|
Cystoisosporiasis
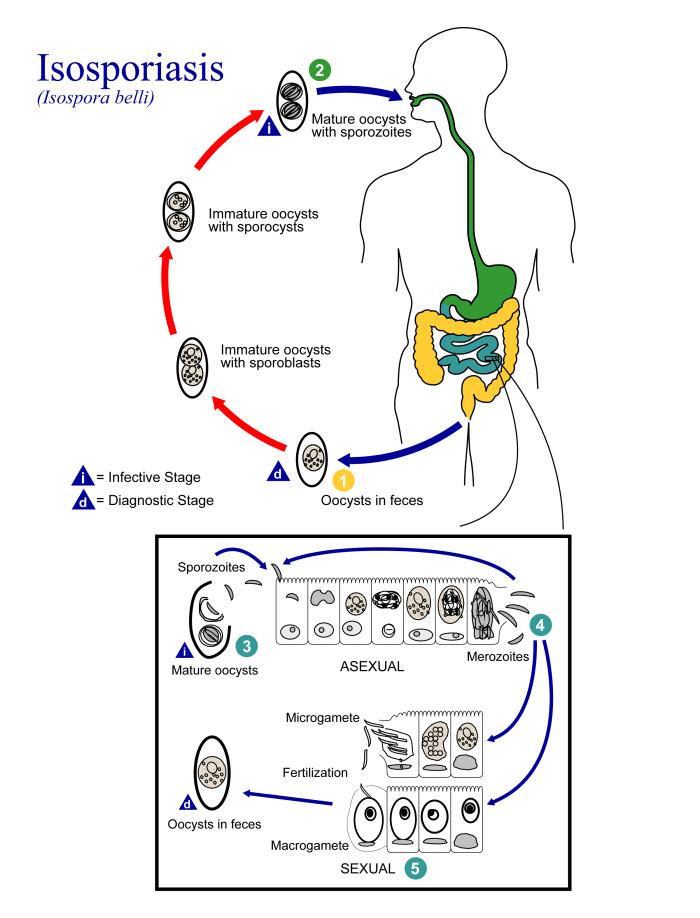
Isosporiasis, also known as cystoisosporiasis, is a human intestinal disease caused by the parasite ''Cystoisospora belli'' (previously known as ''Isospora belli''). It is found worldwide, especially in tropical and subtropical areas. Infection often occurs in immuno-compromised individuals, notably AIDS patients, and outbreaks have been reported in institutionalized groups in the United States. The first documented case was in 1915. It is usually spread indirectly, normally through contaminated food or water (CDC.gov). Signs and symptoms Infection causes acute, non-bloody diarrhea with crampy abdominal pain, which can last for weeks and result in malabsorption and weight loss. In immunodepressed patients, and in infants and children, the diarrhea can be severe. Eosinophilia may be present (differently from other protozoan infections). at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystoisospora Belli
''Cystoisospora belli'', previously known as ''Isospora belli'', is a parasite that causes an intestinal disease known as cystoisosporiasis.Centers For Disease Control: https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/cystoisospora/index.html This protozoan parasite is opportunistic in immune suppressed human hosts. It primarily exists in the epithelial cells of the small intestine, and develops in the cell cytoplasm. The distribution of this coccidian parasite is cosmopolitan, but is mainly found in tropical and subtropical areas of the world such as the Caribbean, Central and S. America, India, Africa, and S.E. Asia. In the U.S., it is usually associated with HIV infection and institutional living. Morphology A fully mature (sporulated) oocyst of genus ''Isospora'' is a spindle-shaped body that has two sporocysts that contain four sporozoites each. The oocysts of ''Cystoisospora belli'' are long and oval shaped. They measure between 20 and 33 micrometers in length and between 10 and 19 micromet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infectious Disease (medical Specialty)
Infectious diseases or ID, also known as infectiology, is a medical specialty dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of infections. An infectious diseases specialist's practice consists of managing nosocomial ( healthcare-acquired) infections or community-acquired infections and is historically associated with hygiene, epidemiology, clinical microbiology, travel medicine and tropical medicine. Scope Infectious diseases specialists typically serve as consultants to other physicians in cases of complex infections, and often manage patients with HIV/AIDS and other forms of immunodeficiency. Although many common infections are treated by physicians without formal expertise in infectious diseases, specialists may be consulted for cases where an infection is difficult to diagnose or manage. They may also be asked to help determine the cause of a fever of unknown origin. Specialists in infectious diseases can practice both in hospitals (inpatient) and clinics (outpatient). In hospit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporoblast
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestinal Infectious Diseases
Intestinal infectious diseases include a large number of infections of the bowels including: cholera, typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever, other types of salmonella infections, shigellosis, botulism, gastroenteritis, and amoebiasis Amoebiasis, or amoebic dysentery, is an infection of the intestines caused by a parasitic amoeba '' Entamoeba histolytica''. Amoebiasis can be present with no, mild, or severe symptoms. Symptoms may include lethargy, loss of weight, colonic ... among others. Typhoid and paratyphoid resulted in 221,000 deaths in 2013 down from 259,000 deaths in 1990. Other diseases which result in diarrhea caused another 1.3 million additional deaths in 2013 down from 2.6 million deaths in 1990. References {{Reflist Infectious diseases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Parasites (human)
Endoparasites Protozoan organisms Helminths (worms) Helminth organisms (also called helminths or intestinal worms) include: Tapeworms Flukes Roundworms Other organisms Ectoparasites References {{Portal bar, Biology, Medicine * Parasites Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ... * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, sold under the brand name Bactrim among others, is a fixed-dose combination antibiotic medication used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. It consists of one part trimethoprim to five parts sulfamethoxazole. It is used to treat urinary tract infections, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) skin infections, travelers' diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, and cholera, among others. It is used both to treat and prevent pneumocystis pneumonia and toxoplasmosis in people with HIV/AIDS and other causes of immunosuppression. It can be given by mouth or intravenously. Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines and is also available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 121st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 5million prescriptions. Medical uses ''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' pneumonia Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid-fast Stain
Acid-fastness is a physical property of certain bacterial and Eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells, as well as some Sub-cellular, sub-cellular structures, specifically their resistance to decolorization by acids during laboratory staining procedures. Once stained as part of a sample, these organisms can resist the acid and/or ethanol-based decolorization procedures common in many staining protocols, hence the name ''acid-fast''. The mechanisms of acid-fastness vary by species, although the most well-known example is in the genus ''Mycobacterium'', which includes the species responsible for tuberculosis and leprosy. The acid-fastness of ''Mycobacteria'' is due to the high mycolic acid content of their cell walls, which is responsible for the staining pattern of poor absorption followed by high retention. Some bacteria may also be partially acid-fast, such as ''Nocardia''. Acid-fast organisms are difficult to characterize using standard microbiological techniques, though they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epifluorescence
A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence instead of, or in addition to, scattering, reflection, and attenuation or absorption, to study the properties of organic or inorganic substances. "Fluorescence microscope" refers to any microscope that uses fluorescence to generate an image, whether it is a simple set up like an epifluorescence microscope or a more complicated design such as a confocal microscope, which uses optical sectioning to get better resolution of the fluorescence image. Principle The specimen is illuminated with light of a specific wavelength (or wavelengths) which is absorbed by the fluorophores, causing them to emit light of longer wavelengths (i.e., of a different color than the absorbed light). The illumination light is separated from the much weaker emitted fluorescence through the use of a spectral emission filter. Typical components of a fluorescence microscope are a light source (xenon arc lamp or mercury-vapor lamp are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duodenal
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine may be used instead of duodenum. In mammals the duodenum may be the principal site for iron absorption. The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest part of the small intestine. In humans, the duodenum is a hollow jointed tube about 25–38 cm (10–15 inches) long connecting the stomach to the middle part of the small intestine. It begins with the duodenal bulb and ends at the suspensory muscle of duodenum. Duodenum can be divided into four parts: the first (superior), the second (descending), the third (horizontal) and the fourth (ascending) parts. Structure The duodenum is a C-shaped structure lying adjacent to the stomach. It is divided anatomically into four sections. The first part of the duodenum lie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Processes such as insemination or pollination which happen before the fusion of gametes are also sometimes informally called fertilisation. The cycle of fertilisation and development of new individuals is called sexual reproduction. During double fertilisation in angiosperms the haploid male gamete combines with two haploid polar nuclei to form a triploid primary endosperm nucleus by the process of vegetative fertilisation. History In Antiquity, Aristotle conceived the formation of new individuals through fusion of male and female fluids, with form and function emerging gradually, in a mode called by him as epigenetic. In 1784, Spallanzani established the need of interaction between the female's ovum and male's sperm to form a zygote in fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trophozoites
A trophozoite (G. ''trope'', nourishment + ''zoon'', animal) is the activated, feeding stage in the life cycle of certain protozoa such as malaria-causing '' Plasmodium falciparum'' and those of the '' Giardia'' group. (The complement of the trophozoite state is the thick-walled cyst form). Life cycle stages Trophozoite and cyst stages are shown in the life cycle of ''Balantidium coli'' the causative agent of balantidiasis. In the apicomplexan life cycle the trophozoite undergoes schizogony (asexual reproduction) and develops into a schizont Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organism i ... which contains merozoites. The trophozoite life stage of '' Giardia'' colonizes and proliferates in the small intestine. Trophozoites develop during the course of the infection into cysts whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelial Cell
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |