|
Crusader Gold
''Crusader Gold'' is an archaeological adventure novel by David Gibbins. First published in 2006, it is the second book in Gibbins's Jack Howard series. It has been published in more than 20 languages and was a New York Times bestseller. Plot summary Following a prologue set in AD 71 when the golden menorah from the Jewish Temple in Jerusalem is locked away in Rome, the novel picks up in present-day Turkey with marine archaeologist Jack Howard on a hunt for ancient treasures in the harbour of Istanbul, formerly Constantinople. One item not among the treasures thrown into the harbour when the Crusaders pillaged the city is the menorah, and Jack soon learns from colleagues Jeremy and Maria that it may have been stolen from Constantinople by Norse warrior Harald Hardrada during his service to the emperor of Constantinople and taken by him on his explorations of the New World. Jack goes to the monastery at Iona in Scotland to see a priest who tells him that the Nazi Ahnenerbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Novels
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were intended to recover Jerusalem and its surrounding area from Islamic rule. Beginning with the First Crusade, which resulted in the recovery of Jerusalem in 1099, dozens of Crusades were fought, providing a focal point of European history for centuries. In 1095, Pope Urban II proclaimed the First Crusade at the Council of Clermont. He encouraged military support for Byzantine emperor AlexiosI against the Seljuk Turks and called for an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem. Across all social strata in western Europe, there was an enthusiastic response. The first Crusaders had a variety of motivations, including religious salvation, satisfying feudal obligations, opportunities for renown, and economic or political advantage. Later crusades were c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Adventure Novels
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *'' Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * Briton ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2006 British Novels
6 (six) is the natural number following 5 and preceding 7. It is a composite number and the smallest perfect number. In mathematics Six is the smallest positive integer which is neither a square number nor a prime number; it is the second smallest composite number, behind 4; its proper divisors are , and . Since 6 equals the sum of its proper divisors, it is a perfect number; 6 is the smallest of the perfect numbers. It is also the smallest Granville number, or \mathcal-perfect number. As a perfect number: *6 is related to the Mersenne prime 3, since . (The next perfect number is 28.) *6 is the only even perfect number that is not the sum of successive odd cubes. *6 is the root of the 6-aliquot tree, and is itself the aliquot sum of only one other number; the square number, . Six is the only number that is both the sum and the product of three consecutive positive numbers. Unrelated to 6's being a perfect number, a Golomb ruler of length 6 is a "perfect ruler". Six is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenote
A cenote ( or ; ) is a natural pit cave, pit, or sinkhole, resulting from the collapse of limestone bedrock that exposes groundwater. The regional term is specifically associated with the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico, where cenotes were commonly used for water supplies by the ancient Maya civilization, Maya, and occasionally for sacrifice in Maya culture, sacrificial offerings. The term derives from a word used by the lowland Yucatec Maya——to refer to any location with accessible groundwater. Similar rock-sided sinkholes like cenotes are common geological forms in low-altitude regions, particularly on islands, coastlines, and platforms with young post-Paleozoic limestone with little soil development. The term ''cenote'' has also been used to describe similar karst features in other countries such as Cuba and Australia. Definition and description Cenotes are surface connections to subterranean water bodies. While the best-known cenotes are large open-water pools measuring t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Civilization
The Maya civilization () of the Mesoamerican people is known by its ancient temples and glyphs. Its Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is also noted for its art, architecture, mathematics, calendar, and astronomical system. The Maya civilization developed in the Maya Region, an area that today comprises southeastern Mexico, all of Guatemala and Belize, and the western portions of Honduras and El Salvador. It includes the northern lowlands of the Yucatán Peninsula and the highlands of the Sierra Madre, the Mexican state of Chiapas, southern Guatemala, El Salvador, and the southern lowlands of the Pacific littoral plain. Today, their descendants, known collectively as the Maya, number well over 6 million individuals, speak more than twenty-eight surviving Mayan languages, and reside in nearly the same area as their ancestors. The Archaic period, before 2000 BC, saw the first developments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L'Anse Aux Meadows
L'Anse aux Meadows ( lit. Meadows Cove) is an archaeological site, first excavated in the 1960s, of a Norse settlement dating to approximately 1,000 years ago. The site is located on the northernmost tip of the island of Newfoundland in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador near St. Anthony. With carbon dating estimates between 990–1050 CE, tree-ring analysis dating to the year 1021 and a mean carbon date of 1014 overall, L'Anse aux Meadows is the only undisputed site of pre-Columbian trans-oceanic contact of Europeans with the Americas outside of Greenland. It is notable as evidence of the Norse presence in North America and for its possible connection with Leif Erikson as mentioned in the Saga of the Greenlanders and the Saga of Erik the Red, which were written down in the 13th century. Archaeological evidence found at the site indicates that L’Anse aux Meadows may have served as a base camp for Norse exploration of North America, including regions to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is the world's largest island. It is one of three constituent countries that form the Kingdom of Denmark, along with Denmark and the Faroe Islands; the citizens of these countries are all citizens of Denmark and the European Union. Greenland's capital is Nuuk. Though a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe (specifically Norway and Denmark, the colonial powers) for more than a millennium, beginning in 986.The Fate of Greenland's Vikings , by Dale Mackenzie Brown, ''Archaeological Institute of Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iona
Iona (; gd, Ì Chaluim Chille (IPA: �iːˈxaɫ̪ɯimˈçiʎə, sometimes simply ''Ì''; sco, Iona) is a small island in the Inner Hebrides, off the Ross of Mull on the western coast of Scotland. It is mainly known for Iona Abbey, though there are other buildings on the island. Iona Abbey was a centre of Gaelic monasticism for three centuries and is today known for its relative tranquility and natural environment. It is a tourist destination and a place for spiritual retreats. Its modern Scottish Gaelic name means "Iona of (Saint) Columba" (formerly anglicised as "Icolmkill"). In 2019, the island's estimated population was 120. Residents engage in farming, using traditional methods. Other occupations include crofting and tourism-related work; some craftsmen make goods for sale locally, such as pottery, tapestries, jewellery and knitted goods. In March 1980, the Hugh Fraser Foundation donated much of the main island (and its off-lying islands) to the current owner, the Nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. Because it is on the North American Plate, North American Tectonic Plate, Greenland is included as a part of North America geographically. North America covers an area of about , about 16.5% of Earth's land area and about 4.8% of its total surface. North America is the third-largest continent by area, following Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. In 2013, its population was estimated at nearly 579 million people in List of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In Americas (terminology)#Human ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
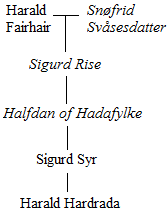
Harald Hardrada
Harald Sigurdsson (; – 25 September 1066), also known as Harald III of Norway and given the epithet ''Hardrada'' (; modern no, Hardråde, roughly translated as "stern counsel" or "hard ruler") in the sagas, was King of Norway from 1046 to 1066. Additionally, he unsuccessfully claimed both the Danish throne until 1064 and the English throne in 1066. Before becoming king, Harald had spent around fifteen years in exile as a mercenary and military commander in Kievan Rus' and as a chief of the Varangian Guard in the Byzantine Empire. When he was fifteen years old, in 1030, Harald fought in the Battle of Stiklestad together with his half-brother Olaf Haraldsson (later Saint Olaf). Olaf sought to reclaim the Norwegian throne, which he had lost to the Danish king Cnut the Great two years prior. In the battle, Olaf and Harald were defeated by forces loyal to Cnut, and Harald was forced into exile to Kievan Rus' (the sagas' ). He thereafter spent some time in the army of Grand P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه , alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ("the Great City"), Πόλις ("the City"), Kostantiniyye or Konstantinopolis ( Turkish) , image = Byzantine Constantinople-en.png , alt = , caption = Map of Constantinople in the Byzantine period, corresponding to the modern-day Fatih district of Istanbul , map_type = Istanbul#Turkey Marmara#Turkey , map_alt = A map of Byzantine Istanbul. , map_size = 275 , map_caption = Constantinople was founded on the former site of the Greek colony of Byzantion, which today is known as Istanbul in Turkey. , coordinates = , location = Fatih, İstanbul, Turkey , region = Marmara Region , type = Imperial city , part_of = , length = , width ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)