|
Crystal River Archaeological State Park
Crystal River State Archaeological Site is a Florida State Park located on the Crystal River and within the Crystal River Preserve State Park. The park is located two miles (3 km) northwest of the city of Crystal River, on Museum Point off U.S. 19/ 98. Under the title of Crystal River Indian Mounds, it is also a U.S. National Historic Landmark (designated as such on September 29, 1970). History The park contains a six-mound complex, occupied from the Deptford period through Santa Rosa-Swift Creek culture and up to the Late Fort Walton period. This timespan makes it one of the longest continually occupied sites in Florida, believed to have been occupied for 1,600 years. Native Americans traveled long distances to the complex to bury their dead and to engage in trading activities. An estimated 7,500 people may have visited the complex annually when it was occupied. The complex contains burial mounds, temple/platform mounds, a plaza area, and a midden. The earliest buri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal River, Florida
Crystal River is a city in Citrus County, Florida, United States. The population was 3,108 in the 2010 census. According to the U.S. Census estimates of 2018, the city had a population of 3,162. The city was incorporated in 1903 and is the self professed "Home of the Manatee". Crystal River Preserve State Park is located nearby, and Crystal River Archaeological State Park is located in the city's northwest side. Crystal River is at the heart of the Nature Coast of Florida. The city is situated around Kings Bay, which is spring-fed so it keeps a constant temperature year round. A cluster of 50 springs designated as a first-magnitude system feeds Kings Bay. A first-magnitude system discharges 100 cubic feet or more of water per second, which equals about 64 million gallons of water per day. Because of this discharge amount, the Crystal River Springs group is the second largest springs group in Florida, the first being Wakulla Springs in Wakulla County near Tallahassee. Kings Bay c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roberts Island Complex
The Roberts Island complex is an archaeological site in Citrus County, Florida, near the Gulf of Mexico, dating from the late Woodland period. It is located on an island in the Crystal River midway between the springs at the head of the river and the mouth of the river on the Gulf of Mexico. The site is a geographically separate unit of the Crystal River Archaeological State Park. The site includes three shell mounds and three middens. Two of the mounds may have had stepped sides. The Roberts Island complex was developed as the Crystal River site declined and most other ceremonial sites in the region were abandoned during the 7th or 8th century. Description Roberts Island divides Crystal River and Salt River, a distributary of Crystal River, as they diverge. Both rivers are tidal. The site is downstream from the Crystal River archaeological site, Roberts Island has Hallandale-Rock Outcrop as the primary soil type, with some areas of soil produced by prehistoric human activiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Parks Of Florida
State may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Literature * ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State * ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States * '' Our State'', a monthly magazine published in North Carolina and formerly called ''The State'' * The State (Larry Niven), a fictional future government in three novels by Larry Niven Music Groups and labels * States Records, an American record label * The State (band), Australian band previously known as the Cutters Albums * ''State'' (album), a 2013 album by Todd Rundgren * ''States'' (album), a 2013 album by the Paper Kites * ''States'', a 1991 album by Klinik * ''The State'' (album), a 1999 album by Nickelback Television * ''The State'' (American TV series), 1993 * ''The State'' (British TV series), 2017 Other * The State (comedy troupe), an American comedy troupe Law and politics * State (polity), a centralized political organizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Historic Landmarks In Florida
The National Historic Landmarks in Florida are representations of a broad sweep of history from Pre-Columbian times, through the Second Seminole War and Civil War, and the Space Age. There are 47 National Historic Landmarks (NHLs) in Florida,. which are located in twenty-two of the state's sixty-seven counties. Sixteen of the NHLs in the state are significant examples of a particular architectural style, eleven have military significance, ten are archaeological sites, three were the homes of well-known American authors, and one is associated with the development of the U.S. Space Program. Six sites are in state parks and managed by the Florida Department of Environmental Protection. Also included is a site determined eligible for National Historic Landmark status, and a list of historical sites in Florida managed by the U.S. National Park Service which also have national significance. The National Historic Landmark program is administered by the National Park Service, a branc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Florida
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Museums In Florida
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museums In Citrus County, Florida
A museum ( ; plural museums or, rarely, musea) is a building or institution that cares for and displays a collection of artifacts and other objects of artistic, cultural, historical, or scientific importance. Many public museums make these items available for public viewing through exhibits that may be permanent or temporary. The largest museums are located in major cities throughout the world, while thousands of local museums exist in smaller cities, towns, and rural areas. Museums have varying aims, ranging from the conservation and documentation of their collection, serving researchers and specialists, to catering to the general public. The goal of serving researchers is not only scientific, but intended to serve the general public. There are many types of museums, including art museums, natural history museums, science museums, war museums, and children's museums. According to the International Council of Museums (ICOM), there are more than 55,000 museums in 202 cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native American Museums In Florida
Native may refer to: People * Jus soli, citizenship by right of birth * Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory ** Native Americans (other) In arts and entertainment * Native (band), a French R&B band * Native (comics), a character in the X-Men comics universe * ''Native'' (album), a 2013 album by OneRepublic * ''Native'' (2016 film), a British science fiction film * ''The Native'', a Nigerian music magazine In science * Native (computing), software or data formats supported by a certain system * Native language, the language(s) a person has learned from birth * Native metal, any metal that is found in its metallic form, either pure or as an alloy, in nature * Native species, a species whose presence in a region is the result of only natural processes Other uses * Northeast Arizona Technological Institute of Vocational Education (NATIVE), a technology school district in the Arizona portion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Appalachian Mississippian Culture
The Mississippian culture was a Native American civilization that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 CE to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building large, earthen platform mounds, and often other shaped mounds as well. It was composed of a series of urban settlements and satellite villages linked together by loose trading networks. The largest city was Cahokia, believed to be a major religious center located in what is present-day southern Illinois. The Mississippian way of life began to develop in the Mississippi River Valley (for which it is named). Cultures in the tributary Tennessee River Valley may have also begun to develop Mississippian characteristics at this point. Almost all dated Mississippian sites predate 1539–1540 (when Hernando de Soto explored the area), with notable exceptions being Natchez communities. These maintained Mississippian cultural practices into the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
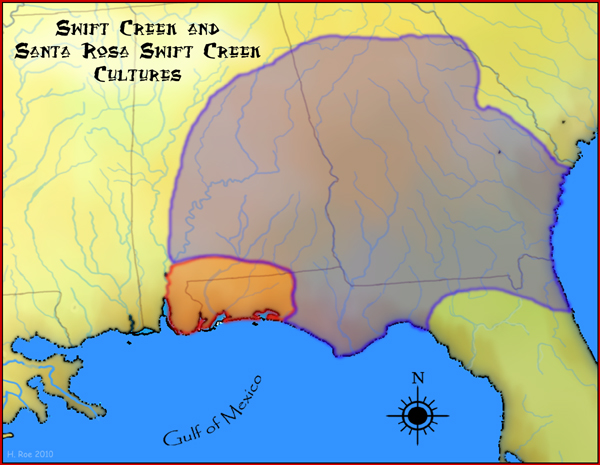
Swift Creek Culture
The Swift Creek culture was a Middle Woodland period archaeological culture in the Southeastern Woodlands of North America, dating to around 100-800 CE. It occupied the areas now part of Georgia, Alabama, Florida, South Carolina, and Tennessee. In Florida, Swift Creek ceremonial practices and burial complexes are referred to technically as the Yent-Green Point complex. The Swift Creek culture was contemporaneous with and interacted with the Hopewell culture; Swift Creek is often described as "Hopewellian." The type site for the Swift Creek culture was the Swift Creek mound site, which was located in Bibb County, Georgia. The Leake Mounds are another significant Swift Creek Culture site in Georgia. Swift Creek peoples practiced mound-building but were generally non- sedentary. Their sustenance resulted from hunting, gathering/collecting, and fishing. Swift Creek are characterized by earthenware pottery with complicated stamped designs, involving mostly curvilinear elements. Exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthwork (archaeology)
In archaeology, earthworks are artificial changes in land level, typically made from piles of artificially placed or sculpted rocks and soil. Earthworks can themselves be archaeological features, or they can show features beneath the surface. Types Earthworks of interest to archaeologists include hill forts, henges, mounds, platform mounds, effigy mounds, enclosures, long barrows, tumuli, ridge and furrow, mottes, round barrows, and other tombs. * Hill forts, a type of fort made out of mostly earth and other natural materials including sand, straw, and water, were built as early as the late Stone Age and were built more frequently during the Bronze Age and Iron Age as a means of protection. See also Oppidum. * Henge earthworks are those that consist of a flat area of earth in a circular shape that are encircled by a ditch, or several circular ditches, with a bank on the outside of the ditch built with the earth from inside the ditch. They are believed to have been use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mound Builder (people)
A number of pre-Columbian cultures are collectively termed "Mound Builders". The term does not refer to a specific people or archaeological culture, but refers to the characteristic mound earthworks erected for an extended period of more than 5,000 years. The "Mound Builder" cultures span the period of roughly 3500 BCE (the construction of Watson Brake) to the 16th century CE, including the Archaic period, Woodland period (Calusa culture, Adena and Hopewell cultures), and Mississippian period. Geographically, the cultures were present in the region of the Great Lakes, the Ohio River Valley, and the Mississippi River valley and its tributary waters. The first mound building was an early marker of political and social complexity among the cultures in the Eastern United States. Watson Brake in Louisiana, constructed about 3500 BCE during the Middle Archaic period, is currently the oldest known and dated mound complex in North America. It is one of 11 mound complexes from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)