hosts' meals. Numerous birds perch on bodies of large mammal herbivo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson characterised parasites' way of feeding as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutualism (biology)
Mutualism describes the ecological Biological interaction, interaction between two or more species where each species has a net benefit. Mutualism is a common type of Ecology, ecological interaction. Prominent examples are: * the nutrient exchange between vascular plants and mycorrhizal fungi, * the Fertilisation, fertilization of flowering plants by pollinators, * the ways plants use fruits and edible seeds to encourage animal aid in seed dispersal, and * the way corals become photosynthetic with the help of the microorganism zooxanthellae. Mutualism can be contrasted with interspecific competition, in which each species experiences ''reduced'' fitness, and Cheating (biology), exploitation, and with parasitism, in which one species benefits at the expense of the other. However, mutualism may evolve from interactions that began with imbalanced benefits, such as parasitism. The term ''mutualism'' was introduced by Pierre-Joseph van Beneden in his 1876 book ''Animal Parasites an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demodicosis
Demodicosis , also called Demodex folliculitis in humans and demodectic mange () or red mange in animals, is caused by a sensitivity to and overpopulation of ''Demodex'' as the host's immune system is unable to keep the mites under control. ''Demodex'' is a genus of mite in the family Demodecidae. The mites are specific to their hosts, and each mammal species is host to one or two unique species of ''Demodex'' mites. Therefore, demodicosis cannot be transferred across species and has no zoonotic potential. Signs and symptoms Humans Demodicosis in humans is usually caused by '' Demodex folliculorum'' and may have a rosacea-like appearance. Common symptoms include hair loss, itching, and inflammation. An association with pityriasis folliculorum has also been described. Demodicosis is most often seen in folliculitis (inflammation of the hair follicles of the skin). Depending on the location, it may result in small pustules (pimples) at the base of a hair shaft on inflamed, co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trombidiformes
Trombidiformes is a large, diverse order of mites. Taxonomy In 1998, Trombidiformes was divided into the Sphaerolichida and the Prostigmata. The group has few synapomorphies by which it can be defined, unlike the other major group of acariform mites, Sarcoptiformes. Its members include medically important mites (such as ''Demodex'', the chiggers, and scrub-itch mites) and many agriculturally important species, including the spider mites (Tetranychidae). The superfamily Eriophyoidea, traditionally considered members of the Trombidiformes, have been found to be basal mites in genomic analyses, sister to the clade containing Sarcoptiformes and Trombidiformes. The 2004 classification retained the two suborders, comprising around 125 families and more than 22,000 described species. In the 2011 revised classification, the order now contains 151 families, 2235 genera and 25,821 species, and there were another 10 species with 24 species that present only as fossils. These 151 famili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animals Described In 1963
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are motility, able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million extant taxon, living animal species have been species description, described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and biological interaction, interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |