|
Decarbonization Pathway
A decarbonization pathway is a way for something, such as a country or energy system, to reach a greenhouse gas emissions target, such as net zero by 2050. Nineteen of the G20 countries have announced net-zero targets for this time frame. Decarbonization pathways aim to limit climate change, and include technology, economy and policy. Some pathways cover a particular sector: for example, the Road Transport Decarbonization Pathway (RTDP) tool, and the Deep Decarbonization Pathways initiative which is for the energy sector. Whereas others cover a country or city, such as London. There can also be pathways for organizations, such as companies, or things such as buildings. Pathways may include behavioral change, such as sometimes riding a bicycle rather than travelling by car. Some countries plan and discuss their decarbonization pathways years in advance, for example the 2025 consultation on extending the UK Emissions Trading Scheme beyond 2030. Whereas some other countries have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy System
An energy system is a system primarily designed to supply #Energy-services, energy-services to end user, end-users. The intent behind energy systems is to minimise energy losses to a negligible level, as well as to ensure the efficient use of energy. The IPCC Fifth Assessment Report defines an energy system as "all components related to the production, conversion, delivery, and use of energy". The first two definitions allow for demand-side measures, including Daylighting (architecture), daylighting, retrofitted building insulation, and passive solar building design, as well as socio-economic factors, such as aspects of energy demand management and remote work, while the third does not. Neither does the third account for the Informal sector, informal economy in traditional biomass that is significant in many Developing country, developing countries. The analysis of energy systems thus spans the disciplines of engineering and economics. Merging ideas from both areas to form a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
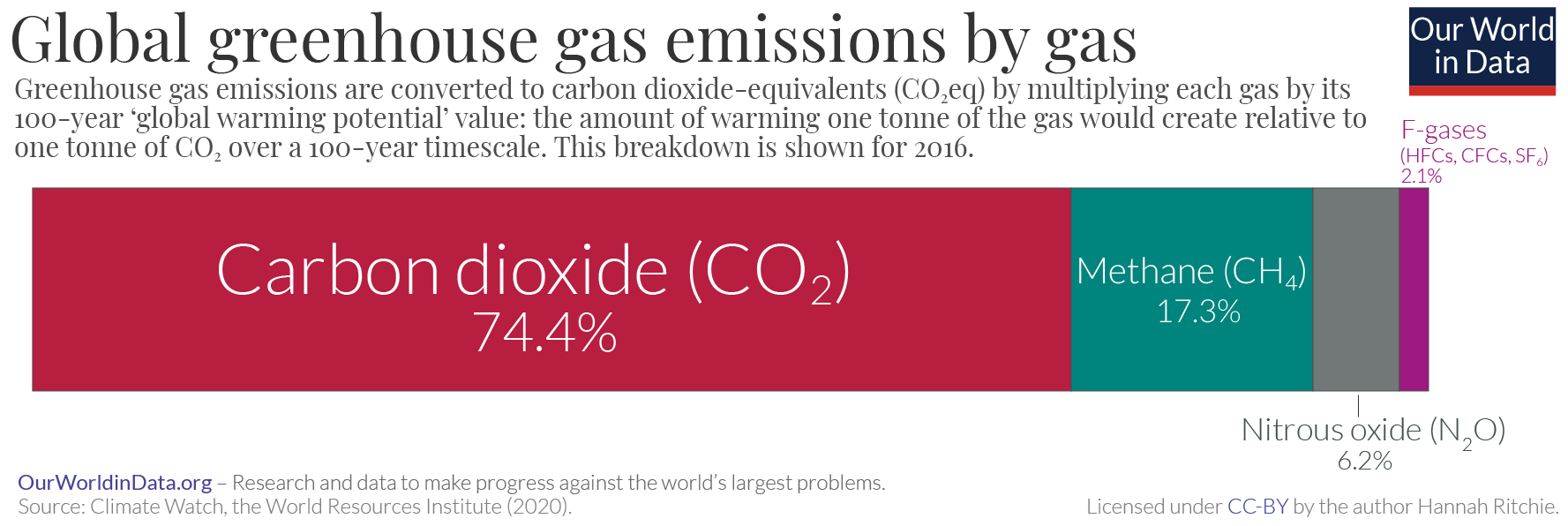
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate change. The top contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, largest annual emissions are from China followed by the United States. The United States has List of countries by greenhouse gas emissions per capita, higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are Big Oil, large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 (2575 ), of which 484±20 (177 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Net-zero Emissions
Global net-zero emissions is reached when greenhouse gas emissions and removals due to human activities are in balance. It is often called simply net zero. ''Emissions'' can refer to all greenhouse gases or only carbon dioxide (). Reaching net zero is necessary to stop further global warming. It requires deep cuts in emissions, for example by shifting from fossil fuels to sustainable energy, improving energy efficiency and halting deforestation. A small remaining fraction of emissions can then be offset using carbon dioxide removal. People often use the terms ''net-zero emissions'', ''carbon neutrality,'' and ''climate neutrality'' with the same meaning. However, in some cases, these terms have different meanings. For example, some standards for ''carbon neutral certification'' allow a lot of carbon offsetting. But ''net zero standards'' require reducing emissions to more than 90% and then only offsetting the remaining 10% or less to fall in line with 1.5 °C targets. Organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change Mitigation
Climate change mitigation (or decarbonisation) is action to limit the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that cause climate change. Climate change mitigation actions include energy conservation, conserving energy and Fossil fuel phase-out, replacing fossil fuels with sustainable energy, clean energy sources. Secondary mitigation strategies include changes to land use and carbon sequestration, removing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. Current climate change mitigation policies are insufficient as they would still result in global warming of about 2.7 °C by 2100, significantly above the 2015 Paris Agreement's goal of limiting global warming to below 2 °C. Solar energy and wind power can replace fossil fuels at the lowest cost compared to other renewable energy options.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Decarbonization Pathways Initiative
The Deep Decarbonization Pathways initiative (DDPi) is a global consortium formed in 2013 which researches methods to limit the rise of global temperature due to global warming to 2°C or less. The focus of the DDPP is on decarbonization pathways for sustainable energy systems, other sectors of the economy, such as agriculture and land-use, are not directly considered. Methods Analyses of possible scenarios assume no major changes in culture and rely on existing technology. They assume no major changes in the lifestyles of people in developed countries and do not include possible future technologies such as nuclear fusion. Population growth of 1% per year and economic growth of 3% is assumed. Analyses show a need for continued research on energy technologies. The DDPi rejects an incrementalist approach to climate protection. Instead, meeting the climate change mitigation challenge (as set out in the 2015 Paris Agreement) will require backcasting to a suitable attractor, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Western Europe, with a population of 14.9 million. London stands on the River Thames in southeast England, at the head of a tidal estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for nearly 2,000 years. Its ancient core and financial centre, the City of London, was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans as Londinium and has retained its medieval boundaries. The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has been the centuries-long host of Government of the United Kingdom, the national government and Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliament. London grew rapidly 19th-century London, in the 19th century, becoming the world's List of largest cities throughout history, largest city at the time. Since the 19th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UK Emissions Trading Scheme
The UK Emissions Trading Scheme (UK ETS) is the carbon emission trading scheme of the United Kingdom. It is cap and trade and came into operation on 1 January 2021 following the UK's departure from the European Union. The cap is reduced in line with the UK's 2050 net zero commitment. Phase 1: 2021 to 2025 Although initially somewhat similar to the earlier UK participation in the European Union Emission Trading Scheme (EU ETS),Department of Business, Energy and Industrial StrategyParticipating in the UK Emissions Trading Scheme (UK ETS) published 17 December 2021, accessed 15 January 2021 there are differences. The initial cap is 5% lower than the UK’s share under phase four of the EU ETS. Price stabilisation The auction reserve price is £22 per tonne, and the government intends legislating for measures to limit price spikes. Coverage The UK ETS is initially limited to internal flights, electricity generation and industries which use a lot of energy: but the scheme will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decisionmaking Under Deep Uncertainty
Decision making under deep uncertainty (DMDU) is a decision science practice and analytical framework that evaluates potential solutions across multiple plausible future scenarios rather than attempting to predict a single future outcome. This approach is particularly valuable for strategic planning, public policy, and risk management when Stakeholder, stakeholders, analysts, and Decision-maker, decision-makers cannot reach consensus about future conditions or when traditional forecasting methods are inadequate due to fundamental uncertainties. DMDU employs Computer simulation, simulation models and scenario planning to explore potential futures through multiple "States of the World" (SOWs) and alternative scenarios, enabling comparison of how different policy options or decisions might perform across diverse possible outcomes. The methodology focuses on identifying Robust decision, robust and Adaptive management, adaptive decisions that can perform well across a range of uncertain c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate change. The top contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, largest annual emissions are from China followed by the United States. The United States has List of countries by greenhouse gas emissions per capita, higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are Big Oil, large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 (2575 ), of which 484±20 (177 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |